Driving a car to work or for leisure activities is a routine part of life for most of us nowadays. But would we still hop in if we knew that not wearing a seatbelt increases the risk of fatality in a car accident by about 30% compared to wearing a 2-point seatbelt?
In fact, that’s exactly what happened until Nils Bohlin, Volvo’s engineer perfected the now-ubiquitous 3-point seatbelt in 1959. This innovation not only improved safety but also further solidified Volvo’s brand for reliability and safety, an image that thrives to this day.
Indeed, businesses always need to find some sort of differentiation to establish a memorable and impressive brand. Building such an identity through a private label brand, for instance, is one of the business models that represent a faster and more cost-effective route to market. Read on to find out exactly what a private label is, its pros and cons, and how to choose the right private label provider to unlock the path to building a successful brand now!
Table of Contents
What is a private label?
Pros and cons of a private label
Advantages
Disadvantages
Choosing the right private label providers
1) Research
2) Target / Source
3) Evaluate
4) Verify
5) Negotiate
Brand building made easy
What is a private label?

Private labeling is an outsourced business model that allows business owners to sell products with a preferred specific design under their own brand names without the need to produce or manufacture them.
To put this into perspective, in a way, private labeling and dropshipping share some similarities in terms of outsourcing tasks, but private labeling places a stronger emphasis on manufacturing and exclusivity. While dropshippers rely on their suppliers to deliver goods directly to customers, private-label retailers depend on their manufacturers to create custom-designed products.
Private label products are typically unique since brand owners retain full control over the design, functionality, and overall feel of the product. In reality, these controls and exclusivity are key features that clearly distinguish private labeling from white labeling, which is often confused with it. While white labeling also involves outsourced production, it usually provides similar products with little to no customization. Even when some level of customization is available, it is often limited in terms of design modifications or branding options.

Private label products are available across a wide range of industries, from fast-moving consumer goods such as cosmetics, beverages, and packaged foods to high-end goods like luxury apparel and personal care devices, as well as private label smartphones, private label electronics, and even private label vehicles.
Despite these diverse categories, most consumers do not recognize or care whether a product is private-labeled or produced by the actual manufacturer. Instead, they typically assume that the products are directly manufactured by the retail brands themselves.
Pros and cons of a private label
Advantages

The private label business model, having been well-established since the 19th century, continues to offer several advantages that sustain its relevance today. Its benefits mainly fall into three key areas: brand identity, cost efficiency, and operational management.
Brand identity
The most obvious and substantial advantage of launching a private label product lies in the freedom, control, and unique value proposition that brand ownership provides. The differentiation and authority in branding are fully exemplified through product design, including customized specifications and material choices that private label owners can enjoy.
Practically every aspect of the product, from final packaging touches to marketing positioning, remains under the strict supervision and direction of the private label adopter. With such enormous freedom and control in branding, a unique identity that clearly stands out among the competition can hence be built up, effectively promoting customer loyalty and strengthening branding recognition.
Cost-efficiency
Private labeling naturally comes with much lower initial costs compared to traditional manufacturing businesses, since it eliminates the investment requirement in manufacturing plants and equipment. In other words, such an outsourced approach offers a cost-effective solution that offers lower entry barriers, freeing private label companies from heavy initial investments in hardware and infrastructure. Instead, they can focus more on other critical elements in brand building, such as marketing and expansion plans.
One advantage leads to another; these lower production expenses also result in higher profit margins and enhanced pricing flexibility, as businesses avoid intermediary costs like wholesaler markups and reselling fees. This signifies that private label pricing strategies are typically more stable, ensuring affordable products rather than overpriced ones.
Operational management
Another key advantage of private labels is the exclusive operational control that this business model grants to retailers, allowing greater agility and adaptability in business management.
Hence, retailers can formulate and launch corresponding solutions in a more efficient and quicker manner. They may adjust product features and launch new product choices in response to market trends or customer feedback, capture market demand, and boost sales in a timely manner. Such flexibility can be especially advantageous when compared to larger, established brands and traditional manufacturers since they typically are subject to longer times to develop and finalize their solutions through various processes.
Disadvantages

Despite the many advantages of private labels, such a business model does come with a few disadvantages that revolve around production and brand innovation issues.
Production risks
While private label retailers surely have substantial control and freedom in terms of product designs, materials, and packaging, they deeply rely on the manufacturers for overall product quality and production efficiency, including production speeds and supply chain management. What’s more, there’s also a dilemma regarding brand name popularity for private label retailers. This is because, on one hand, the less recognized their brands are, the less negotiation power they may have with manufacturers. Yet, the more established their brands become, the more dependent they tend to be on their suppliers to maintain their existing brand quality and market reputation.
As a result, private label businesses may end up spending more on higher investments in product development due to higher minimum order requirements (MOQs) that manufacturers inevitably impose to recover their relatively higher production costs, which arise due to customization and development from scratch. Higher MOQs also increase overall demand forecast risks since excess orders can easily lead to excess inventory and financial losses.
Innovation challenges
Private label practitioners may also face limited flexibility when it comes to product designs and customizations since production processes ultimately still depend on manufacturer specifications and are subject to certain standardized production methods. These limitations often make it difficult to modify or innovate product designs, particularly for industries or products with fast-evolving trends.
At the same time, another related issue stems from the fact that manufacturers tend to work with rather standard processes or templates, which creates another layer of innovation challenge that constrains businesses in developing products that can truly stand out and exceed customer expectations among all relatively identical competing products. Potential consumer perception bias adds another layer of complexity, as consumers may perceive private labels as generic, less distinctive, and of lower quality compared to well-known brands. Altogether, these factors further complicate efforts to drive innovation.
Choosing the right private label providers
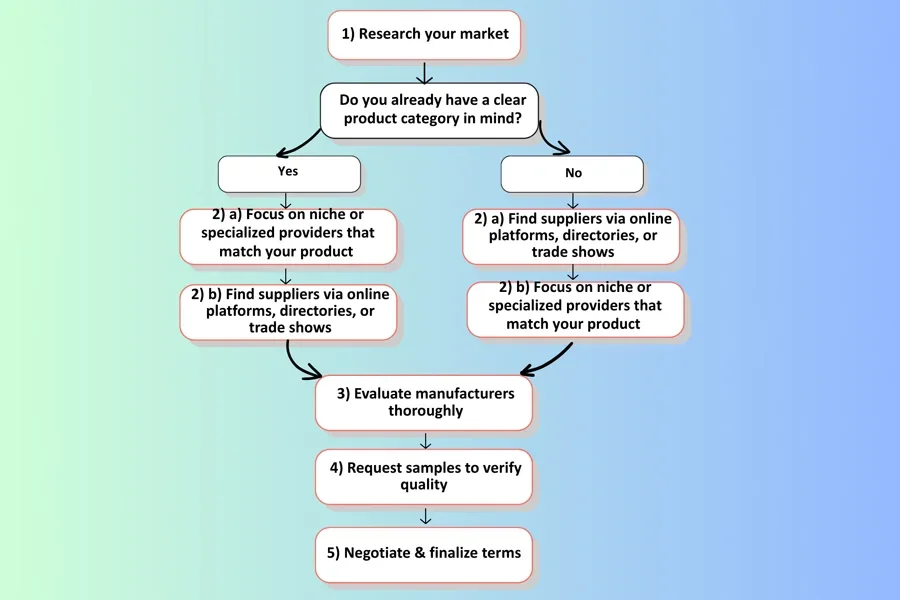
1. Research
The first step in selecting the right private label provider is for retailers to thoroughly research the overall market landscape and product demand before approaching any private label suppliers or manufacturers. The research should focus on gaining a more profound understanding of customer needs and their preferred product features while actively gathering insights about competitor products. Basically, this research forms a solid foundation that defines customer expectations to ensure a clear requirement list for potential manufacturers.
2. Target/Source
For brand owners with a defined product and branding strategy, they may proceed to seek specialized manufacturers aligned with their niche. In the meantime, those still exploring broader options can start with general manufacturer listings on platforms such as Alibaba.com or AliExpress.com, or check trade directories and participate in industry trade shows to identify reliable suppliers. Essentially, brand owners who work with specialized providers that match their intended product category tend to significantly enhance product quality and standards, as these providers offer more expertise and industry-specific experience to ensure compliance and consistency.
3. Evaluate

Once a list of potential suppliers is sorted out, brand owners should conduct a thorough evaluation of product quality, the manufacturer’s production capabilities, and service reliability. Such a comprehensive evaluation is paramount to assessing a manufacturer’s ability and reliability to comply with the required product standards, pricing, and logistics requirements, whether for the short term or as the business scales up.
It’s worth noting that a comprehensive assessment may include details as specific as verifying quality certifications (if applicable) and production capacity, as well as reviewing branding and customization options and shipping processes, including shipping arrangements, lead times, and associated costs.”
4. Verify
The entire evaluation process remains incomplete until requested product samples are received and reviewed. This inspection process provides a hands-on opportunity to confirm that the manufacturer’s promises are indeed aligned with actual production, thereby reducing the risk of potential issues. As a precaution, each sample should be checked and verified for overall quality, packaging, and shipping efficiency.
5. Negotiate
Finally, after narrowing down the list of suppliers, it’s time to negotiate a better deal with the final shortlisted manufacturers. Businesses should select the deal that offers the most balanced combination of overall sample results, pricing structures, payment schedules, and contract terms. Most importantly, it’s essential to note that the main objective at this stage is not just cost reduction but also establishing a long-term agreement that clearly defines product specifications, quality expectations, and production timelines.
When negotiating, brand owners should also prioritize intellectual property protection to ensure that all relevant designs and formulas remain confidential and that their ownership rights are fully secured. Overall, a well-structured contract should clearly define each party’s responsibilities and related penalties in case of failure in compliance.
Brand building made easy

Private label branding is a way to outsource production while retaining the design and identity of products, maintaining exclusivity and uniqueness. It is widely used in the retail industry but also extends to sectors such as food and beverage, healthcare, and cosmetics, covering both retail and professional markets.
With private label manufacturing, brand building becomes much simpler and more accessible. It’s also significantly more cost-effective for new brands to launch since they do not need to invest heavily in manufacturing plants and production infrastructure. Furthermore, responding to market feedback is made easier and quicker, as brand owners do not need to reinvest heavily to make product adjustments.
However, relying on third-party manufacturers for all production needs also increases dependency on manufacturers, which in turn limits creative control and restricts potential differentiation in branding. To choose the right private label manufacturer, business owners should follow a step-by-step process: research the market, identify and source suppliers accordingly, and then evaluate and verify their offerings for final, effective negotiation.
For more wholesale sourcing information and insights on alternative business models such as white labeling, visit Alibaba.com Reads regularly to stay well-informed and discover other resources, including logistics insights, emerging business ideas, and market trends.



