Car engines have a long development history, dating back to the 1800s when Etienne Lenoir invented the first internal combustion engine. Nowadays, they have become incredibly efficient, generating more power with less fuel, which helps to reduce emissions and promote environmental sustainability.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive into the fascinating realm of car engines, exploring their myriad benefits; from the raw power generated by gasoline engines to the eco-friendly efficiency of electric motors, we’ll unravel each type’s inner workings, strengths, and distinctive features.
Table of Contents
Automotive engine market share and size
How car engines work
Typical arrangements of car engines
Various engine cylinder arrangements
Conclusion
Automotive engine market share and size
The global automotive engine market encompasses the production, sales, and aftermarket services related to various vehicle engine types. Precedence Research valued the global car engine market in 2022 at US $102.89 billion, and expects it to grow at a CAGR of 2.8% from 2023 to 2032. Therefore, by the end of 2023, the global car engine market is forecast to be worth US $136.81 billion.
The automotive engine market growing predominantly due to the increasing sales of vehicles, from 66.7 million in 2021 to 67.2 million in 2022. In addition, strict fuel economy regulations have compelled automotive manufacturers to focus on developing more efficient and advanced engines, resulting in a thriving market for innovative engine technologies that meet stringent standards while providing improved performance and reduced emissions.
Regions with high demand for car engines include North America, Asia Pacific, Europe, South America, and the Middle East. In 2021, the revenue share of North America surpassed 30%. This region boasts developed economies, including the United States and Canada. During the forecast period (2023 to 2032), it is anticipated that the Asia Pacific market will experience a compound annual growth rate of 3.2%.
How car engines work
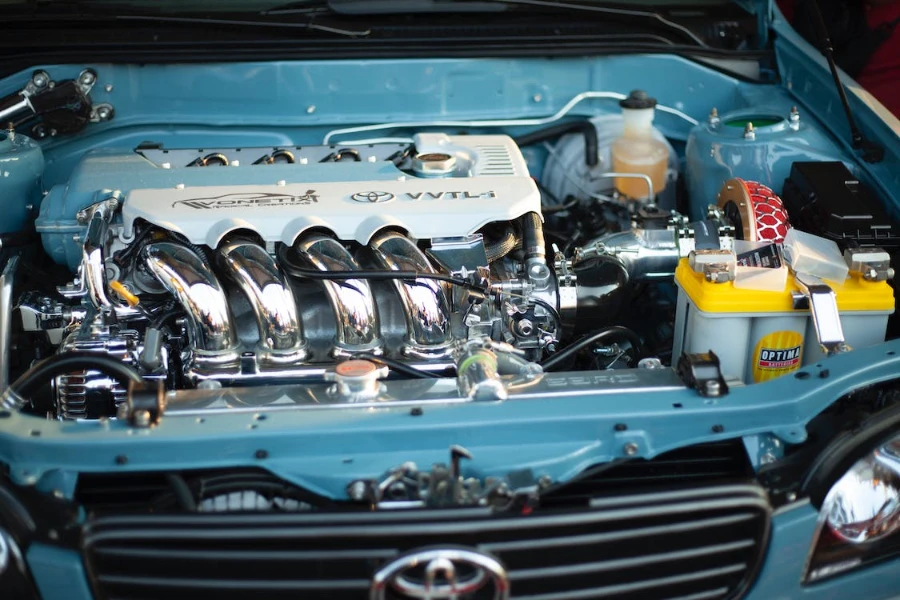

Central to the operation of a car engine is a set of vital components that work in harmony. For example, anchored within the engine block are the cylinders, where controlled combustions take place. Meanwhile, pistons located within these cylinders execute vertical movements, creating the essential power. Transmitting this power from the pistons to the crankshaft are connecting rods, which transform linear motion into a rotational one. Finally, the intricate coordination of valves, overseen by the camshaft, regulates the ingress and egress of fuel and exhaust gases within the cylinders.
Step 1: Air intake
When the engine is running, proper ventilation must first be ensured. This is accomplished by drawing air through an intake manifold equipped with a throttle valve that regulates the airflow entering the engine. To maintain clean and pollutant-free air, air filters help play a crucial role in facilitating optimal combustion. Additionally, high-performance engines may utilize intercoolers to cool the exhaust, enhance volume, and optimize combustion efficiency.
Step 2: Fuel injection
Fuel injection is a precise process that delivers fuel into the engine’s cylinders. Each cylinder has a specialized injector that sprays fuel in a fine mist into the incoming air. Nowadays, most engines use electronic fuel injection (EFI) systems, which automatically adjust the amount of fuel delivered based on factors such as engine load, speed, and temperature.
This innovative technology leads to improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and enhanced overall engine performance when compared to outdated carbureted systems. Some engines even incorporate direct fuel injection, where the fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber for optimal efficiency.
Step 3: Compression
As the piston moves up in the cylinder, it compresses the air-fuel mixture, increasing pressure and temperature. This creates optimal conditions for combustion. The compression ratio, which compares the cylinder’s volume at its lowest stroke versus at its top, is an important factor in engine design. Diesel engines, specifically, depend on high compression ratios for compression ignition, where the high temperature of the air alone ignites the fuel.
Step 4: Ignition
In gasoline engines, a spark plug plays a key role by creating an electric spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture. This spark is generated when current flows through the spark plug’s gap. The timing of this spark is meticulously controlled by the engine’s electronic control unit (ECU). On the other hand, diesel engines don’t rely on spark plugs for ignition. Instead, they achieve ignition through compression-induced high temperatures, causing the spontaneous combustion of the injected diesel fuel.
Step 5: Power stroke
After ignition, the gases from the combustion rapidly expand, forcing the piston to move downward in the cylinder. This movement is then transmitted to the crankshaft, which converts it into rotary motion. It’s during this power stroke that the vehicle gains forward propulsion. Ensuring maximum efficiency during this process is essential for optimal engine performance and fuel economy since any losses or inefficiencies can significantly affect overall vehicle performance.
Step 6: Exhaust stroke
On its way back up, the exhaust valve opens after the piston’s power stroke. The burnt exhaust gases move out of the engine through the exhaust as the piston retracts upwards in the cylinder. The exhaust gases are first carried by a tube through the exhaust manifold, where they move through the exhaust pipe and are finally released into the outside air.
To delve deeper into this mechanical symphony, we will explore two critical sections: typical arrangements of car engines and various engine cylinder arrangements. These sections serve as essential companions to our understanding of how car engines work.
The typical arrangements of car engines shed light on common engine layouts, clarifying how the components discussed earlier come together in real-world scenarios. Meanwhile, various engine cylinder arrangements will delve into the diverse configurations engines can adopt, elaborating on how these arrangements impact engine performance, efficiency, and overall operation.
Typical arrangements of car engines
Whether a car has a typical engine arrangement depends on space efficiency, weight distribution, and performance. The most common is a front-engine, front-wheel drive arrangement. However, front-engine, rear-wheel drive provides better handling but potentially sacrifices interior space. Rear-engine layouts are less common but offer unique benefits, such as improved traction in certain driving conditions. The choice of arrangement depends on the vehicle’s intended use and design priorities.
1. Inline engine layouts
Inline engine layouts arrange the cylinders in a straight line, one after another. This configuration is often seen in four-cylinder engines, where the cylinders are placed in a single row. Inline engines are preferred for their straightforward design, compact size, and well-balanced performance. Representative models include the Honda Civic (four-cylinder inline engine) and BMW 3 Series (four-cylinder and six-cylinder inline engines).
Pros
- Simple design and fewer components
- Compact size and space efficiency
- Well-balanced performance
Cons
- Limited power compared to other configurations
- Some vibration due to the inline arrangement
- Challenges in packaging, especially in certain vehicle designs
2. Straight engine layouts
Straight engine layouts, also known as inline engines, consist of cylinders arranged in a single row, much like inline engine layouts. However, straight engines typically have more than four cylinders, instead boasting six or eight. This arrangement ensures excellent balance, smooth operation, and great power delivery. Representative models include the BMW 5 Series and the Audi A8.
Pros
- Excellent balance and smooth operation due to the inline arrangement of cylinders
- Excellent power delivery, especially in configurations with six or eight cylinders, as seen in the BMW 5 Series and Audi A8
- Simple design and fewer components compared to other multi-cylinder engines
Cons
- It may require a more extended engine bay to accommodate more cylinders
- Some models might experience increased vibration compared to other engine layouts
- Limited space for certain accessories or components due to the longer arrangement
3. V engine layouts
These engines are characterized by cylinders arranged in two banks or “vees” at an angle to each other. The specific angle between the banks can vary, and popular variants include V6, V8, and V12 engines. This layout enables a more compact design, balancing performance and smooth operation. Representative models include the Mercedes-Benz C-Class (V6 engine), Chevrolet Corvette (V8 engine), and Aston Martin DB11 (V12 engine).
Pros
- Compact design and easy fitting into engine bays
- Inherent balance for smoother engine operation
- Offers excellent power output and flexibility
Cons
- Increased complexity in manufacturing and maintenance
- Slightly lower fuel efficiency in some cases
- Higher production costs due to increased complexity
4. Flat engine layouts
Flat engine layouts, also known as horizontally opposed engines, feature cylinders positioned horizontally on either side of the crankshaft. This unique configuration results in a low center of gravity, enhancing stability and handling. Flat engines are frequently utilized in vehicles such as Porsche sports cars (e.g. Porsche 911 with a flat-six engine) and Subaru Boxer engines (e.g. Subaru Impreza with a flat-four engine), showcasing their benefits in terms of performance and control.
Pros
- Low center of gravity helps to improve stability and handling
- Enhanced performance and control, particularly in sports cars like the Porsche 911
- Compact design allows for efficient use of space, as seen in the Subaru Impreza
Cons
- Potentially more complex to manufacture and maintain
- Limited space for specific components due to the compact design
- Slightly higher manufacturing costs compared to other layouts
Various engine cylinder arrangements
A cylinder is where fuel and air mix, ignite, and create the power that propels the vehicle. The number and arrangement of cylinders in an engine matter because they affect how the engine performs, how much power it can produce, how efficient it is, and even how the engine looks and fits in the car. Each layout has its benefits and drawbacks.
1. Three-cylinder engines

The rise in popularity of three-cylinder car engines can be attributed to their well-balanced blend of performance and fuel efficiency. Commonly found in compact cars and even some high-performance models like the Ford Fiesta (1.0L EcoBoost), Mini Cooper (1.5L Turbo), and BMW i8 (hybrid), the three-cylinder configuration strikes a favorable compromise between power, efficiency, and compactness.
With improved fuel economy, these engines deliver ample power for everyday driving needs, making them an attractive choice for those seeking an optimal combination of performance and efficiency.
Pros
- A well-balanced combination of power and efficiency, catering to various driving needs
- Reduced internal friction leads to better fuel efficiency and cost savings
- Smaller and lighter construction enhances weight distribution and handling, making them ideal for compact cars and urban driving
Cons
- May have slightly lower power output compared to larger multi-cylinder engines
- Fewer cylinders can lead to more noticeable vibrations during operation, though this issue has been minimized in modern designs
- While suitable for everyday driving, they may not be optimal for use in high-performance sports cars or demanding conditions
2. Four-cylinder engines

Four-cylinder engines are popular for their harmonious balance between power, fuel efficiency, and compact size. These engines are commonly found in sedans, SUVs, and hatchbacks, showcasing their versatility.
Renowned for practicality and efficiency, four-cylinder engines deliver adequate power for daily commuting while maintaining commendable fuel economy. Representative models include the Honda Civic, known for reliability and fuel efficiency, the Toyota Camry with its various four-cylinder engine options, and the Volkswagen Golf, praised for its fun-to-drive nature and good blend of performance and fuel economy.
Pros
- Harmonious balance between power, fuel efficiency, and compact dimensions
- Prevalent in sedans, SUVs, and hatchbacks, catering to various vehicle types
- Adequate power for daily commuting and commendable fuel economy
Cons
- May lack power and performance compared to larger engines, limiting high-performance applications
- In some cases, additional stress on the engine may result in reduced longevity
- In specific heavy-load scenarios, may exhibit decreased torque compared to larger engines with more cylinders
3. Six-cylinder engines
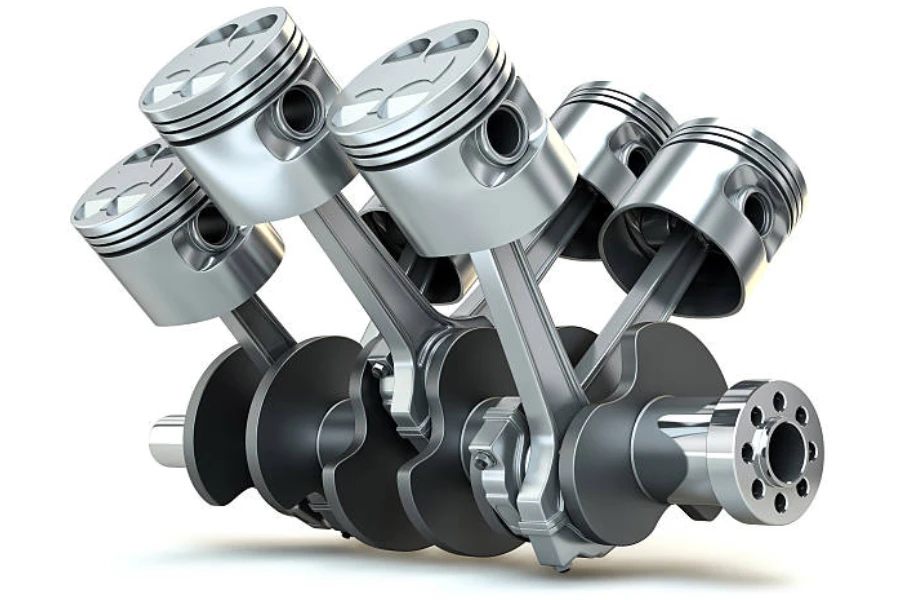

Six-cylinder engines are well-regarded for their reliable and strong performance. They are found in various vehicles, including sedans, SUVs, and sports cars, striking a balance between power and fuel efficiency and offering an enhanced driving experience. Representative models include the BMW 3 Series, known for their sporty driving dynamics, the Toyota Highlander, offering a smooth and capable midsize SUV option, and the Ford Mustang, with their powerful six-cylinder engines catering to performance enthusiasts.
Pros
- Strong performance and more power for spirited driving
- Versatility in various vehicle types, including sedans, SUVs, and sports cars, etc.
- Smooth operation with reduced vibrations due to additional cylinders
Cons
- Higher fuel consumption, leading to potentially higher operating costs
- Higher cost compared to smaller engine options
- Limited fuel efficiency, especially in stop-and-go city driving
4. Eight-plus cylinder engines
Eight-cylinder engines offer exceptional power, making them popular in high-performance cars, luxury vehicles, and trucks. They provide a thrilling driving experience with significant horsepower and torque but consume more fuel and have higher manufacturing costs. Representative models include the Lamborghini Aventador (V12), Mercedes-Benz S-Class (V8), and Chevrolet Silverado (V8).
Pros
- High horsepower and torque for impressive acceleration and performance
- Popular in various vehicle types, such as sports cars, luxury sedans, and trucks
- The abundance of cylinders provides dynamic acceleration and a commanding presence
Cons
- More fuel usage leads to increased operating costs
- Complexity and additional components result in higher production expenses
- Increased fuel consumption and emissions may have a larger environmental footprint
Conclusion
Each type of engine configuration features unique advantages tailored to different vehicle applications, from compact and efficient twin-cylinder engines to robust and powerful eight-cylinder engines. Whether you prioritize fuel efficiency, high performance, or a balance between the two, there is an engine type that caters to your specific needs. To further explore the realm of car engines, visit Alibaba.com and browse thousands of automotive products and components.