Tachometers are indispensable tools in the realm of automotive diagnostics and performance tuning. By measuring the rotation speed of an engine, they provide crucial data for both maintenance and optimization. This article explores the intricacies of tachometers, offering insights into their function, selection, lifespan, replacement, and cost.
Table of Contents:
– What is a tachometer?
– What does a tachometer do?
– How to choose a tachometer?
– How long do tachometers last?
– How to replace a tachometer?
– How much are tachometers?
What is a tachometer?
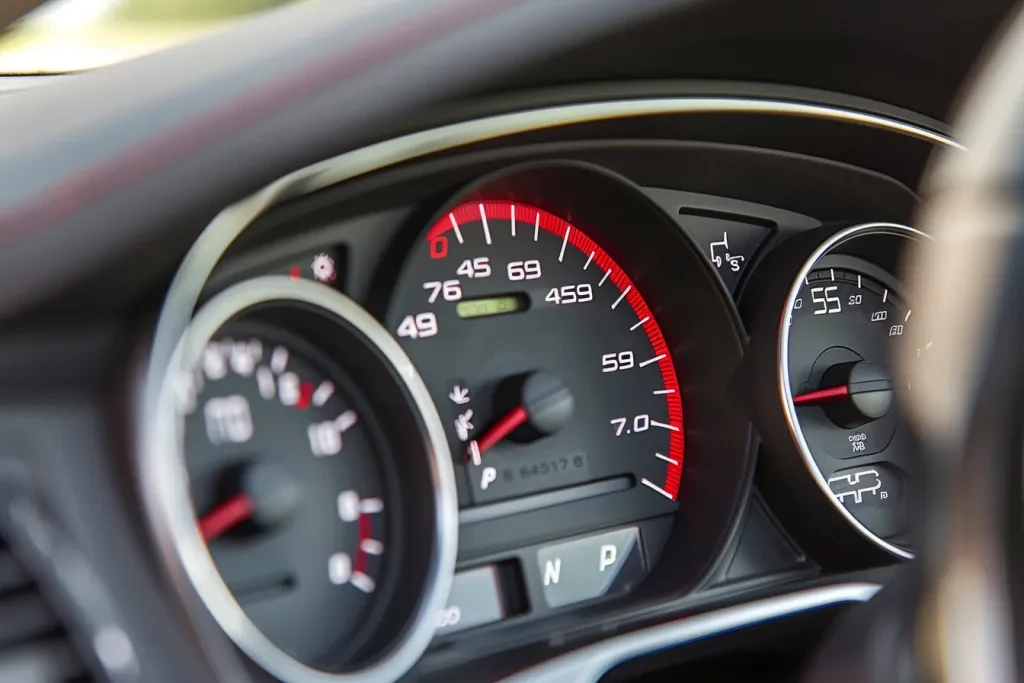

A tachometer, often referred to as a tacho or RPM gauge, is an instrument designed to measure the rotation speed of an engine’s crankshaft. Typically calibrated in revolutions per minute (RPM), it provides real-time data crucial for both performance and safety. The device can be found in various forms, from analog dials with a sweeping needle to digital displays offering precise numerical values. Its presence is ubiquitous across a range of vehicles, including cars, motorcycles, and boats, highlighting its importance in engine monitoring and maintenance.
What does a tachometer do?
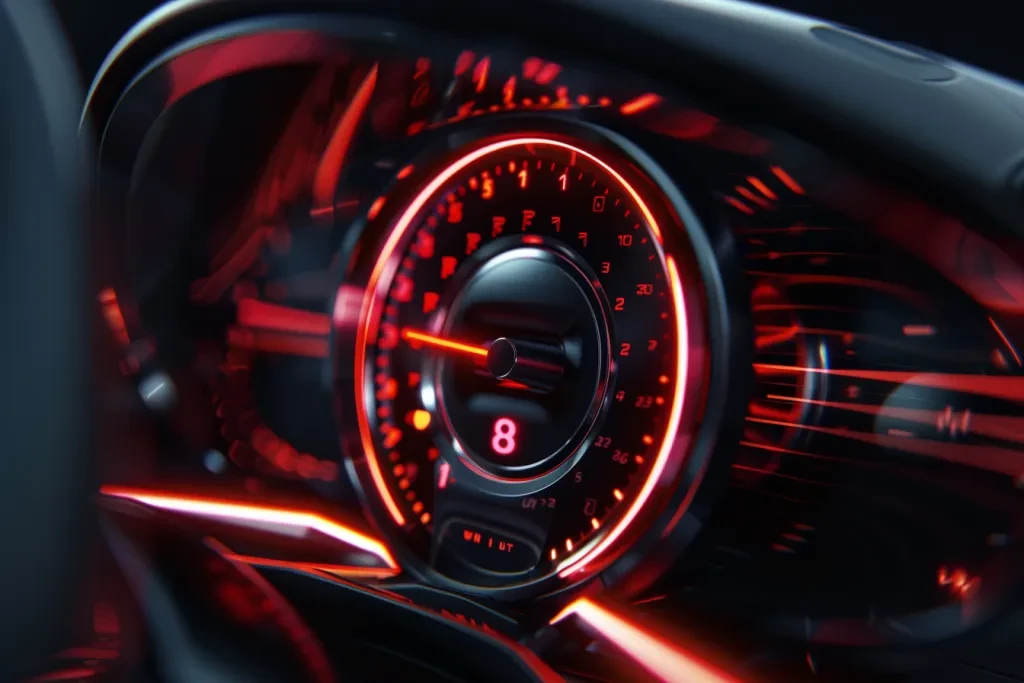

The primary function of a tachometer is to monitor the engine’s rotation speed, enabling drivers to operate the vehicle within safe and efficient RPM ranges. This is particularly important during scenarios like shifting gears, where maintaining optimal RPMs can significantly impact fuel efficiency and engine longevity. Furthermore, a tachometer serves as a diagnostic tool, helping identify issues such as misfires, improper idle speeds, and potential over-revving that could lead to severe engine damage. By providing a visual representation of the engine’s workload, it assists in preventing operational abuse and facilitates timely interventions.
How to choose a tachometer?
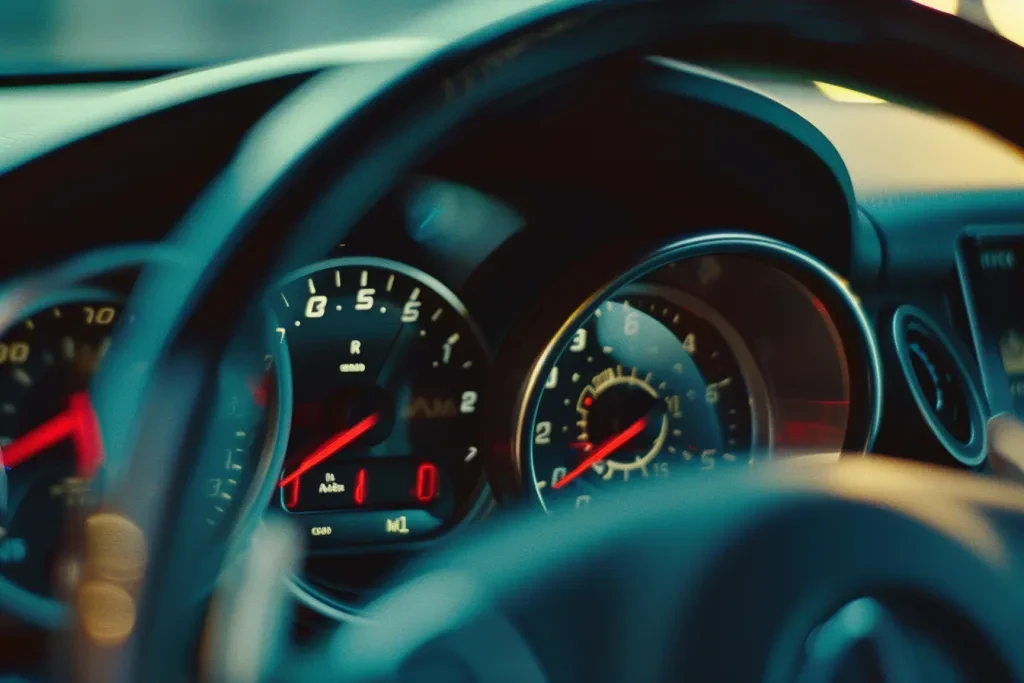

Selecting the right tachometer involves considering several factors, including compatibility, display type, and additional features. Firstly, ensure the tachometer is compatible with your vehicle’s engine type and ignition system. Analog tachometers, with their traditional needle display, offer a quick visual cue for RPMs but may lack the precision of digital models, which provide exact numerical readings. Features like shift lights or data logging can further enhance the utility of a tachometer for performance driving or diagnostics. Ultimately, the choice depends on personal preference, specific vehicle requirements, and the intended use, whether for everyday driving or specialized applications.
How long do tachometers last?
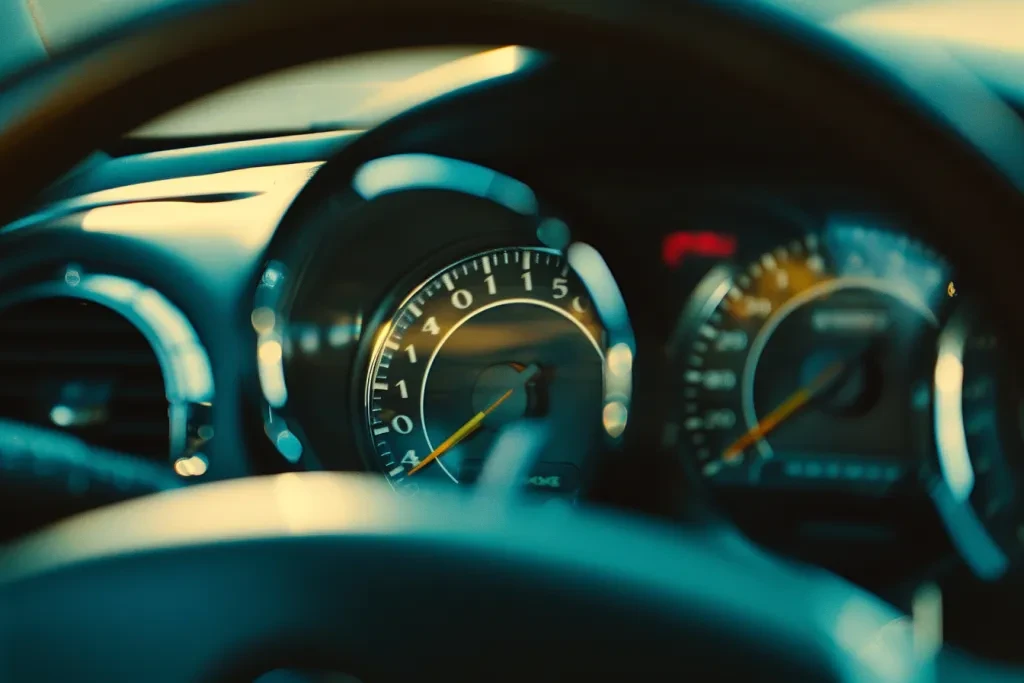

The lifespan of a tachometer largely depends on its type, quality of construction, and exposure to environmental factors. Mechanical tachometers, which rely on a cable driven by the engine, are susceptible to wear and tear but can last many years with proper maintenance. Electronic tachometers, on the other hand, have fewer moving parts, reducing physical wear but potentially facing issues with electronic components over time. With adequate care, a high-quality tachometer can last the lifetime of the vehicle. However, factors like moisture, dust, and electrical surges can shorten this lifespan, necessitating periodic checks and maintenance.
How to replace a tachometer?

Replacing a tachometer involves several steps, starting with selecting a replacement that fits your vehicle’s specifications. Begin by disconnecting the battery to prevent electrical shorts. Remove the dashboard panel or cluster to access the old tachometer, carefully disconnecting it from the wiring harness and any mechanical drive cables if applicable. Install the new tachometer by reversing the removal process, ensuring all connections are secure and free of obstructions. Finally, reconnect the battery and test the tachometer to verify its proper operation. While the process can be straightforward, consulting a professional is recommended for those unfamiliar with automotive electrical systems.
How much are tachometers?
The cost of a tachometer varies widely based on type, features, and brand. Basic analog tachometers can be found for as low as $30 to $50, making them accessible for most budgets. Mid-range models, including those with digital displays and additional functionalities like shift lights, may range from $100 to $200. High-end tachometers, designed for performance vehicles or with advanced diagnostic features, can exceed $300. When considering a purchase, it’s important to balance cost with the specific needs of your vehicle and the value of the added features.
Conclusion:
Tachometers play a vital role in monitoring and maintaining engine performance, offering drivers valuable insights into their vehicle’s operational state. Whether you prioritize precision, durability, or advanced features, understanding the function and selection criteria of tachometers can enhance your automotive experience. With proper care and maintenance, a quality tachometer can be a long-lasting investment in your vehicle’s health and efficiency.



