Overview of the agricultural machinery industry
Definition and classification of the agricultural machinery industry
Agricultural machinery refers to various machinery used in crop cultivation and livestock production, as well as in the primary processing and treatment of agricultural and livestock products. Agricultural mechanization is the application of agricultural machinery to replace human and animal power in the economic process of agricultural production and a means of improving the efficiency of agricultural production, the rate of land output, and the utilization of resources, reducing the cost of agricultural production, resisting natural disasters and making sustainable and rational use of agricultural resources.
Most agricultural machinery is specially designed and manufactured based on the characteristics of agriculture and the requirements of various operations. According to its purpose, it can be divided mainly into types such as tillage and land preparation machinery, planting and fertilization machinery, field management machinery, harvesting machinery, post-harvest processing machinery, and agricultural product preliminary processing machinery.
Classification of the agricultural machinery industry
Land leveling
- Farming and land preparation machinery
- Farming machinery, land preparation machinery, other farming and land preparation machinery
Seeding and fertilization
- Planting and fertilization machinery
- Seeding machinery, seedling equipment, planting machinery, fertilization machinery, plastic film machinery, and other planting and fertilization machinery
Field management
- Field management machinery
- Cultivating machinery, plant protection machinery, pruning machinery, and other field management machinery
Harvesting
- Harvesting machinery
- Grain harvesting machinery, corn harvesting machinery, fruit harvesting machinery, vegetable harvesting machinery, flower (tea) harvesting machinery, grain crop harvesting machinery, cotton and hemp crop harvesting machinery, rootstock crop harvesting machinery, feed crop harvesting machinery, stem collection and processing machinery, and other harvesting machinery
Post-harvest processing
- Post-harvest processing machinery
- Threshing machinery, cleaning machinery, shelling (peeling) machinery, drying machinery, storage machinery, seed processing machinery, and other post-harvest processing machinery
Agricultural product processing
- Primary processing machine for agricultural products
- Rice milling machinery, flour (pulp) machinery, oil squeezing machinery, cotton processing machinery, fruit and vegetable processing machinery, tea processing machinery, and other agricultural product preliminary processing machinery
Others
- Agricultural handling machinery, drainage and irrigation machinery, animal husbandry and aquaculture machinery, power machinery, rural renewable energy utilization equipment, farmland basic construction machinery, facility agricultural equipment, and other machinery
Development history of the agricultural machinery industry
The development of the agricultural machinery industry is a symbol of the evolution from traditional agriculture to modern one. The domestic agricultural machinery industry in China can be roughly divided into five development stages from its inception to the present:
Starting period (1949-1958): At the beginning of the establishment of New China, the industrial foundation of agricultural machinery was still weak. The total power of agricultural machinery equipment in China was only about 80,000 kW, and the number of farm tractors was about 100. Other heavy agricultural machinery was even more scarce, such as fully automatic corn threshers and agricultural trucks, which were almost zero.
Exploration and adjustment period (1959-1965): During this period, the Chinese government invested over 2 billion yuan in the agricultural machinery industry, and several large manufacturers in agricultural machinery, including YTO Group Corporation and Tianjin Tractor Manufacturing Corp. Ltd., were successively put into operation.
Government-led period (1966-1980): Constructing new agricultural machinery companies for manufacturing and accessory production and establishing an industry system in China agricultural machinery that roughly matched market demand for agricultural machinery manufacturing, maintenance, and accessory production, with a relatively complete range of categories. All agricultural production machinery is manufactured basically and independently in China.
Mechanism transformation period (1981-1994): Farmers independently purchase, own, and operate agricultural machinery, gradually becoming the main body of agricultural mechanization investment and operation.
Market-oriented period (after 1994): The agricultural machinery industry has entered a market-oriented development stage, and related manufacturing enterprises are participating in market competition from the production, sales, and use of agricultural machinery products, gradually developing from the initial price level to quality, service, and other aspects. Gradually fierce market competition has led to a decrease in the prices of agricultural machinery products, reducing farmers’ purchasing costs and promoting mergers and acquisitions among enterprises, forming large agricultural machinery corporations such as the YTO Group.
Since 2020, the agricultural machinery industry has experienced significant growth, and the machinery market in China continues to move towards structural adjustment under the background of the country’s emphasis on agricultural production and food security.
Business mode of agricultural machinery industry
(1) Profit mode
Agricultural machinery industry enterprises mainly achieve revenue and profits by providing machinery equipment, accessories, and services for downstream distributors, as well as directly selling agricultural machinery products to traders.
(2) Procurement mode
1) Procurement mode for general components
General components mainly include four major components, such as diesel engine, gearbox, hydraulic transmission device, and track as cast iron parts, sheet metal welding parts, cast steel parts, and hardware standard parts. After the production department of agricultural machinery industry enterprises enters the planned production quantity into the system, the system will generate the required material procurement quantity according to the set material list. The procurement department adjusts and allocates the supply quantity of each supplier according to the material procurement quantity generated by the system and then sends a purchase order to the supplier. The supplier receives the order through the ERP information system and confirms it before organizing production and delivering the goods. The quality control department inspects the materials and puts them into storage after passing the inspection. The warehouse personnel issue a warehouse receipt to the supplier, and the supplier issues an invoice based on the warehouse receipt. After that, the finance department of the enterprise makes payment.
2) Procurement mode of outsourced parts
Most agricultural machinery industry enterprises, while retaining their independent intellectual property rights and the principle of self-made core components, hand over customized parts such as sheet welding parts and metal processing parts to outsourced manufacturers for production. At present, there are two forms of outsourcing processing: ① Outsourcing manufacturers customize production according to the design drawings and process requirements provided by agricultural machinery industry enterprises. After selecting qualified outsourcing manufacturers, the enterprise shall purchase raw materials and organize personnel to complete the processing of relevant outsourced components. ② For components such as vibrating screen wall panels, header wall panels, and large grain tank panels that require high cutting process requirements, agricultural machinery industry enterprises purchase steel and cut it for processing. Outsourced manufacturers shall process according to the design drawings and process requirements provided by the enterprise.
After the steel is purchased and cut by agricultural machinery industry enterprises, outsourced manufacturers process it according to the design drawings and process requirements provided by the enterprise.
(3) Production mode
Agricultural machinery production has strong seasonality. To ensure timely supply during the peak sales season, the above agricultural machinery industry enterprises adopt a production mode that combines production based on sales and moderate stocking. According to the industry experience and analysis of market information data, a company predicts the sales situation for the next year, combines it with the sales volume of the company’s products this year, and formulates sales targets and plans for the following year.
(4) Sales mode
The sales modes of agricultural machinery products are divided mainly into two types, including non-buyout distribution and buyout sales. Among them, the non-buyout distribution mode aims at the domestic market, and the buyout sales mode aims at the foreign market.
1) Non buyout distribution mode
The enterprise signs an Annual Framework Contract with the distributor to determine the distribution cooperation relationship. When distributors have procurement needs, they submit orders to the enterprise sales system. After the sales department verifies a distributor’s credit status, it can submit it to the finance department for review. After the finance department verifies the distributor’s accounting information and reviews the order, the sales department sends the products to the distributor and the distributor signs for the products.
2) Buyout sales mode
The sale of agricultural machinery products to foreign markets is mainly achieved through buyout sales by import and domestic export traders.
Barriers to entry into the agricultural machinery industry
(1) Entering the agricultural machinery subsidy directory requires corresponding qualifications
Since 2004, the Chinese government has provided direct subsidies to farmers for purchasing agricultural machinery included in the national promotion support catalog. Subsidized machines and tools must be products within the scope of China agricultural machinery purchase subsidies and must also possess one of the following qualifications: ① Obtaining the Agricultural Machinery Test Appraisal Certificate (Agricultural Machinery Promotion Appraisal Certificate); ② Obtaining a mandatory certification certificate for agricultural machinery products; ③ Listed in the pilot scope of voluntary certification and acceptance of agricultural machinery, and obtained the certificate of voluntary product certification for agricultural machinery. Therefore, whether the product can get the corresponding qualifications is crucial for newly entered industry enterprises.
(2) Technical and talent barriers
Agricultural machinery equipment has a complex structure, multiple categories, and high processing accuracy requirements. The current market requirements for products have shifted from the previous “Simplicity, Affordability, and Solidity” to the direction of mechatronics and hydraulics integration, information technology, and comprehensive application of biological sciences. The technical level and added value of agricultural machinery equipment are gradually increasing. Agricultural machinery enterprises with low technological levels and outdated production processes are no longer able to gain competitive advantages in the market. Therefore, new industry entrants face high technical barriers.
Meanwhile, the R&D and manufacturing of agricultural machinery equipment require high-level and experienced professional R&D teams and production personnel. The sales and after-sales service of agricultural machinery products require versatile talents who possess marketing skills, maintenance skills, and service awareness. The above talents are currently relatively scarce, and the cultivation and introduction of talents is also one of the problems for new companies to face.
(3) Establishment of a sales network and after-sales service network
China’s agricultural machinery consumption has the characteristics of decentralization and differentiation, and users have high requirements for pre-sales and after-sales services. Then, industry companies mainly sell through distributors or agents. Therefore, it is crucial to establish a comprehensive and extensive sales and after-sales service network. Agricultural machinery manufacturing enterprises often need to invest a large amount of manpower, material resources, and financial resources in the early stage to establish a comprehensive distribution and service network, and the more dealers there are, the greater the difficulty of management. New entrants often find it hard to obtain this advantage in the short term.
(4) Financial barriers
Agricultural machinery manufacturing is a capital-intensive industry, and all the construction of production lines, product R&D, and improvement require large-scale capital investment. Meanwhile, the seasonal demand for agricultural machinery equipment is higher, and agricultural machinery enterprises often face significant cash flow pressure. In addition, the sales mode for agricultural machinery enterprises is distribution or agency sales, and end users also have high requirements for the response speed of after-sales service. Establishing and maintaining a scale of sales and after-sales service network for agricultural machinery manufacturing enterprises also requires significant financial investment. Therefore, there are high financial barriers in the industry.
(5) Management level barriers
Agricultural machinery enterprises need a high level of management to ensure the management of R&D, production, procurement, sales, personnel, and the establishment of corporate culture in the production and operation process. The above business processes will directly or indirectly affect the quality, performance, and cost of agricultural machinery products and ultimately determine their market competitiveness. Therefore, establishing a scientific and comprehensive management system is crucial for the long-term development of agricultural machinery manufacturing enterprises.
(6) Brand barriers
The widely recognized agricultural machinery brand is a comprehensive reflection of the accumulation of enterprise product quality, after-sales service, management level, and market channels. It takes quite a while for agricultural machinery brands to establish and gain user recognition. In addition to traditional brand promotion methods, what is more important is that users gain wider recognition and praise for the brand through years of personal use and word of mouth. Product quality, service speed, management level, and technological innovation are all factors that affect user experience and evaluation. Therefore, brand recognition will become a barrier for new industry entrants.
Analysis of the industrial chain in the agricultural machinery industry
The agricultural machinery industry chain mainly includes upstream suppliers of raw materials and components, midstream suppliers of complete agricultural machinery, downstream distribution channel providers, and end users of agricultural machinery.
The upstream of China’s agricultural machinery manufacturing industry chain consists of raw material suppliers (steel, non-ferrous metals, rubber, etc.) and component manufacturers (internal combustion engines, bearings, tires, fasteners, etc.). Regarding raw materials, steel, and non-ferrous metals are raw materials for manufacturing agricultural machinery products. Due to the relatively stable development of China’s steel industry, the supply of raw materials in the agricultural machinery industry is also showing a steady trend, which is less affected by price factors. In terms of components, the technical level of standard components and machined parts in China has improved rapidly, and a comprehensive industry system has gradually formed. These parts and components required by the agricultural machinery industry have become an industrial scale in China, and there were many industry companies available for selection.
The policy environment for the agricultural machinery industry
(1) Regulatory system
According to the Industry Classification Guidelines for Listed Companies (revised in 2012), the R&D, production, and sales of agricultural machinery and equipment are divided into specialized equipment manufacturing industries in the manufacturing industry, with industry code C35. According to the Industrial Classification of the National Economy (GB/T 4754-2017), it belongs to the “Specialized Equipment Manufacturing Industry” with an industry code of C35.
The competent departments for agricultural machinery wholesale and mechanized agriculture and horticultural equipment manufacturing industry are the Agricultural Mechanization Management Department of the Ministry of Agriculture, the Development Planning Department of the Ministry of Agriculture, and the Agricultural Mechanization Station of the Ministry of Agriculture. The relevant industry associations are the China Agricultural Mechanization Association and the China Agricultural Machinery Circulation Association.
(2) Related Policies
In recent years, to promote the development of the agricultural machinery industry, China has successively issued many policies, such as the “14th Five Year Plan for Promoting Agricultural and Rural Modernization” by the State Council in 2022, which steadily implemented agricultural machinery purchase subsidy policies, created 300 demonstration counties for complete mechanization of crop production, constructed 300 demonstration counties for complete mechanization of facility agriculture and large-scale aquaculture, and promoted deep loosening and land preparation of agricultural machinery and the transformation of farmland suitable for mechanization in hilly and mountainous areas, and strengthen the construction of agricultural machinery’s ability to rush for planting, harvesting, and drying services.
In response to the national call, each province and city actively promotes the development of the agricultural machinery industry. For example, Tianjin has released the “14th Five Year Plan for Promoting Agricultural and Rural Modernization”, which aims to improve the level of agricultural mechanization, accelerate the transformation and upgrading of agricultural mechanization, promote the mechanization of grain crop production from cultivation, planting, and harvesting to the entire process of plant protection, drying, and straw treatment, focus on improving the comprehensive mechanization level of key economic crops, facility agriculture, animal husbandry and aquaculture, and initial processing of agricultural products, and promote the comprehensive, high-quality, and efficient development of agricultural mechanizations throughout the entire process.
Current situation of the agricultural machinery industry
Since 2020, under the background of China’s emphasis on agricultural production and food security, the agricultural machinery industry has experienced significant growth. China’s agricultural machinery market will continue to move towards structural adjustment. In the medium to long term, driven by the dual cycle, China’s agricultural machinery industry is facing a period of strategic opportunities, with five major trends in development. The first is that low-speed development has become the new normal. The second is that market demand presents fragmentation and differentiation. The third is that the mechanization problem of economic crops has become more prominent when the cultivation and harvest stages of the three major grain crops have achieved mechanization. The fourth is the coexistence of large-scale and small-scale. The fifth is that high-end intelligence has become the dominant direction. The market size of China’s agricultural machinery manufacturing in 2022 is 382.05 billion yuan.
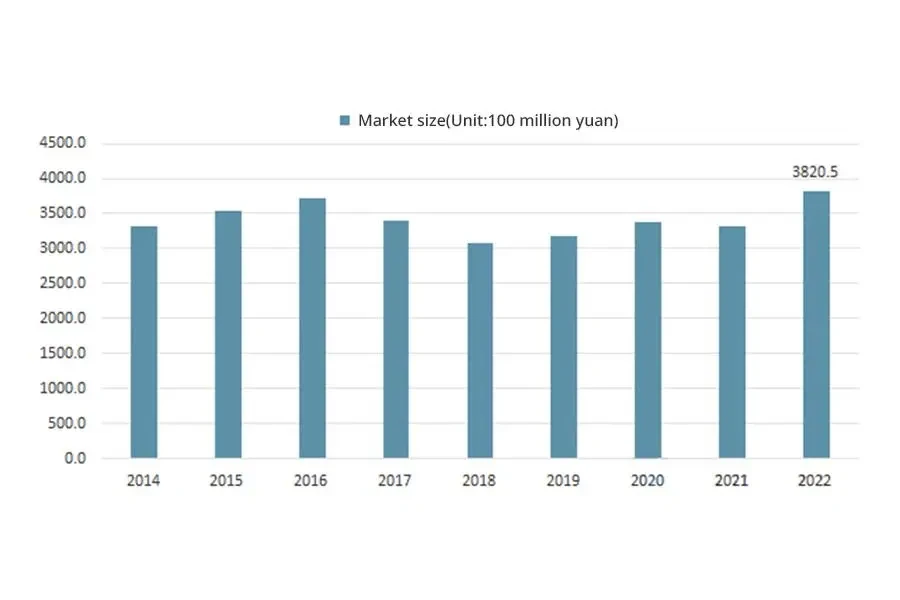
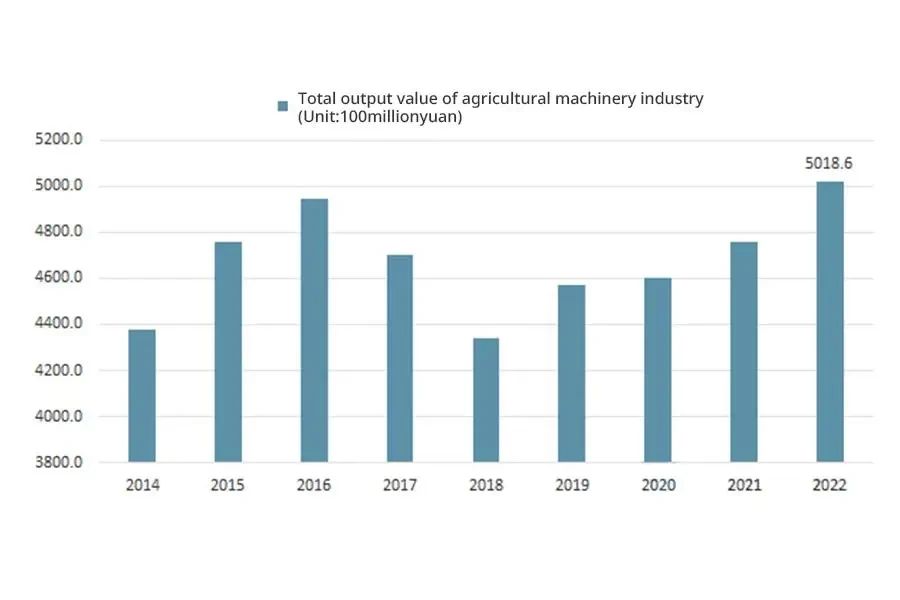
As a traditional agricultural country and the largest developing country in the world, China has a development space in the Chinese agricultural machinery market. The high yield is worth benefiting from a series of actively promoting agricultural mechanization policies issued by the Chinese government in recent years, which improved agricultural machinery productivity. In addition, China’s terrain is complex and diverse, and production and operation machinery needs to adapt to different geographical environments. As a result, China has a wide range of agricultural machinery types, which is also why Chinese agricultural machinery output value can occupy a place in the global agricultural machinery industry. In 2021, the total output value of the agricultural machinery manufacturing industry in China was 475.85 billion yuan. In 2022, the total output value of the agricultural machinery manufacturing industry in China was around 501.86 billion yuan.
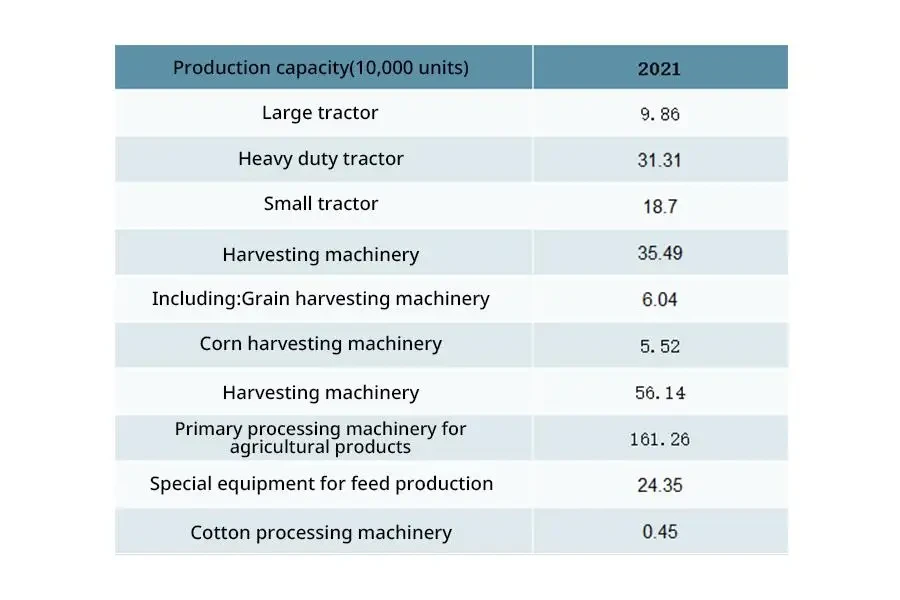
Opportunities and challenges in the agricultural machinery industry
Opportunities
(1) China’s agricultural machinery industry policies promote sustainable development of the industry
In recent years, China has made solving the “Three Rural” issues a top priority of government work, and agricultural machinery is a material foundation for the development of modern agriculture. Agricultural mechanization is a symbol of agricultural modernization.
In 2004, China issued the “Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Promotion of Agricultural Mechanization”, encouraging and supporting farmers and agricultural production and operation organizations to use advanced machinery, promoting agriculture mechanization, and building modern agriculture. In 2010, the State Council issued the “Opinions of the State Council on Promoting the Good and Fast Development of Agricultural Mechanization and Agricultural Machinery Industry”, proposing to “encourage the formation of several large enterprise groups and industrial clusters with advanced manufacturing levels and strong competitiveness, improve the industrial-organizational structure, form an industrial system and cluster led by large enterprises and supported by small and medium-sized enterprises, and enhance industrial concentration and professional division of labor and cooperation level”.
In 2018, the State Council issued the “Guiding Opinions of the State Council on Accelerating the Transformation and Upgrading of Agricultural Mechanization and Agricultural Machinery Equipment Industry”, proposing to “encourage large enterprises to shift from single machine manufacturing to complete equipment integration, support small and medium-sized enterprises to develop in the direction of specialization, precision, specialty, and innovation, and build an industrial pattern of coordinated development of large and small enterprises”.
The promulgation and implementation of the above policies have pointed out the direction for domestic agricultural modernization and also provided a good policy environment for the development of agricultural machinery enterprises and the advancement of agricultural machinery technology.
(2) Industrial policies promote sustainable development on the demand side
The subsidy policy for the purchase of agricultural machinery implemented since 2004 has played a direct role in promoting the development of China’s agricultural machinery industry. After decades of development, the national agricultural machinery purchase subsidy funds have increased from 70 million yuan in 2004 to 19.2 billion yuan in 2021 and 22 billion yuan in 2022. The scope of subsidies has expanded from 66 counties in 2004 to cover all agricultural and animal husbandry counties (farms) in China. The types of subsidy equipment have been from 9 major categories and 18 subcategories to 15 major categories and 44 subcategories, almost including production machinery for all major grain crops. Meanwhile, China implemented a long-term policy of tax reduction and exemption for agricultural machinery and a preferential tax policy for the agricultural machinery manufacturing industry, with a value-added tax rate of 9%. In addition, local governments have also implemented cumulative subsidies, operational subsidies, and guarantee subsidies for major agricultural machinery products. In some provinces and cities, GSP subsidies for corn harvesting machinery have been implemented for the first time.
The above policy implementation has largely solved the problem of farmers having strong purchasing intentions but lacking purchasing power and has played a positive role in promoting the stable development of the agricultural machinery industry.
(3) The structural shortage of the rural labor force will increase the demand for agricultural machinery products
Due to the significant increase in the wages of migrant workers, which is far greater than the increase in agricultural product prices and relevant national subsidies, the relative economy of farming has continued to decrease in recent years. The economic benefits of working in cities are much higher than those for farming. Therefore, the transfer of rural labor force to nonagricultural industries is accelerating, and the stock of rural labor force is continuously decreasing. Due to the strong seasonality of agricultural production, labor shortages are more pronounced during the sowing and receiving seasons. The increasingly prominent structural shortage of rural labor has led to a continuous increase in labor costs in agricultural production.
Due to the effective substitution of agricultural machinery for rural labor, its economic benefits will gradually emerge. Therefore, the structural shortage of rural labor is an internal driving force for the sustained demand growth in the agricultural machinery market.
(4) Moderate scale land intensive management will objectively accelerate agricultural mechanization
For a long time, the household-based contract responsibility system and the limited circulation of agricultural land have greatly limited the standardization and scale of agricultural production in China, leading to the lack of a practical foundation for achieving large-scale agriculture mechanization in the past. However, the rapid increase in labor costs and the relatively low efficiency of agricultural production have led to a large influx of rural labor into nonagricultural industries. To some extent, the issue of idle land has driven the development process of large-scale agricultural production in China.
In November 2014, the General Office of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the General Office of the State Council issued the “Opinions on Guiding the Orderly Transfer of Rural Land Management Rights and Developing Moderate Agricultural Scale Operation”, proposing to “encourage innovative forms of land transfer, liberalize land management rights, and promote the joint development of various business models such as household management, collective management, cooperative management, and enterprise management based on household contract management”.
Against the backdrop of encouraging the development of moderate-scale agricultural operations, land intensification and production scaling have become the mainstream trend, and the use of agricultural machinery for production operations has also become an inevitable trend. Any agricultural mechanization is not only beneficial for improving agricultural production efficiency but also for reducing labor costs. Therefore, the intensive development of land and the innovation of land management methods provide good opportunities for developing the agricultural machinery industry.
(5) The speed of product updates is accelerating, and national scientific research investment is strengthening
In recent years, the needs of agricultural machinery users have undergone fundamental changes due to factors such as advances in industry technology, changes in user age structure, high popularity of information intelligence, and continuous deepening of industrial adjustments. The demand for agricultural machinery products from users is no longer limited to the level of “high cost-effectiveness and durability” but has put forward higher requirements for the advanced, applicable, comfortable, energy-saving, and environmental protection of machinery. Therefore, the speed of technological upgrading and updating of agricultural machinery products will also become faster and faster to meet the diverse needs of users.
In “Made in China 2025″, agricultural machinery and equipment have been included in the national key development areas. It has determined the development direction, namely ” Focus on the development of the advanced agricultural machinery and equipment used in the main production processes of grain, cotton, oil, sugar, and strategic economic crops, such as cultivation, cultivation, planting, management, harvesting, transportation, and storage. It can accelerate the development of high-end agricultural equipment and key core components such as large tractors and their multiple-operation machines and large and efficient combine harvesters. It can improve the information collection, intelligent decision-making, and precision operation capabilities of agricultural machinery and equipment and promote the formation of information-oriented agriculture production Integrated solutions for information technology. “
In 2017, the National Key R&D Plan launched and implemented 17 key special projects for “Intelligent Agricultural Machinery Equipment”, with a total investment of 350 million yuan from the central government, and the investment in each project exceeds 15 million yuan. In addition, the Ministry of Agriculture has launched the construction of critical laboratories and scientific observation experimental stations during the 13th Five-Year Plan period. The discipline group of “Modern Agricultural Equipment” has added six professional (regional) key laboratories, including the Key Laboratory of Plant Protection Engineering of the Ministry of Agriculture and the Key Laboratory of Agricultural Product Processing Equipment of the Ministry of Agriculture, forming a discipline group laboratory system consisting of 1 comprehensive key laboratory, 14 professional (regional) key laboratories, and five agricultural science observation and experimental stations. It shows that China’s scientific research investment in machinery equipment is strengthening continuously.
In summary, the acceleration of technological upgrading and upgrading of agricultural machinery products, as well as the increase in national scientific research investment in agricultural machinery equipment, have brought new opportunities for developing agricultural machinery manufacturing enterprises.
Challenges
(1) Intensified market competition in the agricultural machinery industry
The prospects for the agricultural machinery industry are enormous. In recent years, agricultural machinery equipment enterprises have also rapidly increased. Despite the influx of various types of capital into the machinery industry, the focus of capital investment is mostly on improving the production capacity rather than the development of new technologies and products. Product homogenization is relatively severe, which can easily trigger low-priced competition. In addition, the rapid development of the agricultural machinery industry has brought opportunities to agricultural machinery manufacturing enterprises and also attracted foreign counterparts. International machinery manufacturing giants have entered the Chinese market through joint ventures or sole proprietorships, such as the construction of factories in Harbin by Case New Holland, the acquisition of Shandong Jinyi by Kras, the construction of factories in Tianjin and Jiamusi by John Deere, and the construction of factories in Suzhou by Japan’s Kubota. The entry of foreign capital has further intensified the competitive situation in the industry.
(2) China’s independent research and development capabilities need to be improved
The development of China’s agricultural machinery industry is based mainly on the model of technology introduction and imitation innovation, with critical products and technologies relying on foreign countries. Most enterprises in the industry do not attach enough importance to intellectual property rights, lack innovation awareness, and rely solely on imitation. The product homogenization is relatively serious. In addition, there is still a significant gap in the performance, quality, and research and development methods of high-end products in China’s agricultural machinery industry compared to internationally renowned companies, and the further improvement required in product standardization, modularization, informatization, and intelligence. Considering the periodicity and accumulation of technological research and development, it is difficult for domestic agricultural machinery enterprises to catch up with international agricultural machinery production enterprises in the short term.
Competitive pattern of the agricultural machinery market
At present, the global agricultural machinery industry has formed a situation where large-scale competition among giants and specialized competition among small and medium-sized enterprises coexist. Overall, the concentration of the industry has shown an upward trend in the past decade. On a global scale, five major agricultural machinery giants have been formed and led by John Deere Company, Case New Holland Global, AGCO Group, Kras Agricultural Machinery Company, and Kubota Corporation. The above-mentioned agricultural machinery giants not only have a complete range of products but also have established a global sales network and production base.
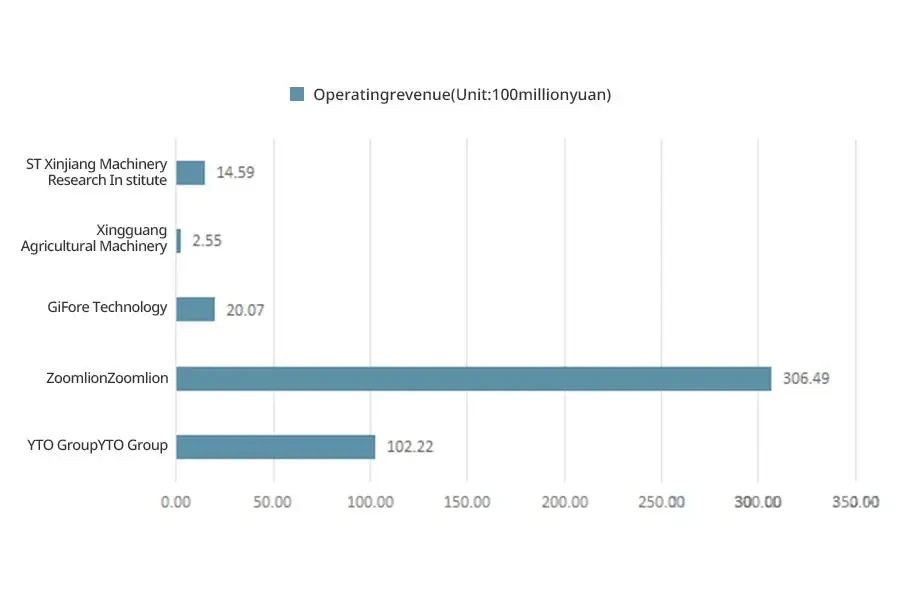
Despite the rapid development of China’s agricultural machinery industry in recent years, there is still a lack of large-scale agricultural machinery manufacturing enterprises with some international influence. Currently, there are many enterprises in the industry, but most are small and medium-sized enterprises with weak strength. The industry competition pattern still presents a small and scattered characteristic. Currently, the leading enterprises in China’s agricultural machinery market are YTO Group, Zoomlion Heavy Technology, Jifeng Technology, Xingguang Agricultural Machinery, and ST New Research.
In addition, China’s agricultural machinery enterprises have some regional characteristics, mainly distributed in Shandong, Zhejiang, Hebei, Henan, and Jiangsu. The unique geographical advantages, active private capital, and foreign investment, great industrial foundation, and strong supporting capabilities of the five provinces mentioned above have led to a rapid expansion of the industry scale, an increasingly complete industrial chain, and powerful cluster effects, occupying an increasingly important position in the development of China’s agricultural machinery industry.
Development trends in the agricultural machinery industry
Now, China is in a critical stage of accelerated development in industrialization, informatization, urbanization, and agricultural modernization, providing complete conditions and broad development space for the agricultural machinery industry. The domestic demand for agricultural machinery is still in a period of rapid growth. The agricultural machinery and equipment manufacturing industry in China must achieve breakthroughs through technological innovation, with product upgrading, filling gaps, and improving core competitiveness as the main direction. It must optimize the industrial structure, improve process level, management level, and product quality, inject new energy into the industry’s development, and achieve a leap from a manufacturing powerhouse to a manufacturing powerhouse. From a global perspective, the development space of agricultural machinery products in China in the future mainly includes the following aspects:
1. Developing high-power agricultural machinery
The application of high-power agricultural machinery is becoming increasingly common in developed countries. Now, the maximum power of the STEIGER535 tractor produced by Case Company has reached 442 kW (602 hp), improving the efficiency of agricultural production operations. The efficient, energy-saving, and intelligent characteristics of new machinery have led worldwide to accelerate the research and development of high-power machinery, and the width and efficiency of field operations of machinery are also increasing.
2. Developing joint tillage machinery and protective tillage machinery
Joint tillage operation refers to a machine that can complete multiple tasks simultaneously in one operation, with the advantage of reducing the number of land entries, minimizing soil tillage disturbance, and reducing soil compaction. If the joint operation machine for plowing and land preparation is applied, it can complete the plowing and land preparation operation in one entry. A combined tillage and sowing machine may finish the operations of plowing, land preparation, sowing, fertilization, and pesticide application at once.
3. Developing multipurpose machinery
After simple modification, a machine can complete multiple tasks, which is another direction in current agricultural machinery research. For example, the German Lemken multifunctional soil preparation and fertilization seeder can have various loosening, soil preparation, fertilization, and seeding devices. There are multiple combinations, allowing one driver to complete machine adjustments in a short amount of time.
4. Developing automated and intelligent agricultural machinery and equipment
Automated and intelligent operation modes are an inevitable trend in the development of modern agriculture and the correct choice for developing efficient, water-saving, and fertilizer-saving agriculture. In recent years, the intelligent technology of agricultural machinery in developed countries abroad has made rapid progress. Especially in facility agriculture in the Netherlands and Japan, modern greenhouse cultivation is widely used, and there is a complete variety of small machinery that can operate in greenhouses.
5. Developing the technical equipment system for supporting precision agriculture
Precision agriculture relies on information platforms and 3S technology to accurately adjust soil conditions and crop management measures according to the specific conditions of each operating unit in the field, scientifically use agricultural inputs, and obtain the highest yield and maximum economic benefits.
Source from Chyxx
Disclaimer: The information set forth above is provided by chyxx.com independently of Alibaba.com. Alibaba.com makes no representation and warranties as to the quality and reliability of the seller and products.




