For the convenience and satisfaction of the customer, most car rental companies ensure a car is prepared for the customer by ensuring that the car is fueled, serviced, and available at the designated pickup location. With such an arrangement, the car rental companies limit their responsibilities to the pickup point once the customer drives away.
In the world of International Commercial Terms (Incoterms), the FCA (Free Carrier) Incoterm operates similarly, as the seller’s duties conclude once the goods are delivered to a specified location, ready for the carrier to take over.
Continue reading to find out the definition of FCA, the key responsibilities and financial commitments of both the seller and buyer under FCA and the impact of FCA on the overall shipping process and decision-making when choosing FCA as a buyer.
Table of Contents
Understanding FCA Incoterms
Key responsibilities and financial obligations
Impact of FCA on shipping and choosing FCA as a buyer
Freedom in logistics control
Understanding FCA Incoterms
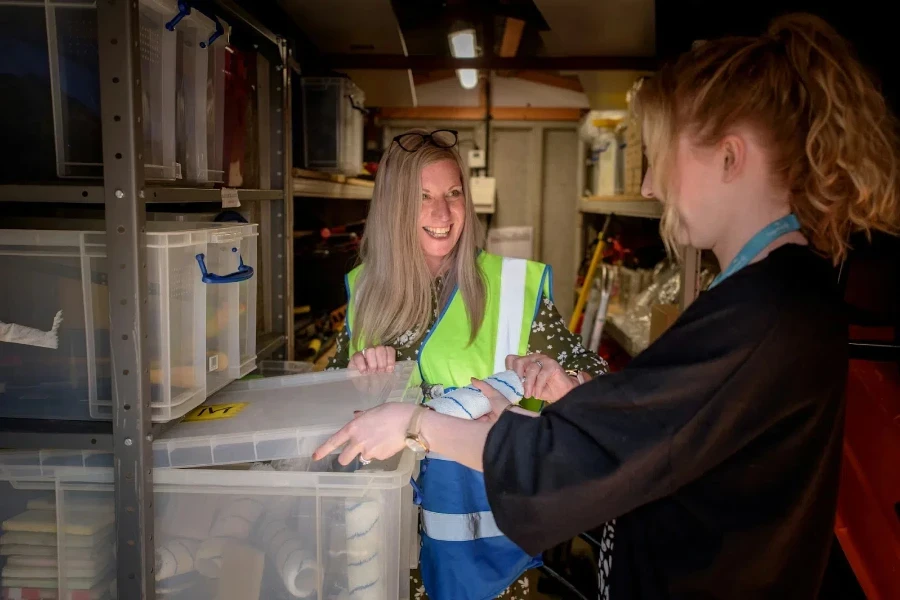

FCA, or Free Carrier, is an Incoterm rule that places the responsibility on the seller to deliver goods to a location designated by the buyer, either at the seller’s premises or another specified place. The seller is also responsible for covering all export clearance requirements. If the named place is at the seller’s premises, the risk transfers to the buyer once the goods are loaded onto the carrier arranged by the buyer. However, if the goods are to be delivered at a separate location, the risk can either be transferred to the buyer when the goods are ready for loading onto the carrier, or it may be transferred when it is delivered to any other designated recipient by the buyer.
FCA applies across all modes of transport, which simplifies the buyer’s logistics operations since it is the seller’s responsibility to ensure that the goods are prepared for international transport, with export customs clearance tasks completed. Buyers then take over the remaining tasks to handle the import process accordingly.

Overall, from the perspective of key responsibility distribution, FCA is one of the moderately balanced Incoterm rules that clearly differentiate the export and import roles between the seller and buyer. It’s also crucial to note that FCA in Incoterms 2020 includes a significant procedural update compared to its 2010 version because of the addition of Bills of Lading with an on-board notation, which will be discussed in-depth later under the section that covers the impact of FCA on shipping.
Key responsibilities and financial obligations
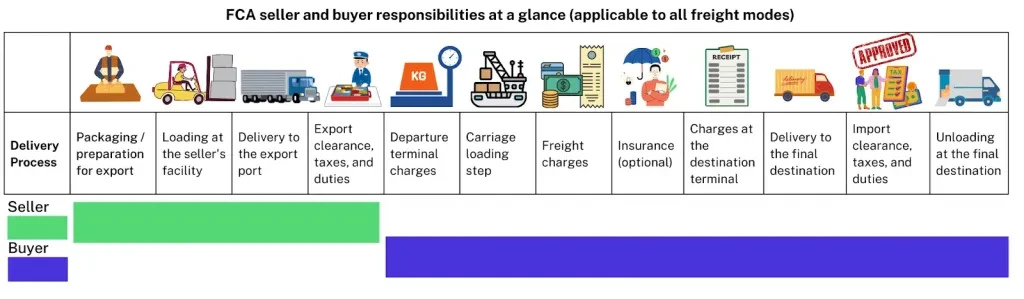
Seller’s responsibilities and financial commitments

The most important and fundamental responsibility of sellers under FCA is to ensure that goods are cleared for export and delivered to the specific location named by the buyers. In fact, the designated delivery place here must be specified up to a precise delivery point within the named location to prevent any disputes on the exact risks and cost transfer point.
All export customs clearance-related duties and formalities, including documentation and information necessary to assist buyers in arranging transportation and insurance, must also be handled by the sellers to support seamless logistics coordination up to the named location. The seller also needs to be responsible for the packaging and marking of goods to ensure product safety throughout the entire journey, regardless of transportation modes and conditions.
In line with these responsibilities, the financial commitments of the seller under FCA cover all costs associated with export clearance, packaging, transportation, and any related duties and taxes up to the designated location. In short, the cost burden of sellers under the FCA Incoterm includes all handling and logistics costs, such as providing proof of delivery to the buyer up to the named place, as well as any other costs required to meet the buyer’s specified requirements.
Buyer’s responsibilities and financial commitments

While FCA Incoterm is considered moderately balanced in terms of key responsibilities and financial obligations between the seller and the buyer, the main carriage arrangements, including the associated costs and import formalities involved during the clearance process to ensure that goods can legally enter the destination country, are all placed under the responsibilities of the buyer.
In other words, buyers must also handle all import-related responsibilities and inspections to ensure full compliance with destination country regulations. Buyers need to organize the main carriage and subsequent transportation, as well as manage the risks involved. In addition to all these, the buyer must also accept the proof provided by the seller on the delivery status of the goods up to the named delivery point.
Aligned with these obligations, buyers need to be responsible for all post-delivery transportation costs once the goods have been delivered to the named delivery point. These include the main transportation costs, terminal charges, loading fees, as well as all post-carriage financial commitments. Fundamentally, the buyer needs to cover all costs of transporting the goods from the point of delivery to the final destination, including related import and transit-related formalities, such as customs clearances, import licenses (if required), and import taxes and duties.
In the event that there are any additional costs arising from the buyer’s request for the assistance of the seller to obtain certain necessary documentation for the delivery process or due to the failure of the buyer in nominating a carrier, the buyer must also be responsible to reimburse the relevant costs to the seller or to cover these additional costs accordingly.
Impact of FCA on shipping and choosing FCA as a buyer
Impact of FCA on shipping

When discussing the impact of FCA on shipping, one can analyze its effects from either the seller’s or buyer’s point of view. The most significant impact of the FCA Incoterms 2020 rule for sellers is the availability of the optional mechanism that allows the buyer to instruct their carrier to issue a bill of lading with an on-board notation to the seller, which was not available in the previous Incoterms 2010 version.
To appreciate the significance of this newly added optional mechanism for sellers, it’s essential to understand the purpose behind a bill of lading with an on-board notation and its relationship with contractual or banking requirements, such as a letter of credit. Also known as an on-board bill of lading, a bill of lading with an on-board notation is often needed to fulfill the requirements of a letter of credit. In order for the letter of credit to work as a form of payment guarantee issued by the buyer’s bank to the seller, the seller must present the on-board bill of lading as proof that the goods have been loaded onto a ship.

Before the implementation of this optional mechanism, issuance of an on-board bill of lading under FCA could be quite a challenge. According to the standard FCA rule, deliveries are considered completed even before the goods are loaded onto a ship, as long as they are handed over to the buyer or the buyer’s carrier.
Under the new optional mechanism now, based on the instructions from the buyer, the carrier can issue the on-board bill of lading to the seller once the goods are loaded onto a ship. However, it’s worth noting that this optional mechanism may still pose some difficulties to the seller in terms of dates, as the in-land delivery date and the loaded on-board date are bound to be different.
Finally, since buyers can opt for various modes of transport under the FCA rule, they also have greater control over choosing their preferred carriers and logistics providers from the point of delivery. The potential disputes between sellers and buyers can be greatly reduced under FCA too since the rules come with clear risk transfer points between both sellers and buyers.
Choosing FCA as a buyer

Even though the key responsibilities of sellers and buyers might not be immediately clear from its name—Free Carrier (FCA)—it is essentially an Incoterm that provides buyers with significant freedom to select carriers and transportation methods, making it an ideal option for buyers seeking increased control over logistics.
This also means that buyers are free to customize their transport arrangements according to their needs, whether for the main carriage or all other subsequent delivery arrangements. With all these flexibilities, buyers also have a higher potential to reduce the overall shipping costs through better-negotiated carriage terms since they control the bulk of the logistics journey.
In addition, since buyers are in charge of import clearance under FCA, buyers who are familiar with import procedures can hence concentrate on import clearance instead of worrying about any export-related complications, thereby gaining better operational and risk control throughout the entire shipping process.
Ultimately, when opting for an Incoterm rule, available carrier, and freight mode options, the efficiency of operational control, as well as total cost and risks involved should be among the main considerations for buyers. From these perspectives, FCA Incoterms serve as a strategic choice that offers flexibility for buyers, as the buyers are free to select and manage their own carrier and shipping process while also maintaining control over the majority of the transportation logistics under FCA.
Freedom in logistics control

Under FCA, sellers are fully responsible for the export clearance process and must ensure that the goods are delivered to the specific delivery point agreed upon with the buyers, including all related export taxes, duties, and all associated costs. On the other hand, buyers are tasked with the responsibility and costs of all subsequent delivery once the goods have been accepted at the named place, including all related import and transit clearance tasks and fees, as well as import taxes and duties. Overall, buyers can benefit from the FCA in terms of flexibility in choosing their preferred transportation modes, carriers, and logistics providers.
Unlock more expert logistics knowledge and wholesale business sourcing ideas at Alibaba.com Reads. Regular visits to Alibaba.com Reads provide insightful updates on market trends and inspire innovative ideas to fuel any business growth.




