For many Xiaomi fans, using the phone as it comes out of the box is never enough. Some of us want more control. We want to install custom ROMs, root the device, or just explore features hidden under the surface. To do any of that, the first step is unlocking the bootloader.
Now that Xiaomi’s new HyperOS is here, a lot of people are wondering how the process works on this system. The good news? It’s not too different from what you might have done before on MIUI. The bad news? You can’t do it on the China versions of HyperOS. Only Global devices can be unlocked, so keep that in mind before diving in.
Why Bother Unlocking?
Some people ask, “Why unlock the bootloader at all?” The simple answer: freedom. With the bootloader unlocked, you can:
- Install a custom ROM that feels lighter or adds missing features.
- Root the phone to get superuser control.
- Use mods that give you deeper customization.
- Flash kernels for better performance or battery life.
- Push updates manually if Xiaomi is too slow.
It’s basically your ticket to making the phone your own. Of course, it’s not all sunshine. Unlocking wipes your phone clean, and if you mess up a step, you can end up with issues. But if you take your time and follow instructions, the risk is low.
What You Need First
Xiaomi has a set of rules for anyone who wants to unlock their bootloader. These aren’t optional — if you don’t meet them, the process simply won’t work. Here’s the checklist:
- The device must be a Global model. HyperOS China models are off-limits.
- Insert a physical SIM card before starting.
- Your Xiaomi account must be at least 30 days old. Brand-new accounts won’t work.
- You can only unlock one device per year per account.
- Back up everything, because unlocking wipes all your data.
Honestly, that last one is the most important. If you skip the backup step, you’ll regret it.
Step 1: Apply for Permission

This is where things begin. Xiaomi wants you to request permission before it allows unlocking. Don’t worry — it’s pretty simple:
- Download the Xiaomi Community app.
- Go into settings and change your region to Global.
- Sign in with your Xiaomi account.
- Look for the Unlock bootloader option.
- Tap Apply for unlocking.
Now here’s the catch: sometimes you’ll see a message saying the daily limit has been reached. If that happens, don’t freak out. Just wait until midnight China time and try again. Yes, it’s annoying, but that’s the system Xiaomi has in place.
Step 2: Enable Developer Options
Next up, you need to unlock a few hidden settings on your phone.
- Restart your device and make sure you’re on mobile data, not Wi-Fi.
- Go to Settings > About phone.
- Tap on the HyperOS version again and again until you see the message: “You are now a developer.”
- Go back to Settings > Additional settings > Developer options.
- Turn on OEM unlocking and USB debugging.
If you’ve ever tinkered with Android before, these steps will feel familiar. They basically allow the computer to communicate with your phone during the unlock.
Step 3: Bind Your Account
This part is crucial. Without binding your Xiaomi account, the unlock will fail.
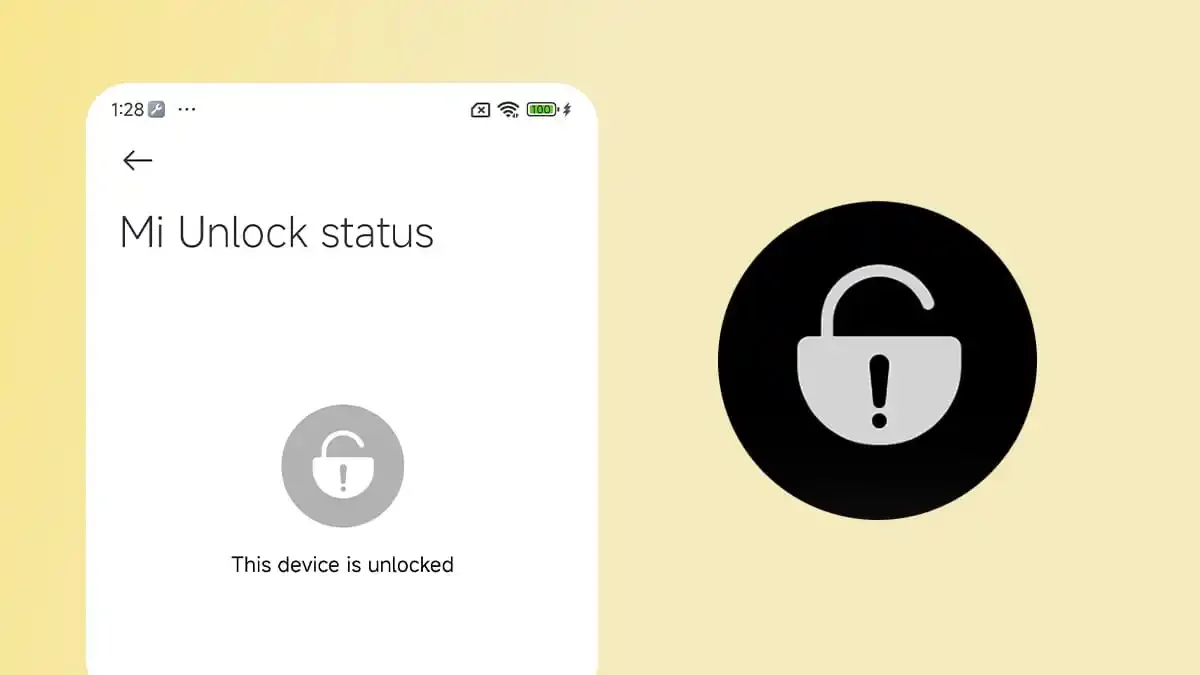
- In Developer options, tap Mi Unlock status.
- Agree to the warning.
- Tap Add account and device.
- Make sure you’re connected through mobile data, not Wi-Fi, when you do this.
If everything works, you’ll see a message saying your account has been successfully added. From here, Xiaomi starts the waiting period. Usually, that’s 72 hours. In some cases, it could be longer.
Please note that making any unusual changes can interfere with the process during this 72hrs waiting period. During this wait, avoid making any changes to your Mi account, removing SIM card or even resetting your phone.
4. Begin Bootloader Unlocking Process
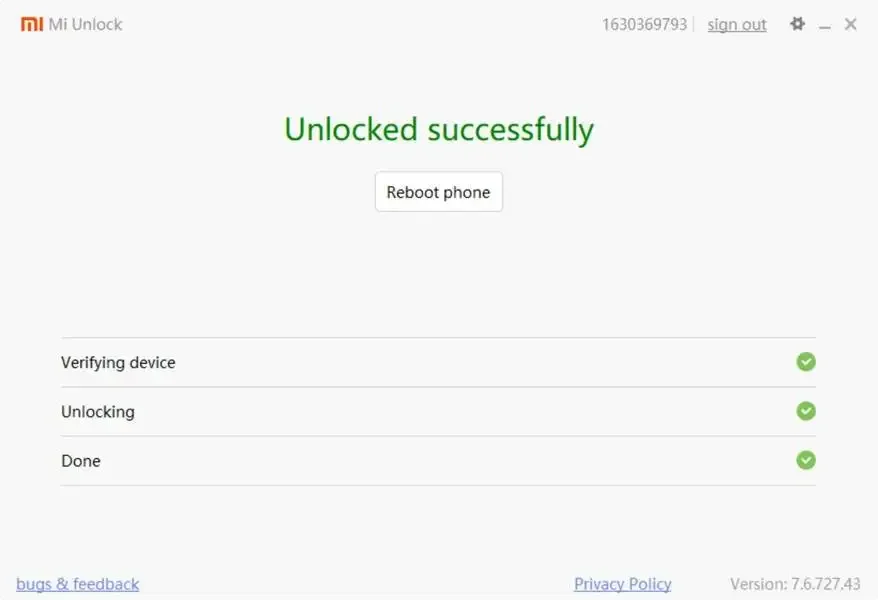
When the 72-hour countdown finally comes to an end, you can begin the unlocking process by following the instructions below:
- You will first need to download the Mi unlock tool onto your PC and install it.
- Open it and sign in with the same Xiaomi account that’s on your phone.
- Power off your device.
- Press and hold Volume Down + Power to boot into Fastboot mode.
- Plug the phone into your PC with a USB cable.
- Click Unlock in the Mi Unlock Tool.
The tool will process everything. When it’s done, your phone will reboot, and all data will be gone. But the bootloader will finally be unlocked.
What Can You Do After Unlocking the Xiaomi Bootloader?
Unlocking the bootloader gives you absolute control over your Xiaomi device. With an unlocked bootloader, you can be able to:
- Flash custom ROMs like Pixel Experience or LineageOS.
- Root the phone using Magisk.
- Install kernels or mods.
- Use advanced backup and recovery tools.
But here’s a heads-up: not everything is smooth sailing. Some apps, like banking apps or streaming services, may complain about the unlocked state. You might need to use Magisk’s hiding features to get them working again.
Final Thoughts
Unlocking the bootloader on Xiaomi HyperOS Global devices is not something you do on a whim. It takes patience, a few days of waiting, and the courage to erase your data. But for many users, it’s worth it.
The process isn’t overly complicated: apply for permission, enable developer settings, bind your account, wait, then use the unlock tool. Follow the steps carefully, and you’ll be fine.
Once unlocked, your phone becomes much more than what came in the box. You can explore, customize, and create the experience you want. HyperOS is already smoother and more connected than MIUI, but with an unlocked bootloader, you can take it even further.
For Xiaomi fans who love control, this is the way forward. Just remember: always back up your data, double-check what you’re flashing, and don’t rush the process. If you stay patient, the reward is huge — your phone, truly in your hands.
Source from Gizchina
Disclaimer: The information set forth above is provided by gizchina.com independently of Alibaba.com. Alibaba.com makes no representation and warranties as to the quality and reliability of the seller and products. Alibaba.com expressly disclaims any liability for breaches pertaining to the copyright of content.



