Pneumatic cylinders are vital components in various industrial applications. They convert compressed air into mechanical motion, offering a clean and efficient power source. Understanding their functionality, applications, and maintenance is crucial for optimizing their performance and longevity. In this guide, we delve deep into the intricacies of pneumatic cylinders, providing practical insights to help you harness their full potential.
Table of Contents:
1. What is a pneumatic cylinder?
2. How do pneumatic cylinders work?
3. Applications of pneumatic cylinders
4. Benefits of using pneumatic cylinders
5. Maintenance and troubleshooting
What is a pneumatic cylinder?
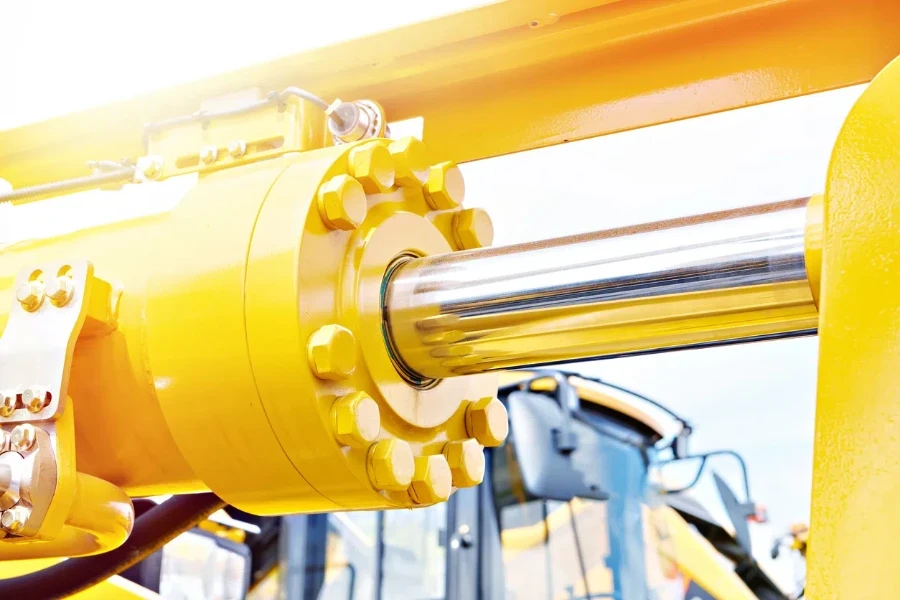

A pneumatic cylinder, also known as an air cylinder, is a device that uses compressed air to produce a force in a reciprocating linear motion. They are widely used in various industrial applications due to their simplicity, reliability, and ease of maintenance.
Pneumatic cylinders come in different types, including single-acting and double-acting cylinders. Single-acting cylinders use compressed air to move the piston in one direction, with a spring or external force returning it. Double-acting cylinders, on the other hand, use compressed air to move the piston in both directions, providing greater control and force.
These cylinders are constructed from various materials such as aluminum, stainless steel, and composite materials, ensuring durability and compatibility with different environments. The choice of material often depends on the application, operating conditions, and required performance specifications.
How do pneumatic cylinders work?

The operation of a pneumatic cylinder is straightforward yet highly efficient. When compressed air enters the cylinder through an inlet port, it exerts pressure on the piston. This pressure forces the piston to move in a linear direction, converting the potential energy of the compressed air into kinetic energy.
The movement of the piston can be controlled by regulating the airflow into the cylinder. This is typically achieved using various types of valves, such as solenoid valves, which can be electronically controlled for precise operation. By adjusting the pressure and flow rate of the air, the speed and force of the piston movement can be finely tuned to meet specific application requirements.
In double-acting cylinders, air is supplied to both sides of the piston through separate ports. By alternating the supply of air to either side, the piston can be moved back and forth. This bidirectional capability makes double-acting cylinders highly versatile and suitable for applications requiring continuous or repetitive motion.
Applications of pneumatic cylinders
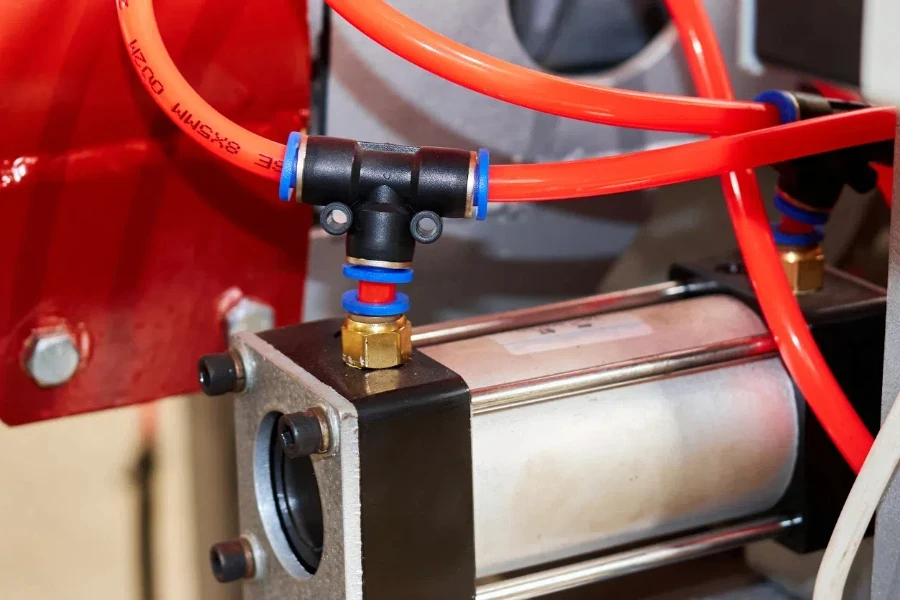
Pneumatic cylinders are employed in a wide range of industrial and commercial applications. Their ability to provide clean, efficient, and reliable motion makes them a preferred choice in many sectors.
In the manufacturing industry, pneumatic cylinders are used for tasks such as material handling, assembly operations, and packaging. They are integral to automated systems, where their precise control and repeatability ensure consistent performance and high productivity.
In the automotive sector, pneumatic cylinders play a crucial role in assembly lines, helping in tasks like clamping, lifting, and moving components. Their robustness and ability to operate in harsh conditions make them ideal for demanding environments.
Beyond manufacturing, pneumatic cylinders are also found in everyday applications such as opening and closing doors, adjusting furniture, and even in medical devices. Their versatility and adaptability mean they can be tailored to a wide range of specific needs, providing efficient solutions across various industries.
Benefits of using pneumatic cylinders

The use of pneumatic cylinders offers several advantages, making them a popular choice in numerous applications. One of the primary benefits is their simplicity and ease of use. Pneumatic systems are generally straightforward to design and implement, with fewer components compared to hydraulic or electrical systems.
Another significant advantage is their cleanliness. Pneumatic systems use air as the working medium, which is inherently clean and non-polluting. This makes them ideal for applications where contamination must be avoided, such as in food processing or pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Pneumatic cylinders also offer excellent safety characteristics. Air is a compressible fluid, which means pneumatic systems can absorb shock loads and provide a cushioning effect. This can help protect both the machinery and the operators from sudden impacts or overload conditions.
Additionally, pneumatic systems are known for their reliability and durability. Properly maintained pneumatic cylinders can provide long service life with minimal downtime. Their construction from robust materials ensures they can withstand harsh operating conditions, including extreme temperatures and corrosive environments.
Maintenance and troubleshooting

Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of pneumatic cylinders. Key maintenance tasks include inspecting for leaks, checking the condition of seals and lubricants, and ensuring that the air supply is clean and dry.
Leaks can significantly impact the efficiency of a pneumatic system. Regularly checking connections, hoses, and seals for signs of wear or damage can help prevent leaks and maintain system performance. Replacing worn or damaged components promptly is essential to avoid further issues.
Proper lubrication is also vital. Many pneumatic cylinders come with built-in lubrication systems, but it is important to ensure that the lubricant is appropriate for the specific cylinder and application. Using the wrong type of lubricant can cause premature wear or even failure of the cylinder.
Ensuring that the compressed air supply is clean and dry is another critical maintenance task. Contaminants such as water, oil, or dust can damage the internal components of the cylinder and reduce its efficiency. Using filters and dryers in the air supply line can help mitigate these issues and prolong the life of the pneumatic system.
Conclusion
Pneumatic cylinders are indispensable components in various industrial applications, providing efficient and reliable motion. Understanding their operation, applications, benefits, and maintenance is key to optimizing their performance and ensuring longevity. By following proper maintenance practices and selecting the right type of cylinder for your specific needs, you can harness the full potential of pneumatic cylinders in your operations.



