Table of Contents
What is a fiber laser?
Fiber laser features
Composition and principle
Fiber laser optics
Types and uses
Fiber laser costs
What is a fiber laser?
A fiber laser is a type of solid-state laser in which the gain medium is glass fiber doped with rare earth elements. This allows for high photoelectric conversion efficiency, a simple structure, and good beam quality.
This system has become mainstream in laser technology developments and industrial applications. Some of the reasons for this include the optical fiber’s small footprint, which means it has wide applicability and a high usage rate in the downstream manufacturing and processing fields. Another reason is the fiber laser’s high processing adaptability, which allows for its usage in many applications. Additionally, it has improved beam quality, which can maximize the effect of cost reduction and efficiency improvement for manufacturing enterprises.
Fiber laser features
- A high-brightness, single-mode laser, achieved by pumping the high-power, low-brightness LD light source from the rare earth elements’ absorption spectrum through the double-clad fiber structure.
- Small and flexible design, high conversion efficiency, and ability to work under harsh conditions thanks to its effective cooling system.
- Production of good quality beams with high conversion efficiency and a low threshold.
- A laser output in the 0.38-4um band, realized by using different rare earth elements.
- An easy and tunable wavelength selection, and a wide tuning range.
- Good coupling and a high degree of compatibility with existing optical communication systems.
- Fiber optic devices and optical fibers, greatly reducing structural costs.
Composition and principle
Like other laser types, a fiber laser consists of three parts: a gain medium, a pump source, and a resonant cavity. For the gain medium, the fiber laser uses active fibers doped with rare earth elements in its core. Generally, a semiconductor laser is used as the pump source. The resonant cavity is usually composed of mirrors, fiber-end faces, fiber loop mirrors, or fiber gratings.
The specific working process is as follows: In the working state, the active fiber (gain fiber) absorbs the energy provided by the pump source. Then, the output laser is amplified by the resonant cavity composed of the active fiber and fiber grating.
Seed source
Also known as the signal source, the seed source is the object of radiation amplification in the laser amplification system. Here, the laser that provides a low-power signal is used as a “seed” to allow the amplification system to be amplified according to the state of this “seed.”
Active optical fiber
The active fiber is used as a gain medium, with the function of achieving amplification by converting the energy from pump light to signal light.
Passive optical fiber
The passive optical fiber mainly realizes the function of light transmission and does not participate in wavelength conversion. There are mainly fiber gratings in fiber laser systems, with passive matching fibers in fiber isolators and passive multimode large-core energy transmission fibers in the laser energy transmission components.
Currently, those passive optical fiber products from domestic suppliers are nearly able to meet production needs, with only a small amount of the passive optical fiber used in ultra-high-power products still using imported optical fiber.
Fiber laser optics
Pump source
The pump source can be used as a direct light source to output the laser light in industrial semiconductor lasers. Additionally, it can be used as a pump light source to provide a high-power, high-brightness pump light for fiber lasers.
Pump combiner
The lasers from multiple pump sources can be combined and fed into the optical fiber to achieve a higher power pump laser output.
Energy combiner
The energy combiner can superimpose energy from multiple high-power fiber laser modules. It is also a core device when creating a multi-mode laser beam output.
Fiber grating
Fiber grating is diffraction grating that is formed by periodically axially modulating the refractive index of the fiber core via a certain method. Fiber grating belongs to a passive filter device as well as being a necessary component in any resonator. It also determines the output wavelength and bandwidth of the laser and can control the laser mode and beam quality.
Laser head
The laser head is an important component for realizing the high-power laser’s long-distance, flexible output in the application site. It is also compatible with the machining system, meaning the laser generated by the laser can be transmitted to the processing material to complete the laser machining application.
Isolator
The isolator protects the laser and prevents the return light from damaging any of the other optical components.
Stripper
The stripper can effectively strip the cladding light in the laser, protect any related devices, and improve the quality of the output laser beam. The acousto-optic modulator is mainly used inside the resonator to modulate the required laser pulse via radio frequency drive modulation technology. It is one of the Q-switched pulse fiber laser’s core components.
Pattern matcher
The pattern matcher is a core device used to connect two different types of optical fibers to minimize connection loss and optimize the matching of the laser mode’s field.
Types and uses
Depending on the working mode, the two most commonly used types of fiber lasers are the continuous laser and pulsed laser. These can be used in cutting, welding, engraving, marking, cleaning, and other scenarios.
Continuous laser
The continuous laser emits a continuous light beam, with a peak power of 120KW. It is used in cutting, welding, brazing, and drilling. The semi-continuous laser (QCW) is still pulsed but with a longer pulse width and a peak power of 23KW, which is used in cutting, arc welding, drilling, brazing, and metal quenching (improving metal ductility and reducing DC resistance). It is especially suitable for replacing lamp-pumped YAG lasers in spot welding, as well as seam welding and drilling applications. There is a certain overlap in functionality with the continuous laser.
Pulsed laser
Pulsed lasers can be divided into nanosecond, picosecond, and femtosecond pulsed lasers. The nanosecond laser with a longer pulse width has a peak power of 1MW and is used for scribing, etching, drilling, surface treatment, quenching, and marking. The nanosecond laser with a shorter pulse width for micro-finishing is used for quenching, silicon wafer, and glass cutting.
The picosecond laser with a pulse width reaching the picosecond level has a peak power greater than 10MW and is used for blackening, sapphire and glass cutting, and photovoltaic and OLED cutting. The femtosecond laser with a pulse width up to the femtosecond level has a peak power greater than 29MW, which is used for sheet metal cutting, drilling, high-precision processing, and ophthalmic surgery.
Fiber laser costs
Fiber laser engraver
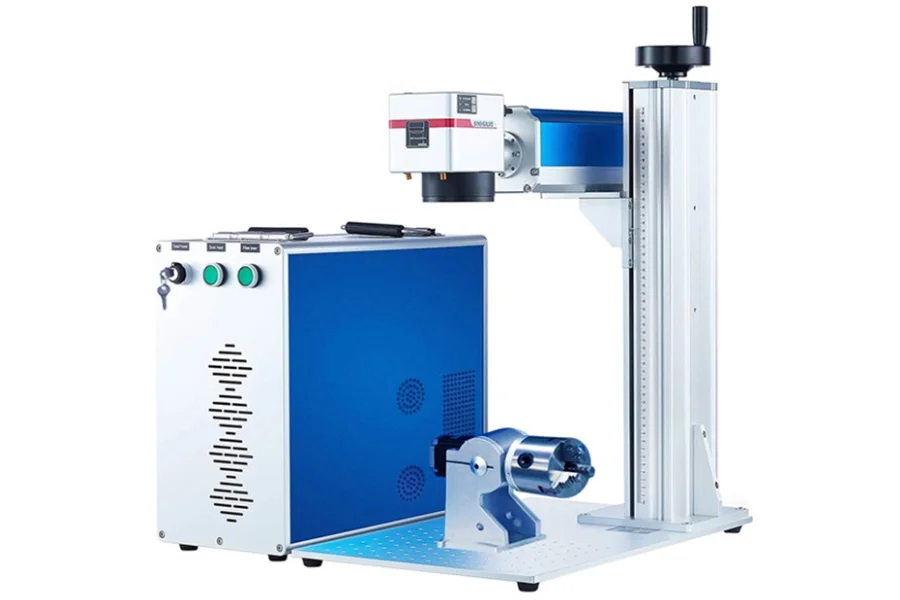

A fiber laser engraving and making machine is usually priced from $3,500 to $28,500 depending on the pulsed laser powers, which range from 20W, 30W, 50W, 60W, 70W, and 100W.
Fiber laser cutter
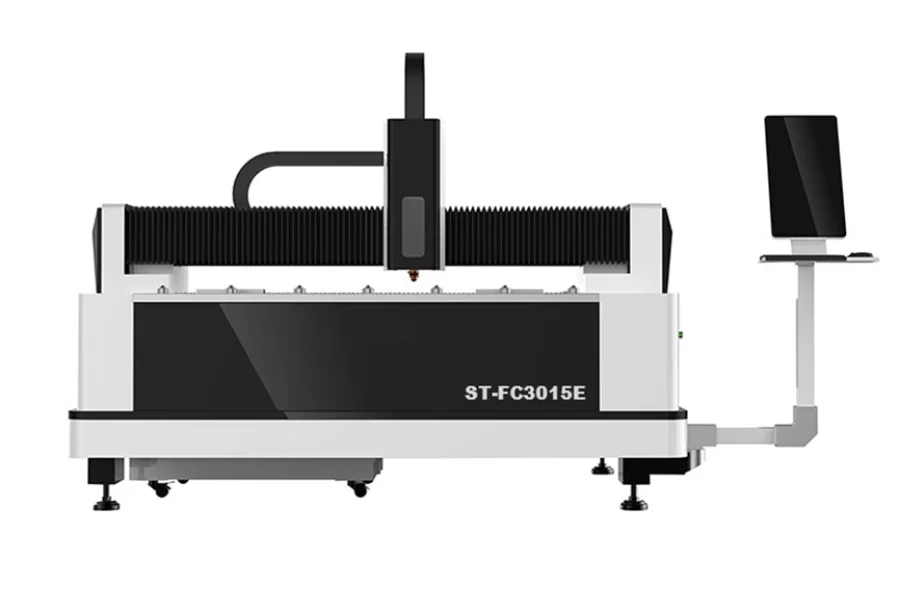

A fiber laser cutting machine costs between $14,200 to $260,000, depending on the continuous laser power which ranges from 1000W, 1500W, 2000W, 3000W, 4000W, 6000W, 8000W, 10000W, 12000W, 15000W, 20000W, 30000W, and up to 40000W.
Fiber laser welder
A fiber laser welding machine ranges in price from $5,400 to $58,000, depending on the different types including portable (handheld laser welding gun) welders, automatic (CNC controller) welders, and robot welders with continuous laser powers of 1000W, 1500W, 2000W, and 3000W.
Fiber laser cleaner
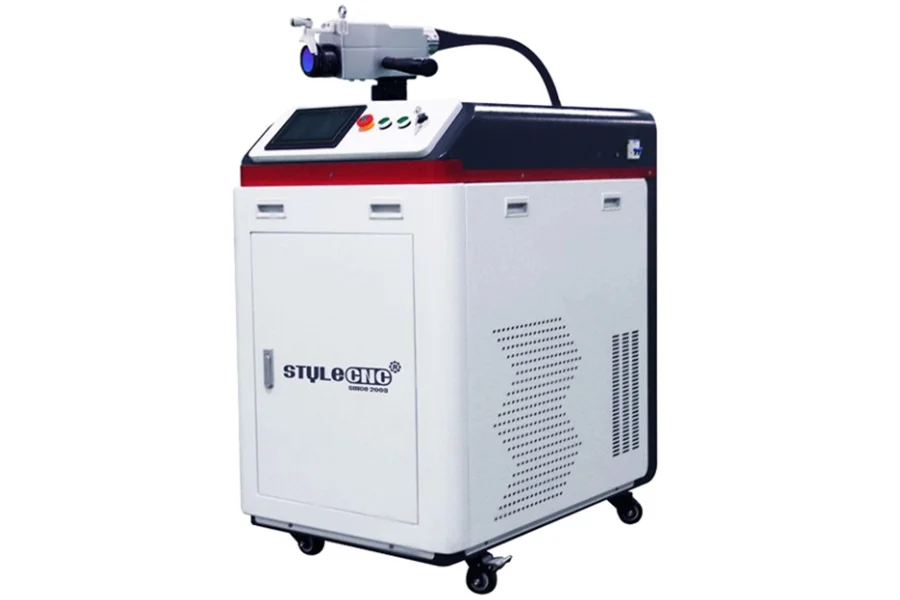

The average price for a new fiber laser cleaning machine ranges from $5,000 to $19,500, depending on the pulsed laser power which ranges from 50W, 100W, 200W, 300W, and the continuous laser power which ranges from 1000W, 1500W, 2000W, 3000W.
Source from stylecnc.com
Disclaimer: The information set forth above is provided by stylecnc independently of Alibaba.com. Alibaba.com makes no representation and warranties as to the quality and reliability of the seller and products.




