The world is facing a global energy crisis. Hundreds of millions of people still lack access to sufficient energy entirely. Fortunately, it’s becoming increasingly clear that solar photovoltaic systems are one of the most promising solutions to this crisis we’re facing—but how do they work? And what are the different types of solar photovoltaic systems available?
Table of Contents
What is a solar photovoltaic system?
Three types of solar photovoltaic systems
Cheat sheet for choosing solar PV systems
What is a solar photovoltaic system?
PV systems have been around since the 1990s and have been increasing in popularity as an alternative renewable energy source. Solar photovoltaic systems use the sun’s energy to convert solar radiation into electricity. They consist of one or more solar panels and other components such as an inverter, a controller, a mounting system, or batteries. PV systems can be used as stand-alone applications or grid-connected systems, and their size varies from rooftop systems to large-scale generation plants, depending on how much electricity is needed and how much space is available for installation.
Solar energy and PV systems

Solar power is a clean, renewable energy source that can be used to generate electricity. It’s an abundant and inexhaustible resource because it comes from the sun. In just one hour, the sunlight that strikes the earth’s surface is enough to power all human energy needs for an entire year. The sun’s light is also called solar radiation and is made up of photons. Photovoltaic cells capture this radiation and turn it into electrons that move in response to an internal electric grid, producing electricity in the process.
Main components of solar PV systems
The four main components of solar photovoltaic systems are solar panels, inverters, cabling, and storage batteries.
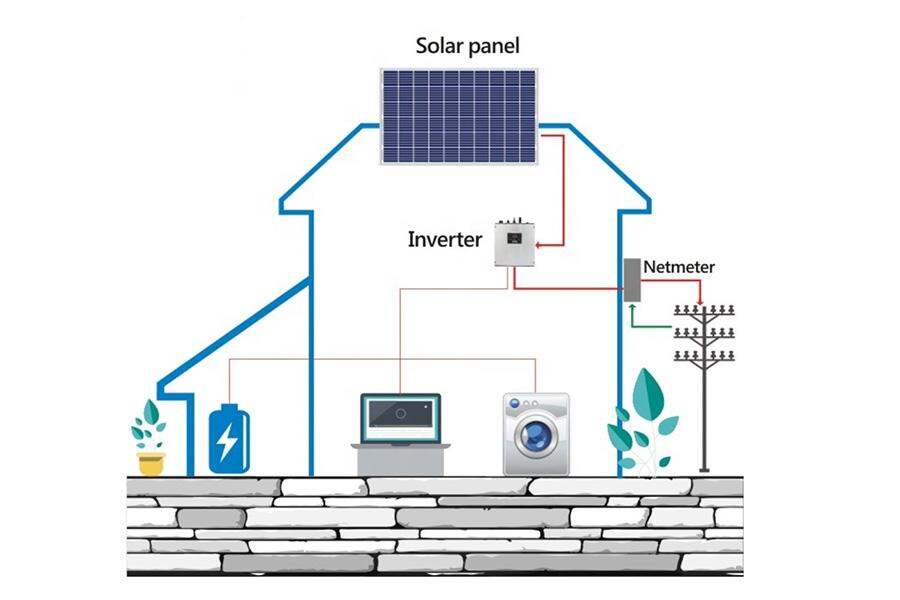
Solar panels
The solar panel is the most important part of a photovoltaic system, and it consists of many cells made from semiconductor materials like crystalline silicon. When sunlight hits the panel, it frees electrons from atoms in the semiconductor material. This results in electricity, which can be used to power electrical devices or recharge batteries.
Inverter
Inverters are a key component of solar photovoltaic systems. They convert direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC), which is the type of electricity used by most household appliances and power-hungry factories.
Cabling

Cabling is an integral part of solar photovoltaic systems. It connects the components of a circuit and serves as a conduit where electricity travels. The PV wires and cables are made of copper or aluminum, which are both excellent conductors of electricity.
Batteries

Batteries play a vital role in solar photovoltaic systems. They store the electrical energy generated by the solar arrays to supply power to the load at any time. Batteries supporting solar photovoltaic systems are mainly composed of lead-acid, cadmium-nickel, or lithium.
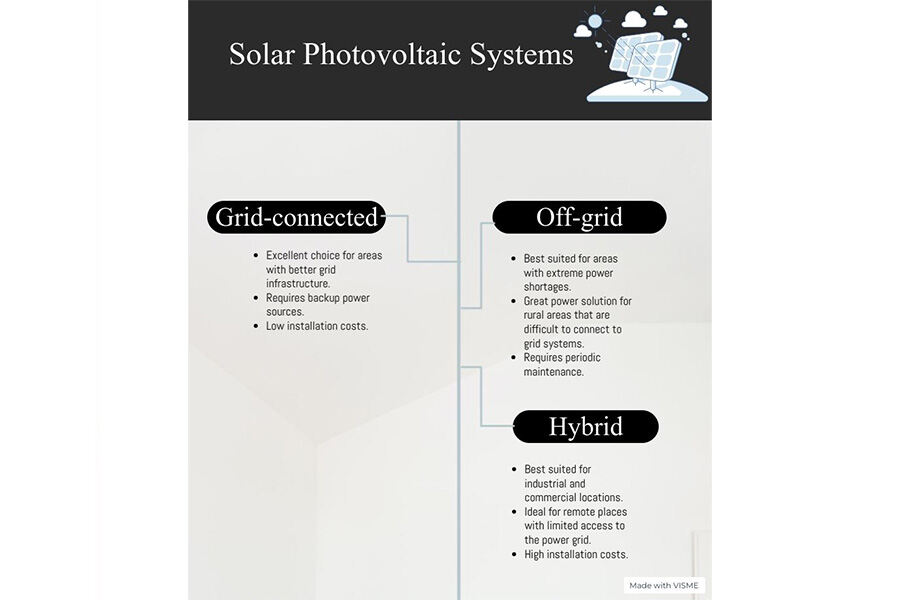
Three types of solar photovoltaic systems
With so many options for harnessing the sun’s power, it can be hard to source the right solar PV system. But no worries! This section will break down the main three types of solar photovoltaic systems, so businesses can easily compare them and figure out which one is best for their needs.
Grid-connected PV systems
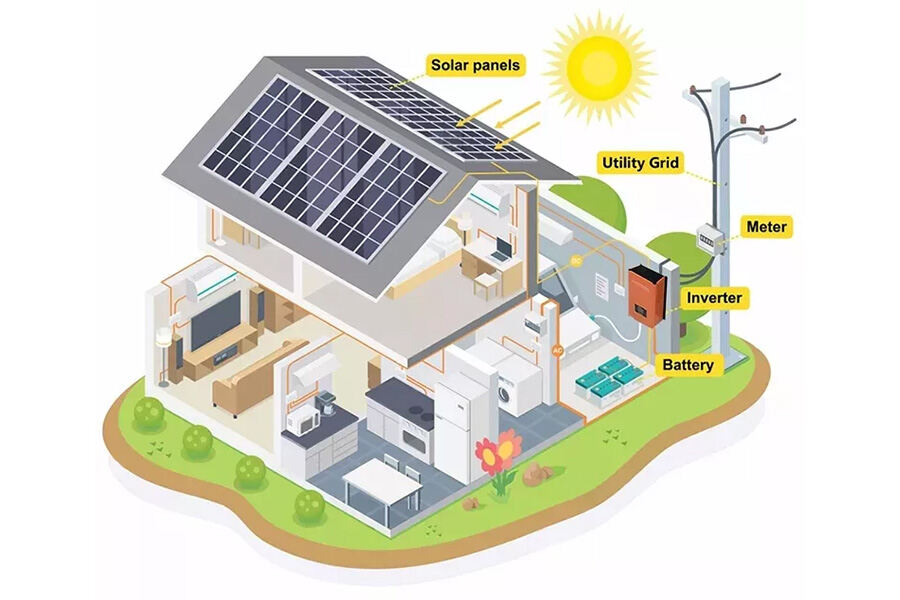
Grid-connected solar PV systems are an excellent choice for users in areas with grid electricity purchase subsidies, especially in areas with better grid infrastructure, as they convert solar energy to alternating current and use the utility grid to balance any power fluctuations. In addition to that, on-grid PV systems allow consumers to offset their electricity bills by redirecting any surplus energy to the grid when the PV system is producing more power than their household needs.
While this type of solar PV system is less expensive than other types, it should be noted that it does not offer any outage protection; so it’s best suited for homes that already have good backup power sources in place. For example, the 5 kW on-grid solar system is a great choice for home and commercial use. The PV arrays feature a high efficiency of 17% and excellent mechanical load resistance. Furthermore, the solar inverter is equipped with overcharge protection and an under-voltage disconnection function, ensuring efficient power storage and transmission quality.

Off-grid PV systems
Off-grid solar PV systems, also known as stand-alone PV systems, are independent of the utility grid and are suitable for rural areas and areas with extreme power shortages that are difficult to connect to grid systems. They come in two forms: DC power systems and AC power systems.
A DC system uses a DC-DC converter to convert the voltage of solar panels from its native value up to an appropriate level for use in DC loads. An AC system, on the other hand, uses an inverter to convert PV voltage into standard household electric current. DC-DC converters can also be used in AC systems to reduce the number of solar panels required.
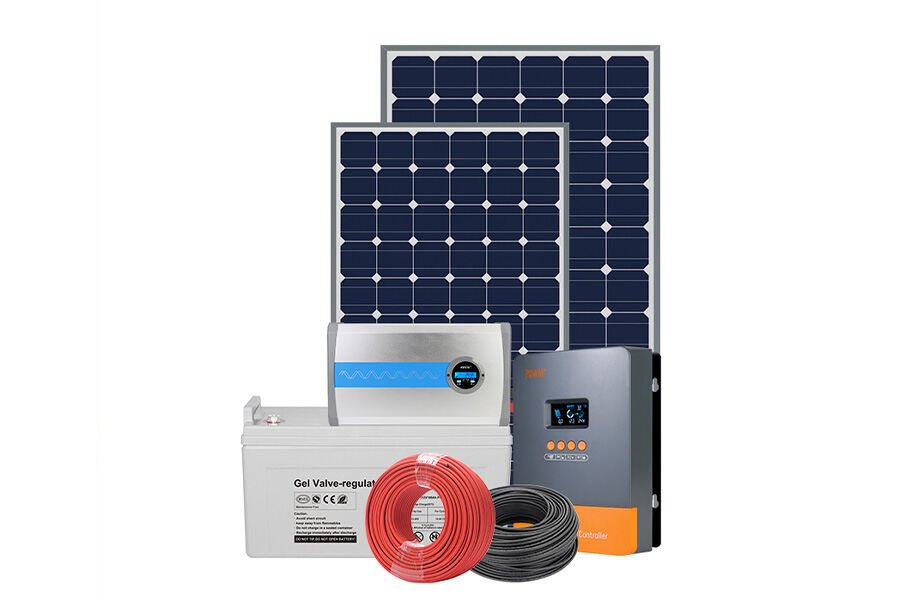
For example, the fully-integrated 5 kW solar PV system includes a DC-AC off-grid solar inverter, charge controller, 5 kWh lithium battery, and 12 modules of 450W solar panels. This system is great for homes in remote locations without access to grid power. Nonetheless, consumers should be aware that this type of PV system will require periodic maintenance, including checking the terminals for corrosion and inspecting the electrolyte level in battery cells.

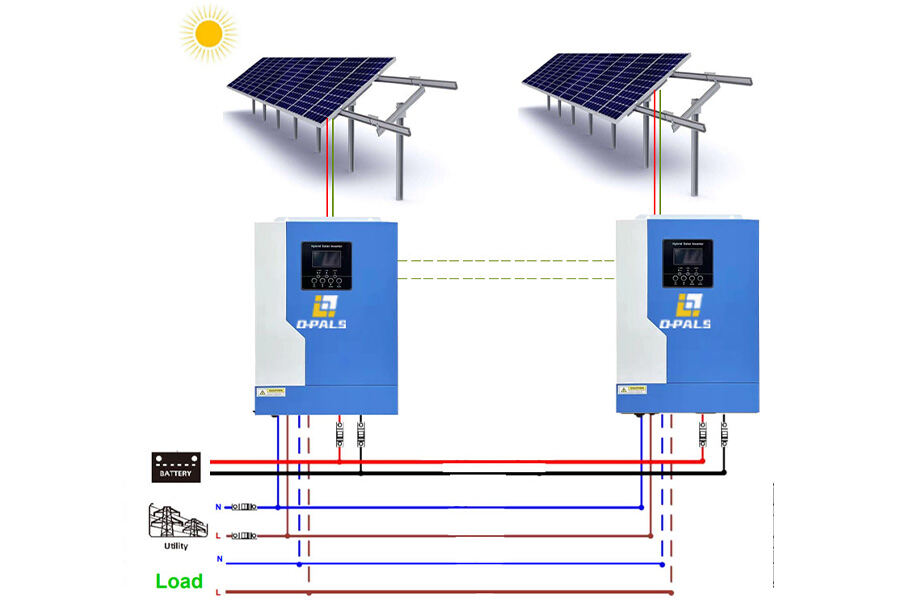
Hybrid PV systems
Hybrid PV systems, such as 10 kW-30 kW solar system banks, are best suited for industrial and commercial locations such as schools, hospitals, etc. in remote and developed areas with limited access to the grid, as they embed other energy sources such as wind turbines and diesel generators. These hybrid systems are paired with lithium batteries to store excess energy, ensuring it doesn’t go to waste.
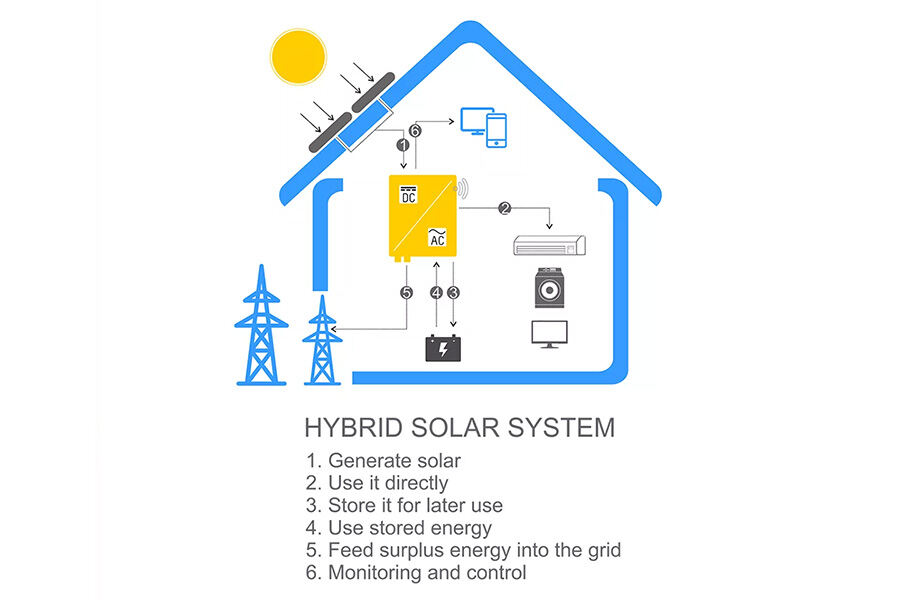
The advantages of using hybrid systems include being able to generate enough electricity even if one source fails or is unavailable. Such systems can provide power even when the sun is not shining or the wind is not blowing. This is an essential consideration for areas that experience harsh winters and long periods without sunlight. While the benefits of hybrid PV systems are many, they can be expensive to install, since they require a complex design and multiple sources of energy.
Cheat sheet for choosing solar PV systems
Solar photovoltaic systems provide a clean, economical, and sustainable way of generating electricity for households, farms, and even large industrial and commercial users such as factories, schools, hospitals, and shopping malls. PV systems are categorized into 3 main types: on-grid PV systems, off-grid PV systems, and hybrid PV systems. The system to choose will depend upon several factors such as the user’s location, budget, and energy needs.
So there you have it! A crash course on the basics of solar photovoltaic systems. Ready to switch from traditional energy sources to solar power? If so, check these cost-effective PV systems for a quick start!



