For over a century, compressors have evolved in many types, from the piston to rotary vane, and to be useful in many sectors. The health, automobile, agriculture, food, and pharmaceutical industries find them essential.
Read on to find out more about compressor types, market statistics, and tips on how to choose one.
Table of Contents
How is the compressor industry doing?
Looking for quality compressors? Here is how to find them
Types of compressors
Time to choose
How is the compressor industry doing?
In 2020, the compressor industry bogged down at USD 15.46 billion after the market value dropped by 5.4%. Experts blame this on an underperforming economy caused by health constraints.
The market has since recovered, and experts optimistically predict it will reach 26.85 billion USD in 2023 with a CAGR of over 4%. Major drivers are the technological advancement in compressor designs and a growing interest in the industries that rely on them.
By 2030, the industry’s value will be over USD 43 billion with close to 500,000 units being ferried annually.
Looking for quality compressors? Here is how to find them
- Lubricating system
Compressors have oiled or lubricated and oilless or non-lubricated systems. Oiled compressors are powerful and durable but at the cost of expensive maintenance and added weight compounded by oil and oil pans.
Oilless compressors are cheap, lightweight, and produce clean air fit for the food and healthcare industries. Unfortunately, they are less powerful and durable. Parts often wear out quickly, resulting in costly maintenance as the compressor ages.
- Size
Compressors are available in varied sizes depending on type and output. For example, rotary screws and vanes are compact because the compression mechanisms are small. Piston compressors are huge.
Buyers can also determine compressor size based on the output, especially airflow measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM) and pressure. Small electric compressors for private uses produce less than 2 CFM, while large multi-stage compressors can reach 1000 CFM.
Likewise, large compressors gush out over 200 psi of pressure, 2 to 4 times more than standard handyman compressors.
- Features
A compressor’s features determine its output, price, and size. Small compressors are simple with a motor, casing, and an on-off key. Some have handles and wheels for portability. Of course, small size and portability tend to limit the power output.
Top-tier compressors are majestically equipped with the latest high-tech features for efficiency and ease of use. A touch screen, power controllers, frequency converters, and AI capabilities run industrial compressors with a sophisticated compression mechanism.
To get brand-specific features, visit an eCommerce website and click on the equipment’s product detail section.
- Compression ratio
The compression ratio is the ratio between absolute discharge pressure and stage suction pressure denoted as “C”. Normally, a high compression ratio decreases power consumption and increases the efficiency of a machine. Thus, aim for a high C to save power.
- Source of power
Compressors obtain power from electricity and fuel. Electric compressors are cheap, clean, and silent. Most of them are compact, work indoors, and are easy to maintain. The downsides are they are less powerful and will not work in areas not connected to the grid.
Diesel and petrol compressors are the go-to machines for immense power output and reliability. Customers praise them for their excellent heavy dutyness and, given their mobility, buyers count on them for outdoor projects. On the flip side, they are noisy, fume out a lot of smoke and must have filters to produce clean air.
- Portability
Portability defines the uses of compressors. Clients such as auto shop owners and painters prefer movable compressors with comfortable handles, sturdy bases, and wheels for mobility.
Beyond mobility, there are large and cumbersome stationary compressors that are difficult to transport and require premade structures. Large compressors are appreciated in oil exploration, steel plants, and commercial agriculture.
A transportable compressor is a grafted version of a portable and stationary compressor. Manufacturers equip them with bases and hooks for crane belts. Components are heavily bolted on steel frames and protected by hardened casings.
- Price
Offer an at-home dad or next-door repair shop owner with affordable, preferably small electric compressors, because they will opt to rent one to save costs.
Medium-sized compressors with a small tank fitted with wheels are slightly expensive, and customers buy them for hundreds of bucks.
In the very end, high-tech, multi-stage compressors, especially those that run on diesel, sell for thousands of dollars.
In terms of types, electric piston compressors are the cheapest compared to fuel rotor vane or centrifugal.
- Capacity FAD
FAD (Free Air Delivery) measures the capacity of air delivered to the compressor outlet and is 66% of the CFM.
Mathematically, if a tool uses 12 CFM, the FAD rating will be 8. This means that for the tool to run, the compressor must be rated 8+ FAD.
The higher the FAD, the bigger the compressor.
- Working pressure
Working pressure is the pressure that the compressor must produce to meet its demand. It is divided into low, medium, and high pressure.
Low-pressure compressors discharge less than 200 psi, which is a fifth of medium-pressure compressors. High-pressure compressors exceed 1000 psi.
Types of compressors
Reciprocating or piston compressor
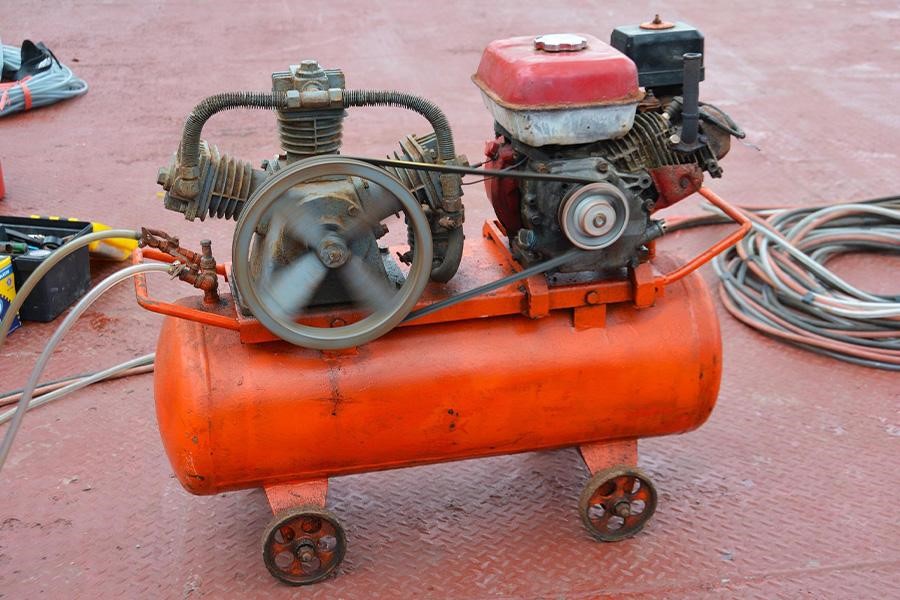

Reciprocating compressors deliver high-pressure compressed air with the aid of a crankshaft connected to moving pistons. Pistons trap, compress, and discharge pressurized air to a storage tank.
Highlighted features
- Airtight storage tanks
- Gears for controlling output pressure
- Wide base with wheels for easy mobility
- Sturdy casings and frames protecting the tank and engine
- On-board high-tech controls
- Works with diesel and electricity
- Powerful cooling fans
Pros
- Most affordable
- High mobility
- Electroplated and painted exterior for improved durability
- Can work when power is muted off
- Low running noises
- Designed for heavy-duty purposes
- Excellent air supply
Cons
- Diesel piston compressors are noisy and difficult to work with
- Some models are heavier and less portable
- Price increases sharply with an increase in operating pressure
Rotary-screw compressor
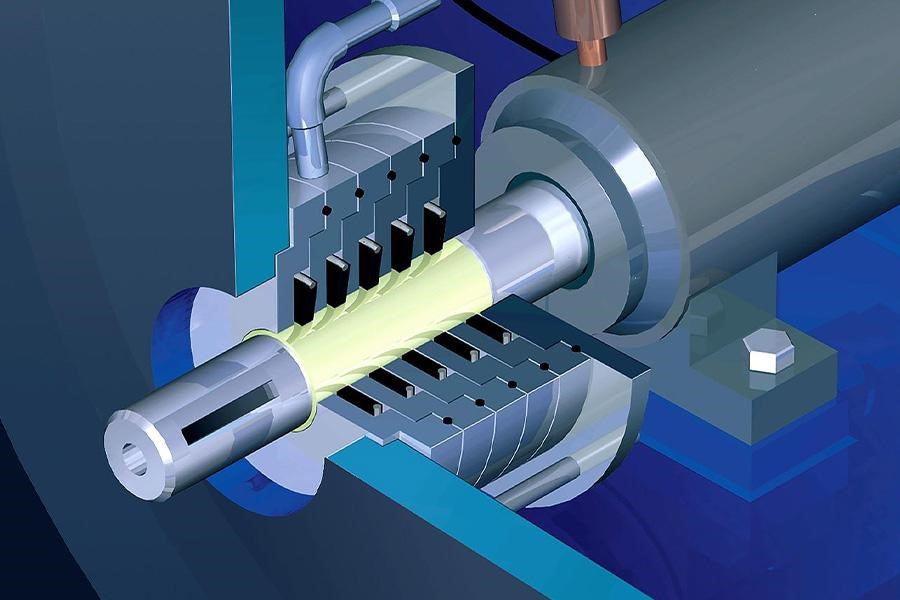
Rotary-screw compressors work with a pair of screws rotating in opposite directions. As they rotate, the air is compressed in between the threads through a positive displacement mechanism.
Highlighted features
- Compact design
- Runs on oiled motors
- Air-ends have pressure control valves
- Work with a system of belts and pulleys
- Smart integration features such as easy-to-press buttons and a digital screen
- Automatic shut down when the tank is full
- Surge protectors for electric compressors
Pros
- Quiet
- Clean, oil-free designs
- Over 10% more efficient than piston compressors
- Easy to assemble and takedown
- More durable and less costly to maintain
- Operates in extreme conditions (between -4 and 45 degrees Celsius)
- High efficiency allows it to save electricity and fuel
Cons
- One of the most expensive compressors
- Designed for immobility
- Only qualified experts can handle breakdowns
Rotary vane compressor

A typical rotary vane compressor consists of a cylindrical cavity and a series of different-sized vanes that connect to a motor. Vanes form airtight contact with the cylinder to trap air as they rotate.
Highlighted features
- Several vanes trap air for compression
- Multi-language and intelligent control system
- Cooling fans
- Barrels for gasoline and energy-saving inverters for fuel-powered compressors
- Air filters
- Thermal overload protectors
- Special heat dissipating parts to improve cooling in summer
Pros
- Noise level below 70 dB
- Saves more electricity than piston compressors
- Stable and vibrates less
- Compact and portable designs exist
- Robust housing to fight elements
- Coolers stabilize ambient air temperature to less than 10 degrees Celsius
- Durable with little maintenance costs
- High reliability of up to 100,000 hours
Cons
- High acquisition cost
- Gasoline compressors require frequent maintenance
- Multi-tanked units pose mobility challenges
Centrifugal compressor
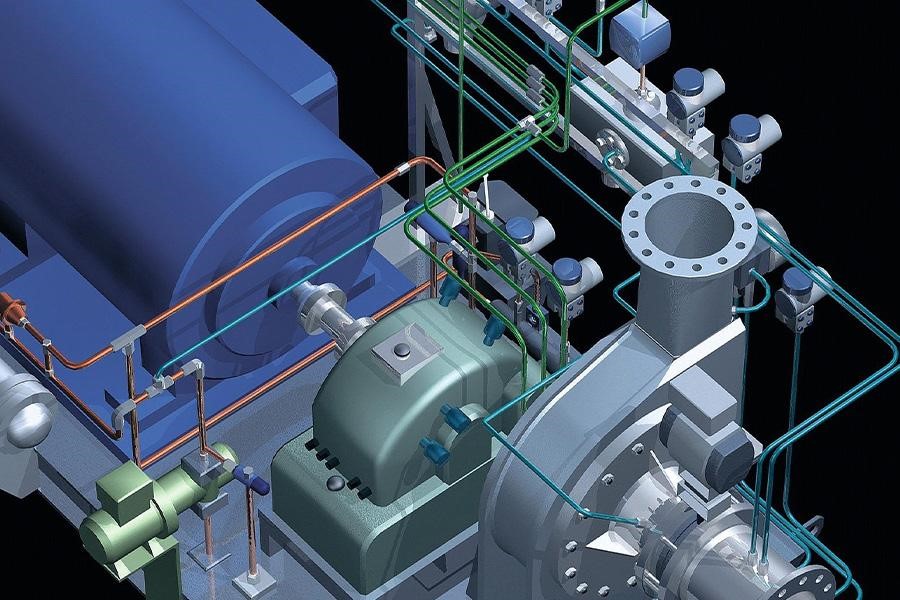
Being a dynamic compressor, a centrifugal compressor rotates air at high speed to increase pressure. For efficiency, only large centrifugal compressors with inbuilt dehumidifiers and coolers exist.
Highlighted features
- High-speed rotors
- Multifaceted digital controller able to work remotely or on-site
- Speed boosting gearbox in some models
- Low friction air seal
- Effective gas coolers
- Heat exchanger with environmentally friendly refrigerant
- Noise umbrellas
- Remote voltage controllers
- Memory and fault reminders in advanced machines
Pros
- Multi-stage compression results in immense pressure of over 2900 psi
- Energy efficient
- Voltage remote controllers improve safety
- Oil-free gearless options exist
Cons
- Environmental conditions affect the efficiency
- Very noisy
- Cumbersome and difficult to transport
- Expensive
- Only available for large-scale purposes
The compressor market
With most industries looking up for compressors to accelerate the creation of goods, the market for these machines is growing. Regionally, China and India (Asia-Pacific) are leading the compressor market demand, accounting for 6.4 billion USD in 2020. This is largely due to a growing oil and gas infrastructure. However, the Middle East and Africa (MEA) is the fastest-growing market.
Globally, oil-free, stationary, and positive displacement compressors with medium pressure contribute the largest revenue share.
Time to choose
Choosing a compressor is very easy when you know its lubrication system, price, source of power, and highlighted features. The job is even easier with market statistics and the types of compressors at hand.
Stay updated with the latest marketing tips and know-how in machinery by reading how to maintain laser cutting machines.




