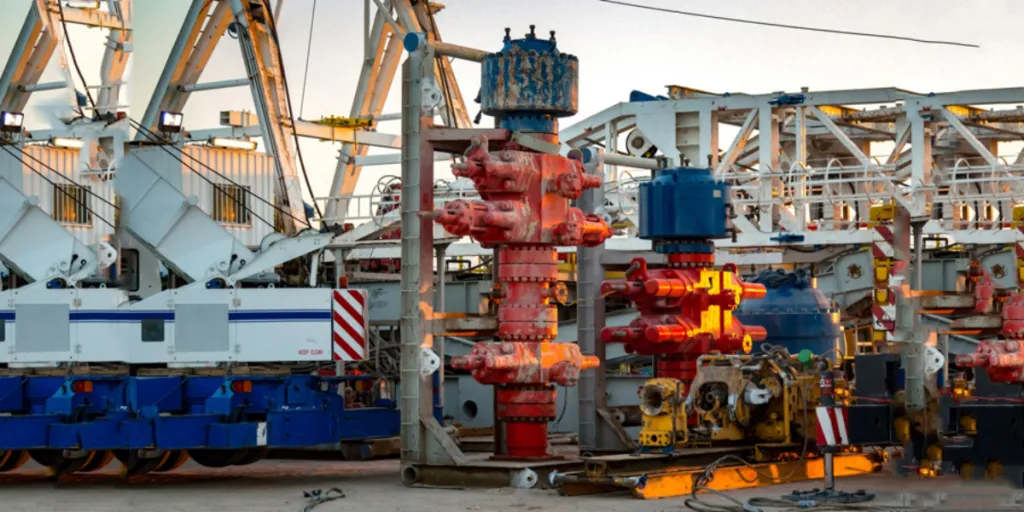
Blowout preventers (BOPs) are crucial in the oil and gas industry, acting as a final safeguard to prevent catastrophic blowouts. These devices have designs that manage and stop the uncontrolled release of oil and gas from wells. More importantly, BOPs come in various types, each customized to handle different oil well conditions and geological challenges.
This guide will explore the different blowout preventers businesses can find on the market today. From annular BOPs to shear, ram, and hybrid options, it will explore what sets each type apart and how they work, so that you can be sure to stock the best options for your buyers.
Table of Contents
What are blowout preventers, and why are they important?
8 types of blowout preventers to consider stocking for 2025
Final words
What are blowout preventers, and why are they important?
Blowout preventers are essential in maintaining the safety and stability of any oil or gas well. They are designed to limit the uncontrolled release of hydrocarbons, which create risks for blowouts. Such blowouts threaten life and often result in severe environmental and financial damage.
Think of BOPs as a shield between the well and drilling equipment. Manufacturers bond them together to work safely under high pressure in harsh conditions. This means that BOPs are one of the most important safety features in the oil and gas field.
Besides preventing blowouts, BOPs can also help control oil wells during drilling, maintenance, and completion. They enable the operator to cut the flow of oil and gas, undertake repairs, and deal with issues that may arise.
8 types of blowout preventers to consider stocking for 2025
1. Annular blowout preventers
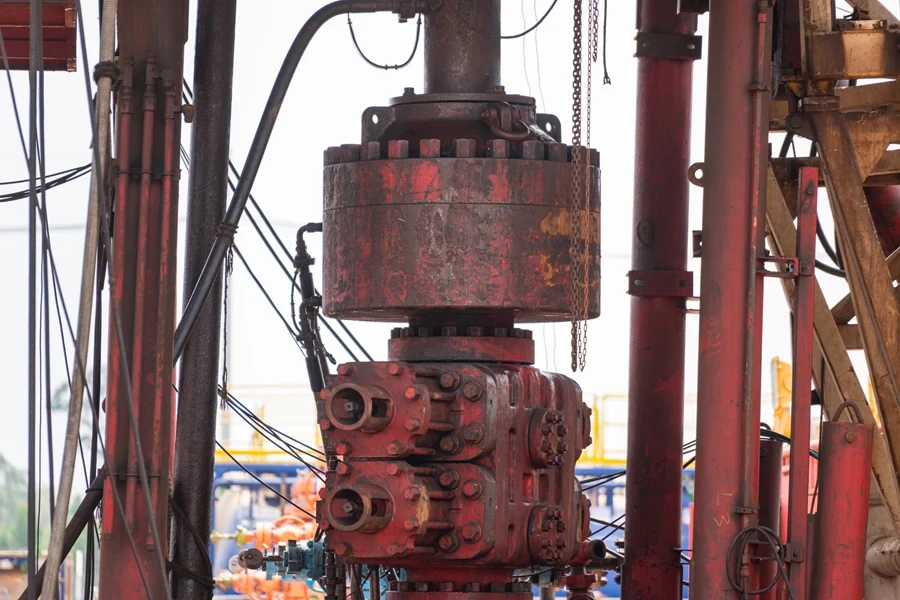

Annual (spherical) BOPs are the most popular in the oil and gas industry. They include a rubber, donut-shaped seal that operators wrap around the drill pipe or casing to provide a tight seal for pressure control.
However, what makes them popular is that they are uniquely flexible. They can maintain the well’s seal even when the pipes move in or out, which is why many consider them perfect for operations that require regular pipe inserting and removal. Annual BOPs also use hydraulic pressure to close around the drill pipe or casing when needed quickly.
2. Shear ram blowout preventers
Shear ram blowout preventers (or emergency shear rams) are specialized types of BOP designed for critical situations. Their job is simple but crucial: they cut through the drill pipe or casing and seal the well in an emergency when other methods have failed.
Typically, operators place these rams at the bottom of the BOP stack, ready for activation when needed. Manufacturers also equip them with sharp blades to let them slice through the drill pipe or casing before clamping down to block the wellbore, preventing any dangerous blowout.
Shear rams also use hydraulic pressure to drive the cutting blades and seal the well. They can handle extreme conditions and high pressure, making them perfect as the final safeguard to keep the well safe in the most demanding situations.
3. Blind shear ram blowout preventers
These are a special type of shear ram BOP that works where their predecessor may fail. One key benefit of these BOPs is that they can act without hydraulic pressure, making them much more reliable in worst-case scenarios. When hydraulic pressure fails, operators can activate these BOPs mechanically to ensure they successfully shut the wellbore and prevent a blowout.
4. Variable bore ram blowout preventers
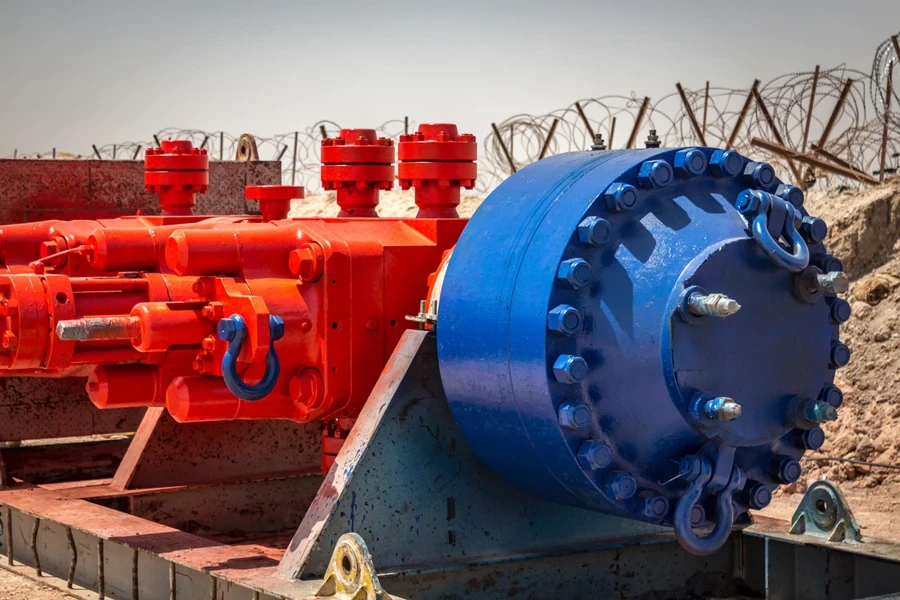

This BOP is another unique type of ram blowout preventer. What makes it different is its ability to seal the wellbore regardless of changes in pipe size, offering flexibility that’s hard to beat. This adaptability is especially helpful when multiple pipe sizes are present in a single well, as it eliminates the need to swap out the entire blowout preventer stack.
Like other BOPs, VBRs are hydraulically powered, allowing operators to adjust the rams to fit different pipe sizes easily. This also makes the operation more efficient and ensures a well-controlled status throughout. Despite their flexibility, VBRs still offer strong sealing integrity, making them a reliable choice for managing high-pressure environments.
5. Dual ram blowout preventers
Double-ram BOPs take a different approach to blowout prevention. Unlike other ram variants, these BOPS feature two sets of rams that can each seal around the drill pipe or casing to stop fluid flow. The main goal of this design is to provide added safety because if one set of rams fails, the other can step in to create a backup seal.
These BOPs are common in critical operations, like deepwater drilling or high-pressure environments, where reliability is essential. Having two sets of rams adds redundancy while increasing the sealing power, ensuring a stronger, tighter seal to help prevent leaks and reduce blowout risks.
6. Stripper blowout preventers
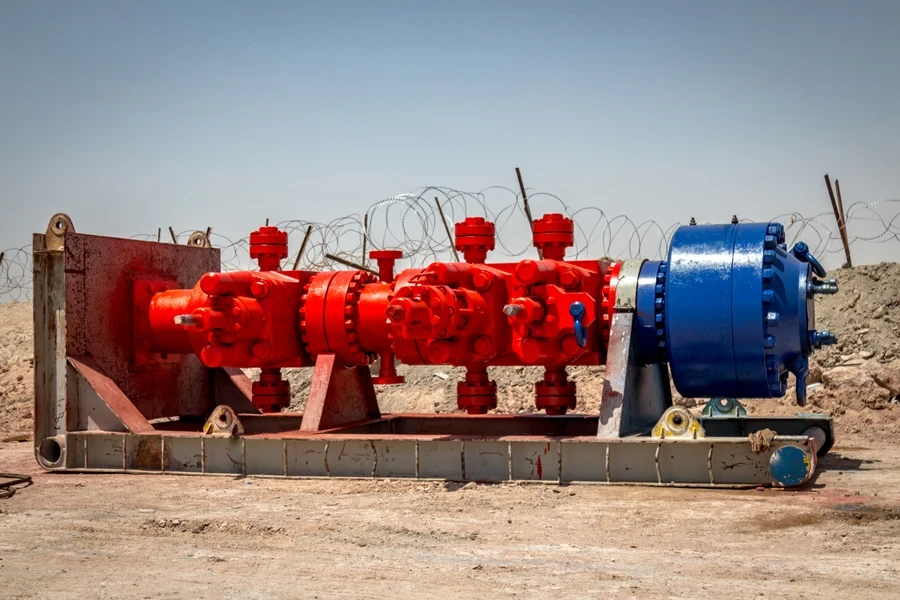

The stripper BOP is a more specialized blowout preventer that helps control wells during tripping operations, where pipes move in or out of the well. In contrast to other BOPs (which focus more on sealing the well during a blowout), the stripper BOP allows pipes to move while maintaining control.
Like an annular BOP, a stripper BOP uses a flexible rubber element that expands or contracts around the pipe as it moves. Stripper BOPs also provide safety during high-risk tripping, helping create a tight seal that stops blowouts. However, operators typically use them with other BOPs (like annular or ram BOPs) for complete oil well control.
Note: The stripper BOP may need regular maintenance and has limitations on the size of pipes it can handle.
7. Stack configurations
Blowout preventers are rarely used alone—they’re usually part of a larger system called a BOP stack. This stack is a vertical assembly of different BOP components tailored to the drilling operation, oil well conditions, and local regulations. Here’s a breakdown of a typical BOP stack:
- Annular BOP: Usually the top of the stack, this versatile component seals around various pipe sizes and shapes.
- Ram BOPs: Often below the annular, ram BOPs, including types like blind shear, pipe, and variable bore rams, offer specific functions (like backup protection).
- Choke and kill lines: These high-pressure lines connect the stack to oil well control systems, helping manage fluid circulation and monitor pressure.
- Valve and manifold: These additional parts ensure the system operates smoothly.
How the BOP stack arranges these components depends on the drilling operation’s needs. Operators sometimes use dual BOP stacks for added safety and redundancy.
8. Blowout preventer control systems
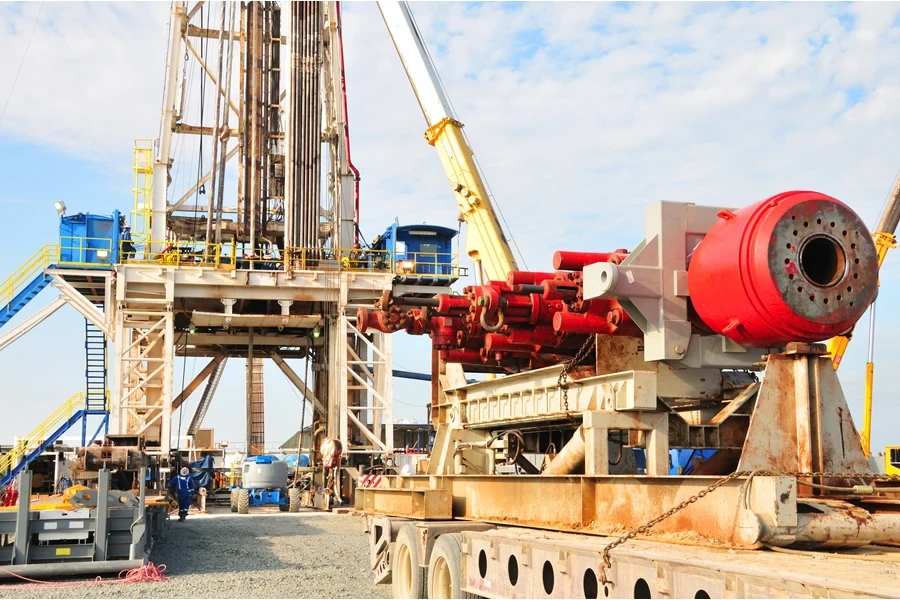

BOP control systems are necessary for keeping oil wells safe. These systems monitor and manage the operation of the BOP stack, ensuring everything works as it should. The control system usually includes hydraulic control panels, valves, and accumulators.
This setup allows operators to open and close the rams, activate shear rams, and monitor the pressure and status of the BOP stack. Operators will also have access to real-time data from sensors and gauges, which help them track pressure, temperature, and overall system health.
This constant monitoring ensures the BOP remains functional and ready for action. Another great thing about these systems is that they allow remote control, giving operators more efficiency while adding an extra safety layer.
Final words
The oil and gas industry can’t do without blowout preventers. They act as necessary safeguards against blowouts and help maintain oil well safety. Choosing the right BOP depends on the oil rig’s needs, as each type offers unique features suited to different situations.
Remember to consider factors like well conditions, bore size, and the environment when selecting BOPs. The right BOP (especially if operators follow solid control practices) will help reduce blowout risks and keep operations running smoothly.




