Table of Contents:
PC possesses several characteristics
PC has four main applications for modification
Mechanism of silicone-containing copolymerized PC
PC (Polycarbonate) is a resin material widely used in the plastic industry. It has excellent light transmission, good impact resistance, and moldability.
To expand the application range of PC, it generally needs to be modified to enhance toughness, improve moldability, reduce residual deformation, and increase flame retardancy. Through modification, PC can be widely used in fields such as electronics, automotive parts, thin-walled products, and medical applications.

PC possesses several characteristics
Optical properties: PC has high transparency with a light transmission rate of up to 90%, ranking second only to PMMA and PS. As a result, it can serve as a substitute for glass in various optical materials.
Chemical resistance: PC is non-toxic and odorless and can resist weak acids, weak bases, neutral oils, and some organic solvents. However, its hydrolysis stability is not high, and long-term exposure to ultraviolet light can cause yellowing.
Mechanical properties: PC products are rigid, possess impact resistance and good toughness, with high elongation, rigidity, bending strength, and tensile strength. They also exhibit good heat and cold resistance. Nonetheless, PC has low fatigue strength and is prone to crack formation.

Electrical properties: PC has excellent dielectric strength and electrical insulation, making it commonly used in the field of electronic and electrical appliances.
Thermal properties: PC can withstand temperatures ranging from -60°C to 120°C, with a heat distortion temperature of 135°C to 143°C. It is not easily combustible and is self-extinguishing. Additionally, it exhibits good heat and cold resistance.
PC has four main applications for modification
Toughened PC
General toughened PC: This type of PCexhibits good impact resistance, adjustable impact properties, minimal molding shrinkage, and good dimensional stability. It also possesses favorable weathering and low-temperature impact properties, making it suitable for electronic and electrical products like mobile phone casings, thin-walled products, and automotive parts.

High fluidity toughened PC: This type of PC offers good toughness, a wide temperature range for use, excellent spraying performance, resistance to stress cracking, and high success rate of oil spraying. It is suitable for ultra-thin-walled products and automotive parts.

Flame retardant PC
Flame retardant polycarbonate boasts excellent mechanical properties, high heat distortion temperature, high dielectric strength, good electrical insulation, and effective flame retardant characteristics. Hence, it finds extensive application in high-end chargers, lamp heads, switch panels, and other products.

Glass Fiber Reinforced PC
Glass Fiber Reinforced PC materials are available with 10% and 20% glass fiber reinforcement. The former is primarily used for mobile phone middle frames, while the latter is suitable for mobile phone middle frames, tablet PCs, and non-steel inserts.

PC/ABS alloy
PC/ABS alloy is a commonly used modified PC material that can enhance the resin’s bending modulus, heat resistance, and plating properties. It can be divided into general-purpose grade ABS/PC, high-impact PC/ABS, and flame retardant PC/ABS varieties. General-purpose grade PC/ABS exhibits high impact resistance, excellent toughness, high fusion line strength, good chemical resistance and heat resistance, high mobility, ease of processing and shaping, and can be used for mobile phone shells and other thin-walled products. High-impact PC/ABS offers good impact resistance and toughness, making it suitable for helmets, sporting goods, etc. Flame retardant PC/ABS alloy comes in various types such as general-purpose grade, high gloss, filler-enhanced, and high heat-resistant. It exhibits good mobility, processing performance, halogen-free flame retardancy, and compliance with environmental requirements. It is commonly used for computer shells, printers, projectors, and other equipment.

In conclusion, PC, as an engineering plastic, has a broad range of applications and modification possibilities in various fields. However, ordinary polycarbonate lacks satisfactory impact resistance and chemical resistance, limiting its application in many industries. To address these issues, methods such as using PC/ABS and PC/PBT alloys are typically employed to modify ordinary PC. Unfortunately, this can result in the loss of transparency or rigidity. One common modification approach involves incorporating silicone-containing copolymerized polycarbonate.
Mechanism of silicone-containing copolymerized PC
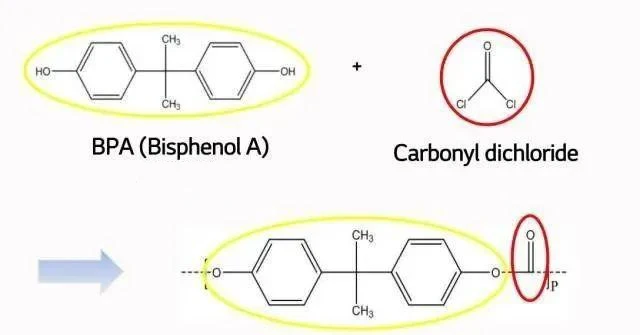
Both conventional PC and silicone-containing PC contain bisphenol A and phosgene as synthetic monomers. However, silicone-containing PC also undergoes copolymerization with polydimethylsiloxane. Ordinary PCs have limited molecular chain flexibility due to the bulky benzene ring stiffening group and the strong polar group -COO (ester group), which forms large intermolecular forces binding the molecular chains together. This further reduces the flexibility of the molecular chains and results in polymers with high glass transition and melting temperatures, high melt viscosities, and reduced molecular chain slip under external forces. Additionally, the ester group in the molecular chain of conventional PCs undergoes hydrolysis reactions when exposed to acids or bases, leading to the production of corresponding acids or alcohols. This renders conventional PCs with low hydrolytic stability, sensitivity to chipping, poor scratch resistance, yellowing upon long-term exposure to ultraviolet light, and susceptibility to turbidity when soaked in certain organic solvents.

Advantages of introducing silicone groups
Increased flexibility: The incorporation of silicone groups can increase the length of the structural unit, reduce the rigidity of the bulky benzene ring, and enhance the flexibility of the molecular chain. This, in turn, improves the fluidity of PC materials.
Improved hydrolysis resistance: Organosiloxane “-Si-O-Si-” is a hydrophobic group that exhibits significant chemical affinity with inorganic silicate materials. Leveraging this property, the properties of the material’s surface can be effectively altered to achieve water repellency. Therefore, the introduction of an organosiloxane structure into polycarbonate can greatly enhance its hydrolysis resistance.
Enhanced high and low-temperature resistance, flame retardancy, and corrosion resistance: Silicone possesses both inorganic and organic material characteristics. It exhibits low surface tension, a small viscosity-temperature coefficient, high compressibility, high gas permeability, and excellent properties such as high and low-temperature resistance, electrical insulation, oxidation stability, weather resistance, flame retardancy, hydrophobicity, corrosion resistance, non-toxicity, odorlessness, and physiological inertness.
By introducing silicone into PC, its high and low-temperature resistance can be improved, allowing it to maintain mechanical properties even at temperatures as low as -30°C to -40°C. Additionally, the oxidation stability and weathering characteristics of silicone can enhance PC’s oxidation resistance and resistance to yellowing.
PC copolymers find extensive use in medical device housings that require frequent disinfection and autoclaving due to their excellent chemical resistance.
Furthermore, the addition of silicone groups improves the flame retardancy of PC, making it more suitable for applications in fields such as construction, transportation, and electronics. Its low surface tension also allows for better adhesion to other materials, enhancing the overall performance of PC-based products.
In summary, the introduction of copolymer PC with silicone groups brings numerous advantages, including increased flexibility, improved hydrolysis resistance, enhanced high and low-temperature resistance, flame retardancy, and corrosion resistance. These properties make it an ideal material for a wide range of applications, from medical devices to construction and electronics. As technology continues to advance, the modification possibilities of PC will only continue to expand, further enhancing its versatility and potential in various industries.
Disclaimer: The information set forth above is provided by Shanghai Qishen Plastic Industry independently of Alibaba.com. Alibaba.com makes no representation and warranties as to the quality and reliability of the seller and products.