Both metal coating and plating are procedures used to apply a protective layer to surfaces. The global market size of metal coatings holds a valuation of $15.3 billion in 2022. By 2032, the size is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.9% to $30.8 billion.
The metal plating global market size was valued at $13.49 billion in 2020. The figure is expected to climb to $16.89 billion by 2028 at a CAGR of 3.26% from 2021 to 2028. This article looks at the main differences between metal coating and plating.
Table of Contents
What is metal coating?
What is metal plating?
Differences between metal coating and plating
Conclusion
What is metal coating?
Coating is a technique of applying a layer to an object’s surface using a chemical composition or a powder. The object on which the coating is being applied is known as a substrate. They can be hard materials that vary from metals to plastic and glass. The coating can either be full or partial.
How metal coating works
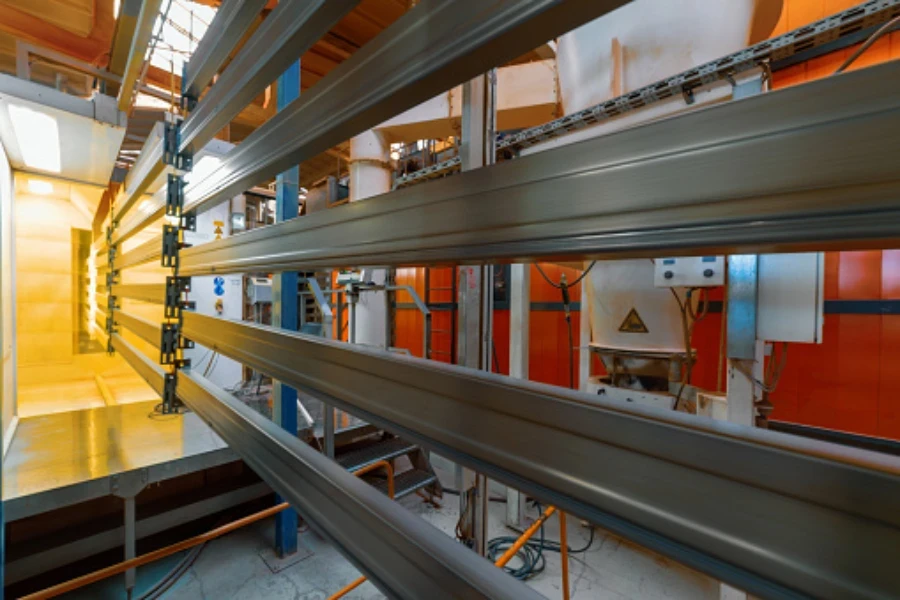

Professionals can use a brush to apply coating material by hand on the substrate. Another method comprises the use of machines that dip the object in the composition and then spin it quickly to eliminate any excesses.
When the object cures, it becomes resistant to water and corrosion, extending its lifespan. The thickness and the type of material used determine the effectiveness of the coating used on the substrate.
Types of coating available in the market today are;
Zinc flake coating: Mostly applied in vehicle and machinery parts, the coating provides protection from wear and tear caused by saline water. Zinc flakes also enhance protection from extreme environmental conditions.
Zinc phosphate and oil coating: This coating gives objects a uniform black finish that can retain oil and resist rust. It works well in construction machines and heavy vehicles.
Black oxide: This coating is applied on heavy machines used indoors that handle loads of daily tasks. Black oxide helps them to resist corrosion.
These coating applications give the surfaces a protective shield. Other types of coating like paint and dye are crucial for beautification.
Pros
- Increased performance of materials
- Decreased use of electricity
Cons
- Works well for materials not exposed to a lot of corrosion
- Needs constant reapplications when worn out
What is metal plating?
Plating is the procedure of depositing a metal on a conductive surface. The technique is not new as it has been used for hundreds of years to add properties to metals. An example of plating is plating jewelry with silver or gold.
How metal plating works
There are two ways in which plating occurs;
Electroplating
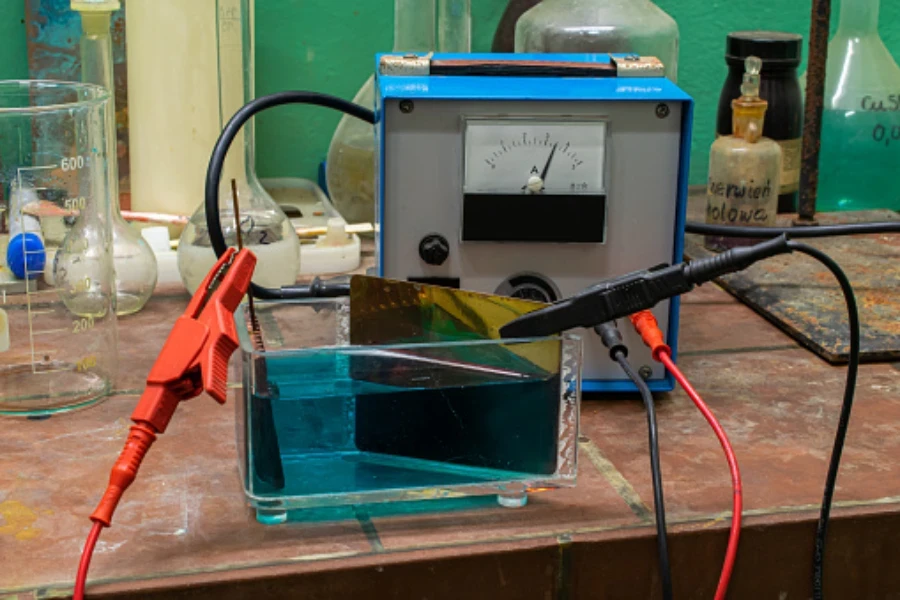
This is a method that involves using an ionic metal to give electrons to the substrate and thus form a non-ionic coating on its surface. The most common way is dipping the metallic substance into a solution containing ions with a cathode and anode that will supply the electrons.
A film of non-ionic metal is formed on the metal through electrolysis. This method is applied in the vehicle manufacturing industry, electronic parts industry, and corrosion protection departments.
Electroless plating
This plating method involves reacting the metallic object in an aqueous solution to add a film to the metal. The chemical reactions here do not need a source of electricity. An example of electroless plating is nickel electroless plating used in the aerospace industry.
The other two plating techniques include sputter deposition and vapor deposition under a vacuum.
Specific variations of plating in the market today are as follows;
Gold plating: Substrates that are being plated are mainly conductive materials like copper used in wires and circuit boards to aid them in resisting corrosion. Non-conductors like glass and plastic can also be gold-plated for aesthetic reasons.
Chrome plating: Chrome plating not only prevents corrosion but also gives a shiny surface for decorative purposes. It is applied in the automotive sector (wheels and other body panels of vehicles).
Silver plating: It is applied in many industries, including music instrument manufacturing and jewelry making.
Zinc plating: Objects made of steel can be zinc-plated to help them resist oxidation. Hardware manufacturers that use stainless steel or aluminum use zinc on most occasions for plating.
Copper plating: It is an alternative to silver because it is cheaper and more readily available.
Tin plating: Tin can be applied to many types of base metals. Its main application is in food processing factories to make food cans. Tin’s non-toxic and corrosion-resistance properties make it an ideal material for plating. However, this material is not suitable for plating steel.
Alloy plating: Objects can have a coating composing two or more metals as their electrolyte. An example of an alloy plating is nickel-cobalt, which provides materials with outstanding strength. Heavy equipment manufacturers use alloy plating on their products.
Pros
- Application on a wide range of metals
- Increased rigidity and stiffness of metals
Cons
- Cracks and chips upon exposure to harsh environment
Differences between metal coating and plating

Substrate
The substrates for coating can be any type of surface, both conductors and semiconductors of electricity. They include metal surfaces, glass, rubber, wood, tile, and plastic.
Substrates of plating are only conductive metals. They do not include glass, rubber, wood, tile, and plastic materials.
Uses
People use coating to enhance adhesion, corrosion resistance, etc.
Plating works best for multiple purposes like decorations, improving solderability, hardening, reducing friction, radiation shielding, etc.
Definition
Coating is the covering of an object’s surface by dipping it in a chemical bath. Plating is the depositing of a metal on a conductive surface to add a protective layer.
Process
For coating, the substrate can be dipped in a chemical bath with complex machinery. Professionals can also coat manually with a brush.
Plating involves the use of electrolysis or simultaneous reactions on the metal’s surface.
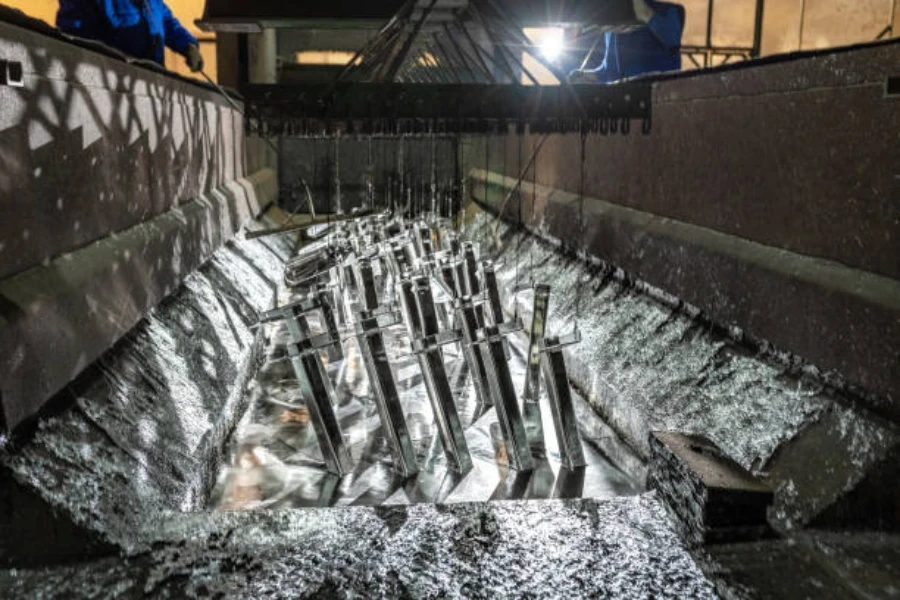

Conclusion
Both plating and coating are effective methods of protecting surfaces from harsh elements and enhancing durability. However, for long-term cover, although they are costly, platings work better than coatings. Coatings give a cheaper short-term alternative to corrosion. In summary, this guide gives the differences between metal coating and plating, as well as their pros and cons.




