The apparel industry continues to be a hotbed of innovation, with activity driven by technology, convenience, and comfort, and the growing importance of technologies such as augmented reality, IoT, artificial intelligence, and digitalisation. In the last three years alone, there have been over 32,000 patents filed and granted in the apparel industry, according to GlobalData’s report on Innovation in Apparel: Size-adjusting prosthetic undergarments.
However, not all innovations are equal and nor do they follow a constant upward trend. Instead, their evolution takes the form of an S-shaped curve that reflects their typical lifecycle from early emergence to accelerating adoption, before finally stabilising and reaching maturity.
Identifying where a particular innovation is on this journey, especially those that are in the emerging and accelerating stages, is essential for understanding their current level of adoption and the likely future trajectory and impact they will have.
20+ innovations will shape the apparel industry
According to GlobalData’s Technology Foresights, which plots the S-curve for the apparel industry using innovation intensity models built on over 13,000 patents, there are 20+ innovation areas that will shape the future of the industry.
Within the emerging innovation stage, yarn chemical treatment, embossed protective clothing, and garment laser embossing are disruptive technologies that are in the early stages of application and should be tracked closely. Fire retardant garments, antistatic fabrics, and interlaced yarn fabrics are some of the accelerating innovation areas, where adoption has been steadily increasing. Among maturing innovation areas are flat knitting machines and coated yarn fabrics, which are now well established in the industry.
Innovation S-curve for the apparel industry
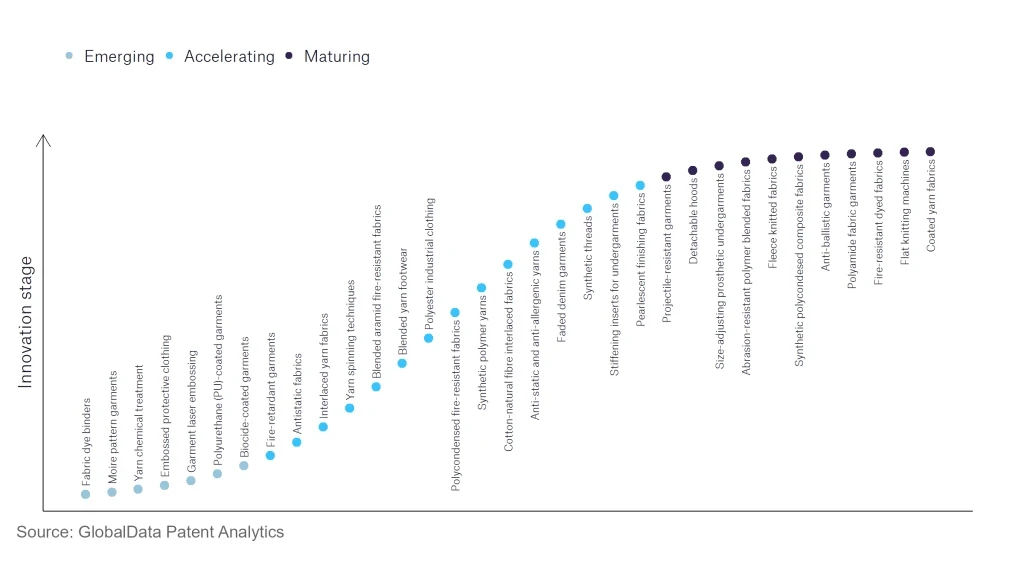
Innovation in Apparel: innovation areas
Size adjusting prosthetic undergarments is a key innovation area in apparel
Prosthetic undergarments are designed to replicate the size and shape of a person’s breast. They are manufactured using silicone gel or similar material. Prosthetic undergarments are typically designed to fit inside the bra cup. These prosthetic devices are made to look feminine while enabling comfort, and are of various types, ranging from external silicone breast prosthesis to partial breast prosthesis, also known as a shaper.
GlobalData’s analysis also uncovers the companies at the forefront of each innovation area and assesses the potential reach and impact of their patenting activity across different applications and geographies. According to GlobalData, there are 10+ companies, spanning technology vendors, established apparel companies, and up-and-coming start-ups engaged in the development and application of size-adjusting prosthetic undergarments.
Key players in size adjusting prosthetic undergarments – a disruptive innovation in the apparel industry
‘Application diversity’ measures the number of different applications identified for each relevant patent and broadly splits companies into either ‘niche’ or ‘diversified’ innovators.
‘Geographic reach’ refers to the number of different countries each relevant patent is registered in and reflects the breadth of geographic application intended, ranging from ‘global’ to ‘local’.
Patent volumes related to size-adjusting prosthetic undergarments
Leading players in terms of patents filed in the size-adjusting prosthetic undergarments space are Hanesbrands, Wacoal Holdings, Clover Mystique, Nike, Fast Retailing, and Top Form International. In May 2022, Hanesbrands, a multi-national clothing company, filed for a trademark in Anatomy shading for garments.
Leading players in the size-adjusting prosthetic undergarments space in terms of application diversity are Utax, Cupid Foundations, Regina Miracle International, Authentic Brands, and Hanesbrands.
Top players in this space in terms of geographic reach are Clover Mystique, Fast Retailing, Triumph Intertrade, Hanesbrands, Wacoal Holdings, and Nike.
3D printing is revolutionising breast prostheses. It is cost-effective, yet faster in production. Personalised prostheses can be produced using this technology and 3D-printed breast models serve as guides for surgeons.
Source from Just-style.com
Disclaimer: The information set forth above is provided by Just-style.com independently of Alibaba.com. Alibaba.com makes no representation and warranties as to the quality and reliability of the seller and products.




