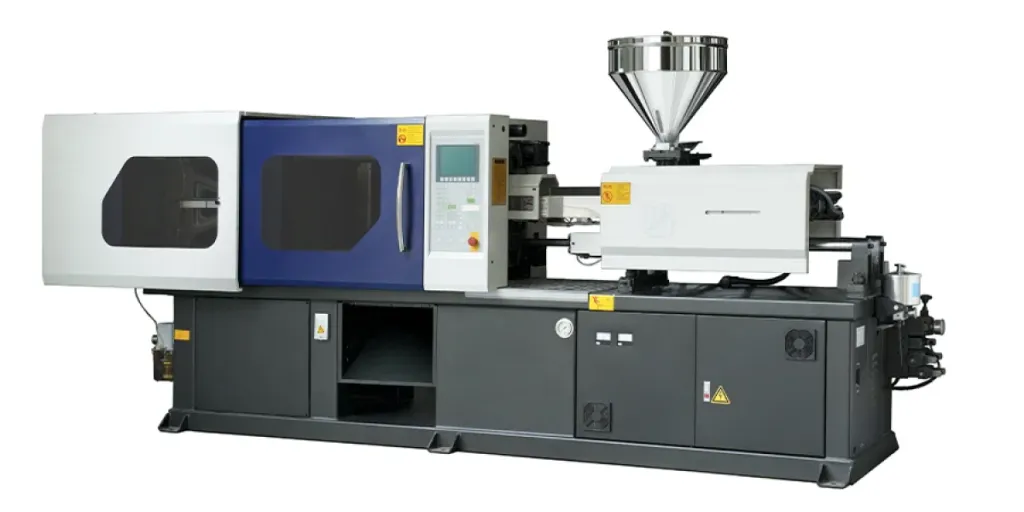
How To Select The Best Injection Molders
With a wide range of machines available on the market, selecting the right injection molder for one’s needs can be a challenge. This article will explore the key factors you need to know in order to make sense of supplier data, as well as explaining how a business’s molding needs will impact their choice of machine. It will also highlight the types of injection molders available so that suppliers can be assured they’re making the best possible purchase.
Table of Contents
The growth of the injection molding market
What to consider when selecting an injection molder
Different types of injection molding machines
Target markets for injection molding machines
Final words
The growth of the injection molding market
The global injection molded plastics market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 4.5%. The worldwide demand for molded plastic parts is being met by an increasing supply of high-quality machines, with China becoming a dominant provider. As a result, innovation in injection molding machine design, power and operation capabilities has led to a diverse range of machines becoming available on the market.
What to consider when selecting an injection molder
The size of the product determines the mold design, and is therefore the starting point for determining machine specifications. However, it’s also important to keep in mind that if a business requires high volume production of small parts, such as bottle tops, then a multi-cavity mold is used, which requires a larger machine.
The size of the mold, in turn, determines the machine size. One should ensure that the machine is big enough to hold the mold, open and close it, and eject the final products. The size of the mold also determines the amount of plastic injected in a single shot to fill the mold. This ‘shot size’ determines the power needed, including injection rate and clamping pressure. Below is a more detailed description of the factors to consider when choosing an injection molder:
Clamping pressure / tonnage
The molding machine must clamp the mold firmly while the plastic is injected under pressure and hold it steady while cooling. Clamping pressure is usually measured in tons. The general guide for clamping pressure specification is 2.5 times the square surface of the mold with an additional 10% safety factor. Therefore, for a part that is 80 square inches, you would require a press size with 200 tons of pressure, plus the 10% safety factor, which results in a total press size requirement of 220 tons. Anything less than that may not meet the clamping force needed for the product.
Injection pressure and injection weight
The melted polymer is injected into the mold under pressure, which must be high enough to fill the entire mold cavity in the required time. Pressures are typically between 70 and 112 MPa (10–16 kpsi).
Shot size
The maximum amount of plastic that can be injected into the mold cavity during a single molding cycle is called the shot size, with size rated in either ounces for U.S. machines or cm3 for European and Asian machines. It is best practice to choose a machine that is capable of producing a shot size substantially greater than the shot size for your product’s mold, and the guide for how much greater depends on the type of plastic used.
For general purpose resins, such as PP, PE and PS, the shot size should be between 20 to 80 percent of the machine’s shot capacity, whereas for engineered resins, such as nylons, ABS, PC and EOM the shot size should be between 30 and 50 percent of machine’s maximum shot capacity.
Platen size
Platens are solid base plates into which the mold is fitted. They provide the stability and pressure to hold the mold together. The platens must be large enough to fit the mold as well as strong enough to take the pressure needed for clamping.
Tie bar spacing
Tie bars provide structural support for the platens to move backwards and forwards during the clamping process and must have sufficient space to allow full movement of the clamp from opening to a tight close. Tie bar spacing is the measurement between the horizontal tie bars.
Ejection stroke
There must be sufficient ejection space to remove the molded products. As a guide, the mold ejection stroke should be at least twice the depth of the product.
Different types of injection molding machines
Hydraulic
Hydraulic injection molding machines were the first types in use and therefore tend to dominate the market. The hydraulics provide the high pressures needed to clamp and hold the mold in place. This is particularly important for large parts that need very high pressures and long hold times, which is why hydraulic mechanisms are popular in the automotive industry for such heavy molded parts such as car bumpers. Although hydraulic machines have led the way in the past, overall global market share by unit is only around 23.5%, almost half that of electric machines, although exceeding the electric market by 50% in value, reflecting the higher cost of hydraulic machines. Asia Pacific has been the larger market to date at around 51% by unit. Overall global growth is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 4.6% with the Americas expected to grow faster at a CAGR 6.4% by 2025.
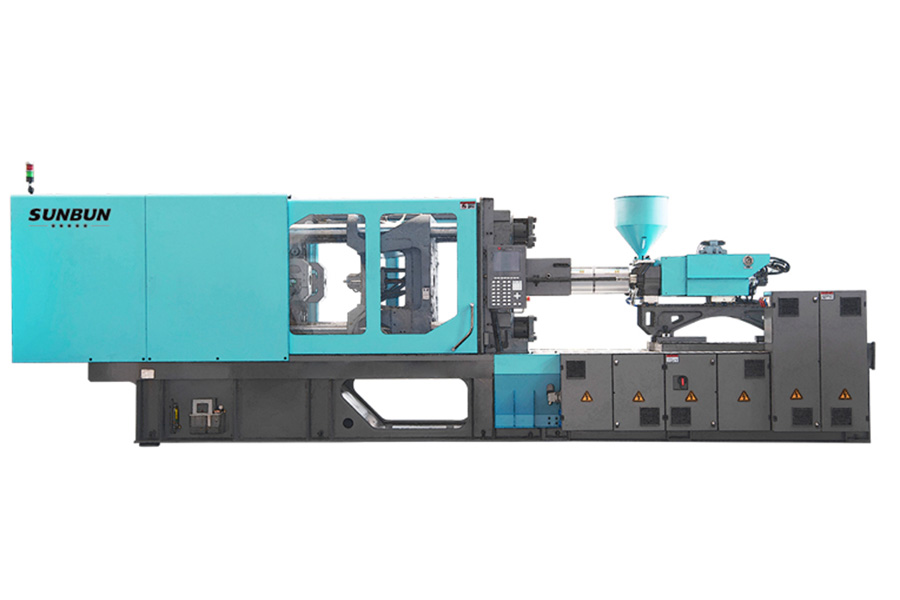
Advantages
- High clamping force, potentially exceeding 8,000 tons
- Better injection and ejection capabilities
- Larger shot size
- Lower initial purchase price
- Low maintenance costs due to availability of parts and experience
- Many choices available on the market
Disadvantages
- Not energy efficient, use large amounts of energy even when idle
- Require higher temperatures for molding
- Require more time for cooling
- Not ideal for clean rooms due to the risk of hydraulic fluid leakages
- Noisy and less precise than electric alternatives
Electric
Electric injection molding machines are run by digital, programmable components using high-speed servo motors rather than hydraulics. This allows for high precision molding especially of small parts (e.g. electronic and medical parts), and for consistent repeatable quality. Asia Pacific has been the larger market to date at around 47% by unit. Overall global growth is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 4.2% with the Americas expected to grow faster at a CAGR 6.0% by 2025.
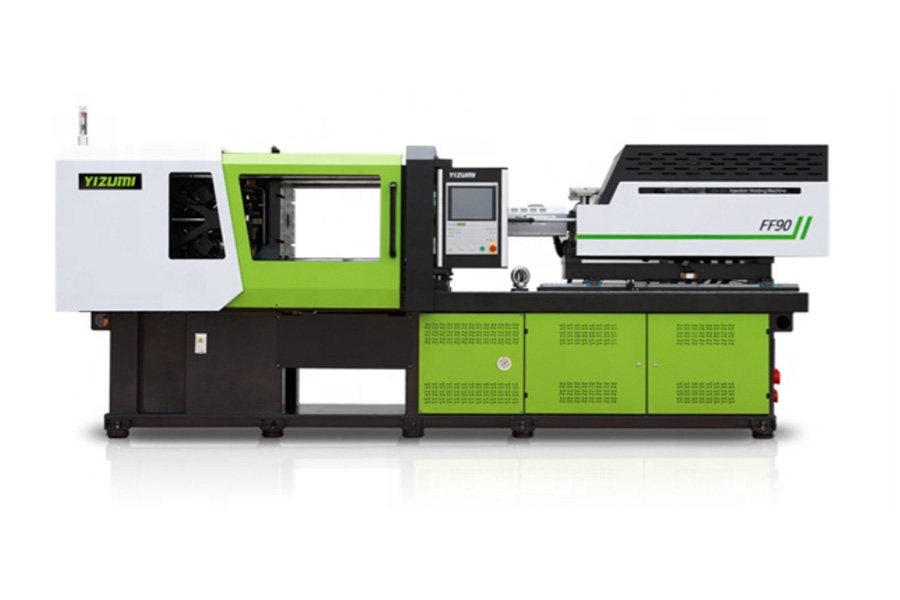

Advantages
- Digitally controlled, programmable, and can run unattended
- Efficient, fast, repeatable, and more precise overall
- Independent motor controls throughout the process
- Quiet and clean, with less consumables such as filters and oils
- Quick start up, rapid injection speeds, and faster cycle time
- Lower power requirements, energy efficient, and reduced operating costs
- Lower unit cost, easier maintenance and less downtime
Disadvantages
- Higher initial purchase cost than hydraulic versions
- Parts may be less easy to find due to the smaller market
- Lower clamping pressures than hydraulics so not suitable for large parts that require high pressure clamping and longer holding times
Hybrid
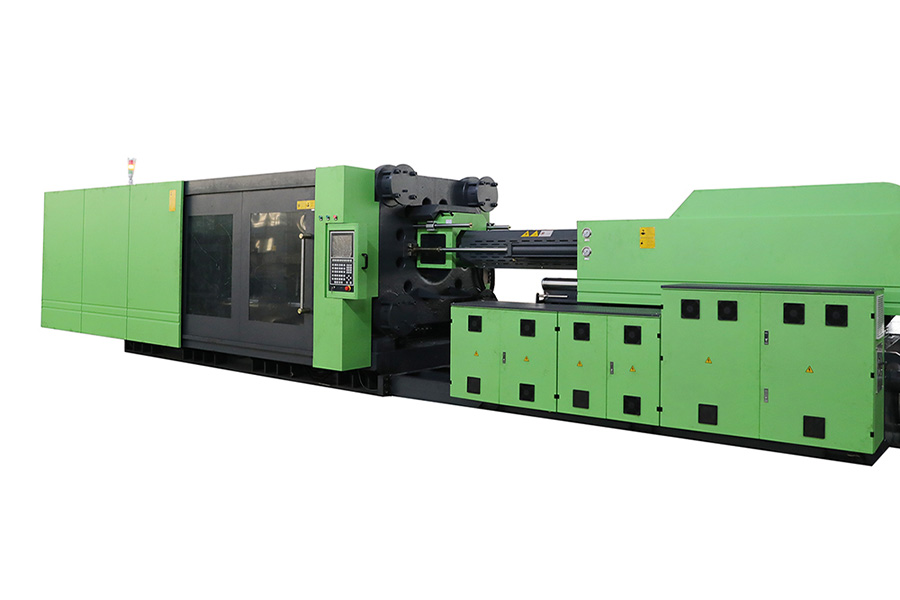

Hybrid injection molding machines use hydraulics for clamping and so can achieve a high range of pressures, but use electrical servo motors for injection and screw recovery. There is a trade-off between the improved control and power saving of the electrical servos, against the loss of efficiency of spreading the hydraulic power across other processes. Hybrid machines are popular, having around 32.8% of units in the global market, compared to around 23.5% for hydraulic and 43.7% for electric machines. Asia Pacific has been the larger market to date at around 60%. Overall global growth is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 4.9% with the lagging Americas market likely to grow faster at a CAGR 6.5% by 2025.
Advantages
- Electrical systems allow for easy adjustments
- Allows for a wide range of choices for product design
- Up front cost is generally somewhere between the lower hydraulic machines and higher electric models
- Offers potential cost savings over time, after the initial setup costs
Disadvantages
- Some energy inefficiencies compared to fully hydraulic or fully electric machines
- Matching available parts to the right machine can be troublesome, which risks extended downtime while finding replacements
- Maintenance engineers must have knowledge of both electric and hydraulic machines
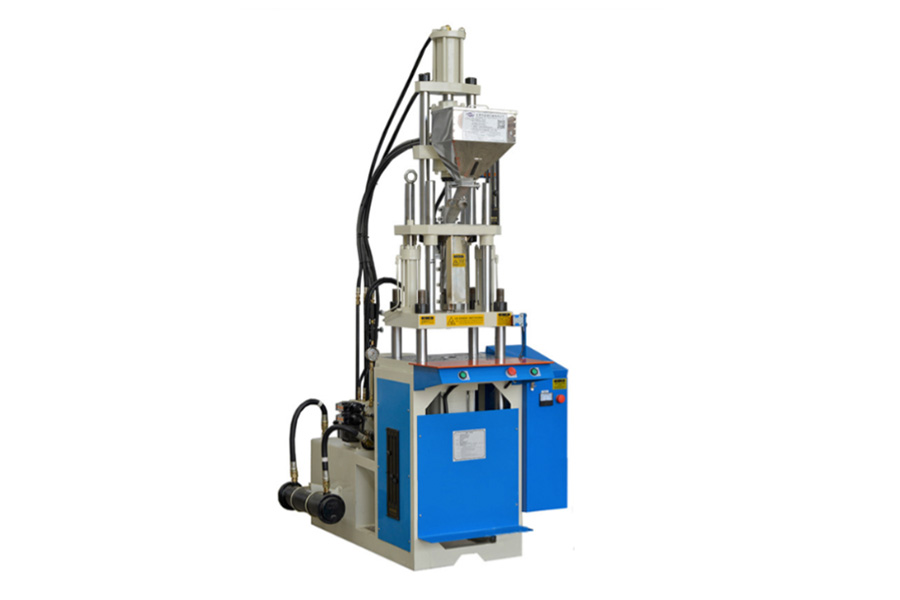
Horizontal or vertical configurations
Large industrial machines are more likely to be found in a horizontal configuration, whether using hydraulic, electrical or hybrid power systems. However, Vertical injection molding machines, coming in both hydraulic and electrical models, can offer a number of advantages for certains uses. Their upright stance makes access easy for insert molding, where a pre-formed part needs plastic formed around it, or for rotary book molds where alternate molds are rotated by the user. Also, the vertical orientation takes up less space than a horizontal machine. A shorter injection path reduces the risk of cooling and shorter runners mean less resin and less wastage. Clamping also has the added advantage of gravity to keep the top mold in place. This means vertical injection molding machines can be a cost-effective and practical choice for more user-involved applications.

Target markets for injection molding machines
Molded plastic parts are commonly used across all industries and demand is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.2% from 2021 to 2028, with an increasing need for small, high quality, and high precision parts that are more eco-friendly and recyclable. The buying potential for injection molding machines is projected to increase across global markets by an overall 4.7% CAGR through 2018-2025. Growth in the construction industry is expected to boost the Asia Pacific market, which already holds around 51% market share, with a projected growth rate of 3.8% CAGR. The growth of the packaging market across Europe will boost a current 25% market share, with a projected 5.2% CAGR. The U.S. and Latin America, Middle East and Africa (LAMEA) are potential markets expected to see higher growth rates, with the increased use of smaller plastic parts in the automobile industry likely to boost U.S. market share beyond its current 18%, at a CAGR of 5.9%, and a boom in construction across LAMEA is fueling a 6.5% CAGR from a current market share of 6.5%.
Final words
With a growing global plastics market, there are many opportunities for suppliers of injection molding machines. This article reviewed the types of machines available and the key factors to consider for making the right purchase. These technical specifications will help narrow down selection, but keep in mind that a good supplier will also help one to make sense of the finer details needed to get the best machine for one’s needs. For more information on injection molders, and to explore the models available on the market today, check out the Alibaba.com showroom.




