Wind power generators are the linchpin of a renewable energy revolution that could finally solve the world’s energy problems staring at our faces. In this article, we’ll look at how they work, what their benefits and problems are, and why they’re becoming a cornerstone of clean energy schemes all over the world. This article aims to demystify wind power generators and prepare readers for a fundamental comprehension of their internal workings, ecological impact, affordability, technological advancements and future prospects.
Table of Contents:
– How wind power generators work
– Environmental benefits of wind energy
– Cost analysis of wind power generation
– Technological advancements in wind turbines
– The future of wind power
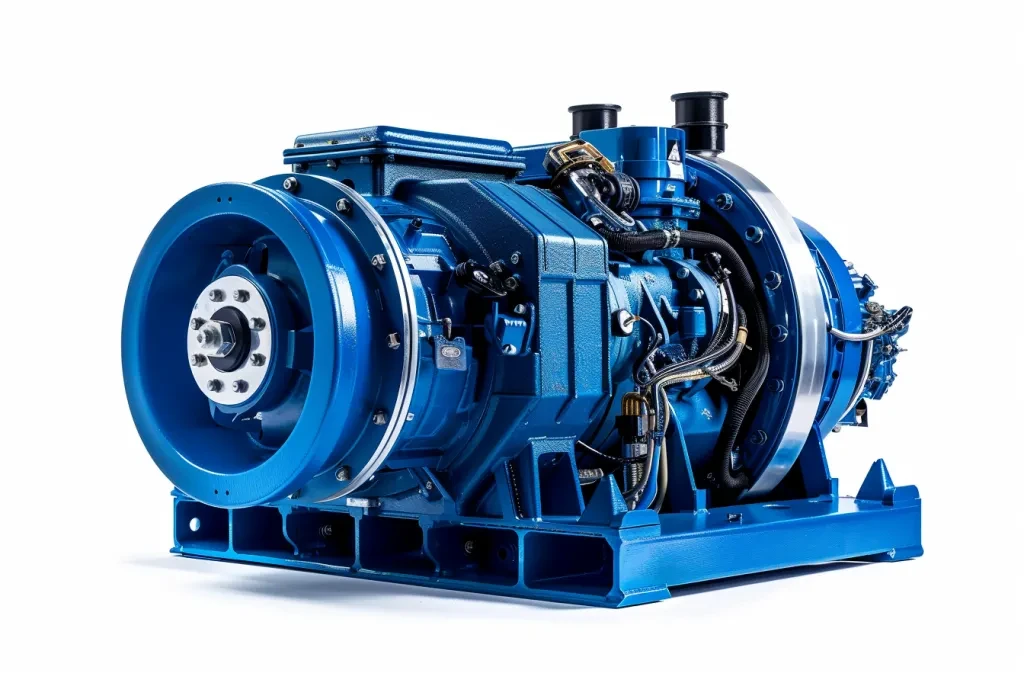
How wind power generators work

Wind power generator is also known as wind turbines which convert the kinetic energy of the wind to electrical energy. The process starts with the wind turns the blades on a wind power generator to make a shaft rotate, which is attached to a generator and cause the mechanical energy convert to electromagnetic energy.
There are several factors that affect the efficiency of converting the energy. First, the wind speed is the most important factor. Besides that, the structure of the turbine is critical. The blades are much larger in size in order to gets more power from the wind. The speed of the blades rotation will be faster in high wind and become slower when the wind is low or gone. The design of the generator is also crucial due to the power and conversion technology.
Environmental benefits of wind energy

The first is that wind power has a remarkably small environmental footprint. Wind farms generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases. They spew nothing but clean air into the skies. It is here that wind power plays a particularly important role in the battle against climate change. Because wind farms can be sited on agricultural land that would otherwise be left fallow, wind power fosters a kind of dual use of land. This not only minimises habitat disruption, but also can bring some continuing economic production to rural areas. Wind power has the smallest lifecycle emissions footprint of any energy source contender for a clean energy future.
Cost analysis of wind power generation
Wind energy has become one of the lowest-cost renewable energy sources available. While the cost of wind turbines has fallen rapidly in recent years due to technological advances and scale, wind energy is highly dependent on the wind. Although windy conditions are generally consistent in the places where they are strongest, there is a significant amount of variability in the wind that must be accounted for. In order to make sense of these costs, it is necessary to evaluate the relationship over the long-term of upfront energy savings to environmental benefits.
Technological advancements in wind turbines

Important technological changes in the wind energy market have taken place in recent years. These changes indicate an escalation in the manufacturing of wind power generators and the integration of more advanced technology.
Over the past decades, we have witnessed noticeable design and material upgrades to wind turbines. In particular, turbine sizes have increased, most notably their blades, which led to capturing more wind energy. Moreover, wind power forecasting technology and better grid integration have improved the predictability of wind power, increasing its stability.
These developments are crucial for wind turbines in terms of either revenues or survival. The next years will definitely show us further attempts in making wind energy an affordable and available alternative to fossil fuels.
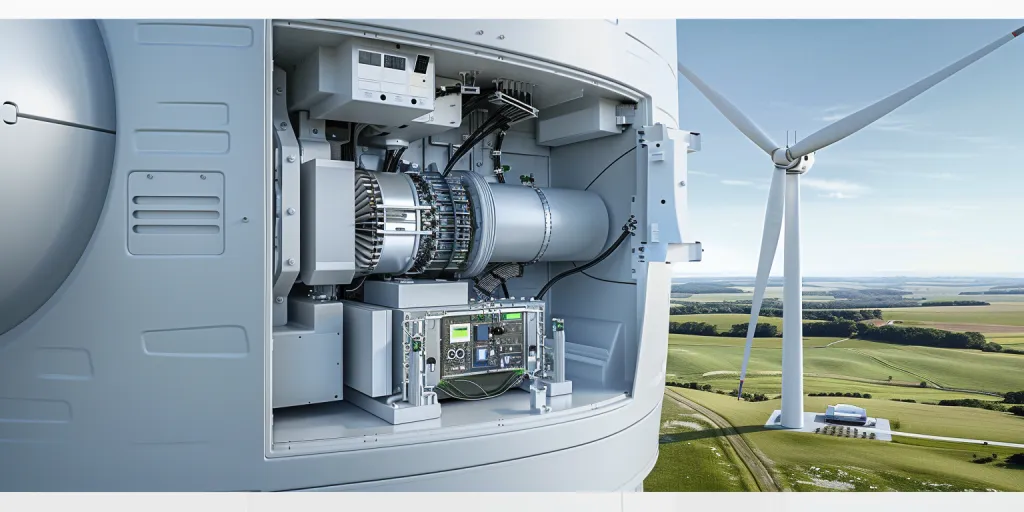
The future of wind power

The future of wind power looks bright too, and research and development efforts are likely to increase efficiency, and ensure a more reliable power supply from wind turbines. New floating wind turbines and energy storage technologies give us more options to use and rely on wind power. As the world has become more concerned about sustainability issues, its interest in wind power to achieve renewable energy targets and to reduce greenhouse gas emissions should increase.
Conclusion:
Wind power generators are a vital technology in the shift to a sustainable and renewable future. As we delve into how these generators work, their environmental benefits, the financial aspect, technological developments, and the future of the technology, we can better appreciate the potential of this power source and jumpstart its development. As the winds pick up, we will begin to enjoy a greener, more sustainable world for the generations to come.





 Afrikaans
Afrikaans አማርኛ
አማርኛ العربية
العربية বাংলা
বাংলা Nederlands
Nederlands English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch हिन्दी
हिन्दी Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu മലയാളം
മലയാളം پښتو
پښتو فارسی
فارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português Русский
Русский Español
Español Kiswahili
Kiswahili ไทย
ไทย Türkçe
Türkçe اردو
اردو Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt isiXhosa
isiXhosa Zulu
Zulu