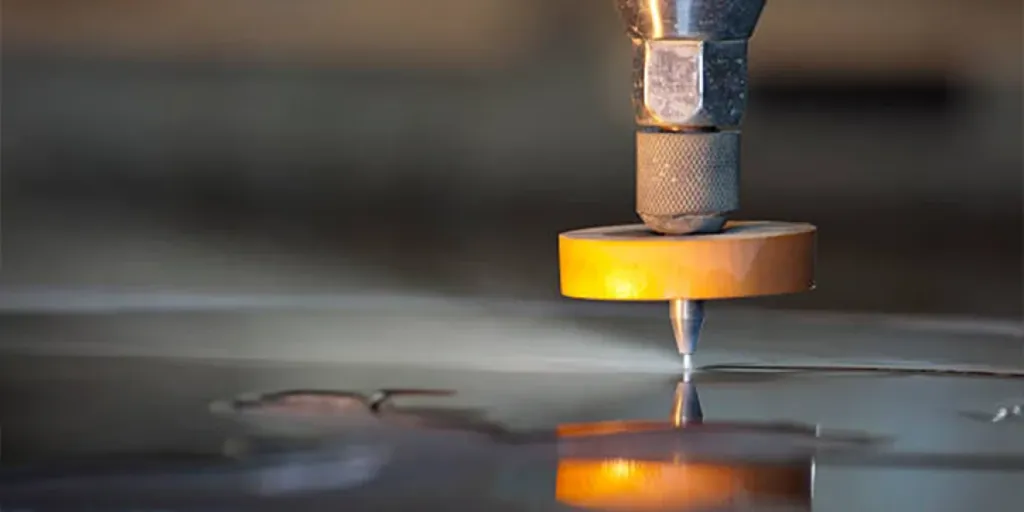
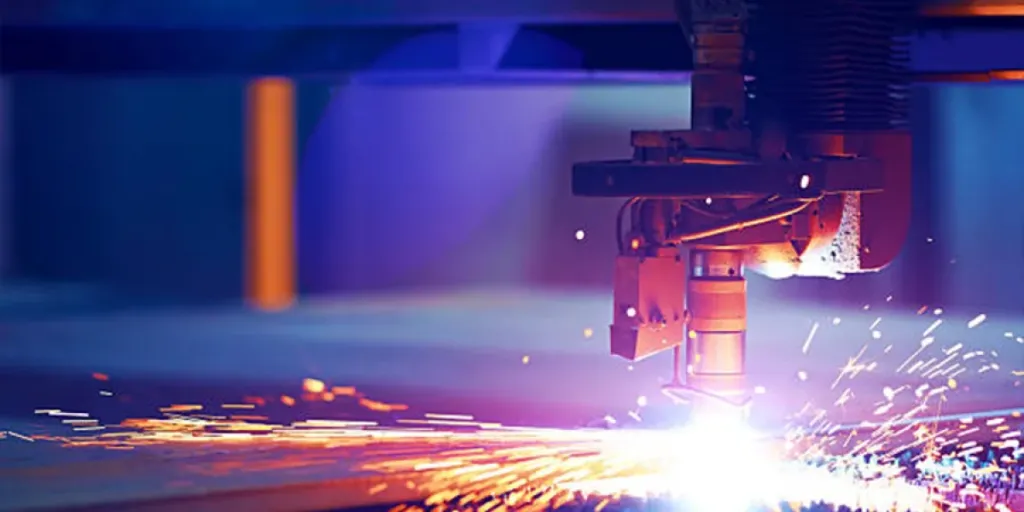
The two most popular cutting techniques in manufacturing are laser and water jet cutting. The best method will be determined by the type of material to be processed and the desired outcome. But before that, it’s critical to consider the fundamental variations between the two processes and the materials with which they are compatible. Continue reading to understand each cutting method thoroughly.
Table of Contents
The laser and water jet cutting market
Understanding laser and water jet cutting processes
Laser vs water jet cutting: which method is more efficient?
The laser and water jet cutting market
The global water jet cutting machine market was worth USD 969.2 million in 2019 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.1% from 2020 to 2027. The increasing adoption of eco-friendly cutting processes across various industries such as textile, automotive, packaging, and electronics is one of the primary factors driving the market growth. Furthermore, a rise in process automation has increased demand across industries for cutting-edge machinery.
The global laser-cutting machine market was valued at USD 5.96 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.40% by 2030. Increased production requirements across manufacturing industries and the need to reduce human involvement in improving metal processing outputs have fueled growth in this sector.
Understanding laser and water jet cutting processes
What is laser cutting?
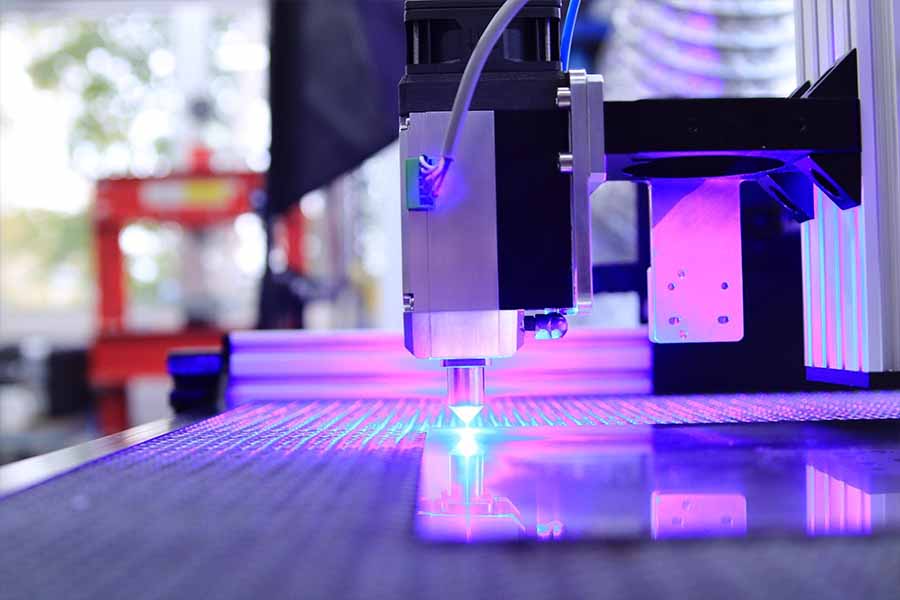

A laser cutting machine generates energy using a CO2 laser, which is then transmitted through a beam guided by mirrors and directed at the material. The laser source is housed within the machine, and the beam can produce between 1500 and 2600 watts. They work with various materials, including wood, glass, plastic, and all metals except reflective metals. However, cutting mixed materials with different melting points can get challenging with lasers. Because of the rigid beam guidance, structures with cavities and 3D materials are also difficult to cut with a CO2 laser beam.
Laser cutting works well on materials with thicknesses of 0.12 and 0.4 and is commonly used to cut flat sheets of medium thickness. In addition to cutting, a CO2 laser cutting machine can perform ablation, engraving, welding, drilling, and structuring.
Precision and safety measures
Precision is not an issue with laser cutting because the minimum size of the cutting slit can reach down to 0.006 inches, depending on the laser’s speed. On the other hand, thinner materials may be subjected to gas pressure if the proper distance is not maintained, resulting in partial burring. Thermal stress can also cause deformation and minor structural changes, and the material can appear striated.
Laser cutting may produce smoke and dust; some metals and plastic can produce toxic fumes; thus, ventilation is required when operating a CO2 laser machine. However, the overall risk of using such a machine is relatively low, as are the amount of waste produced and the time required for cleanup.
What is water jet cutting?
Water jet cutters use pressurized water to cut through materials, and the work area and pump are frequently separate, as opposed to laser cutters, which have the laser source inside the machine. Abrasives such as aluminum oxide and garnets are frequently used to improve cutting ability. The overall process is similar to erosion in nature but faster and more concentrated—a high-pressure pump delivers water through a rigid hose, resulting in a water jet. This water jet has a power range of 4 to 7 kilowatts.
Water jet cutters can cut through any material, including material combinations, but they risk delamination. These machines can handle 3D material cutting on occasion but struggle with sandwich materials and cavities, and cutting materials with restricted access is possible but challenging.
Water jets can perform ablation, cutting, and structuring and are especially useful for materials such as ceramics, stones, and thick metals, with thicknesses ranging from 0.4 to 2 inches.
Precision and safety measures
Water jet cutting is less precise than laser cutting because the minimum cut size is 0.2 inches. Furthermore, because a high level of force is used, small materials perform poorly and must be handled gently.
Although thermal stress is not an issue, when eliminating burring, the added abrasives to the water jet can cause the materials’ surface to appear sandblasted. Therefore, goggles must be worn to protect the eyes when using a water jet cutter. Additionally, the entire process is noisy and requires significant cleaning time because the abrasives are mixed with water.
Differences between laser and water jet cutting
Type of materials: Both water jet and laser are effective for cutting metals. However, because of its high-pressure functionalities, water jet is better suited for more rigid materials with thicknesses ranging from 0.4 to 2 inches. In contrast, laser cutting works best for thinner materials with 0.12- and 0.4-inch thicknesses.
Precision rate and speed: Laser cutting is much faster than water jet and has higher precision capabilities, with tolerances of +/-0.005 inches depending on the speed of the laser machine. On the other hand, water jet cutters have a tolerance of +/-0.03 inches.
Cost: Laser cutters do not have any tooling cost and have low component cost due to the high demand for the process. On the other hand, water jet cutters have a high component rate due to consumables but no tooling cost. A laser cutter is more expensive than a water jet cutter in general, but aside from the initial purchase price, the maintenance and operation costs are much lower.
Cleanup time: Laser cutting can occasionally leave burring on the cut surfaces of components, necessitating deburring for maximum smoothness, safety, and functionality. In contrast, water jet cutting leaves the cut components smooth and ready to use, requiring minimal cleanup after cutting.
Similarities between water jet and laser cutting

Flexibility: Both laser and water jet cutting processes are highly versatile and can work with many materials, including metals, wood, copper, and bronze. They are also highly adaptable, allowing customization to meet specific business needs.
Designed for automation: Both processes provide high precision and accuracy across a wide range of applications, making them suitable for the repetitive nature of automated processes. They can repeatedly make the same cuts with exactitude, ensuring consistency across product batches.
Narrow kerf width: The term “kerf width” in material cutting describes the quantity of material lost with each cut. Laser and water jet cutting both produce small kerf widths, with the former having incredibly thin kerf widths and the latter averaging around 0.01 inches. These lean cuts allow for complex designs and fine detailing.
Applications of laser cutting
– Laser cutting provides high precision, tolerance, and accuracy, is cost-effective, and is used in many industries. For example, it is used in the automotive industry to cut various parts such as hoods, roofs, and doors and to engrave the interiors.
– Laser cutting is also used in the mold, die, and tool industries due to its high tolerance, high speed, and ability to cut into different depths of materials, making it suitable for sturdy materials.
– Laser cutting is popular in the jewelry industry because it can carve intricate designs into materials like gold, silver, and diamonds to produce complex pieces. It is also a primary cutting process in this industry due to its small kerf, minimizing waste.
Applications of water jet cutting
– Water jet cutting is most commonly used on materials with high thermal requirements. It is widely used in the automotive industry to produce parts such as skid plates, metal gaskets, and custom vehicle body parts. Because the cutting process produces no mechanical stress, it is suitable for thick parts.
– Water jet is also used in the aerospace industry to manufacture components of turbine blades, cabin panels, and jet engines. This method is popular because it does not generate heat, which lessens the possibility of microscopic cracks and warping in the components.
Laser vs water jet cutting: which method is more efficient?
This article investigated the underlying mechanisms of laser and water jet cutting processes without deciding which is superior. Rather, it seeks to identify the similarities and differences between the two processes. In fact, the best cutting method will be determined entirely by the project and the materials to be used.
To summarise, laser cutting provides greater precision and is better suited for fine detailing and engraving projects. On the other hand, a water jet is best suited for thicker materials and has no material limitations.