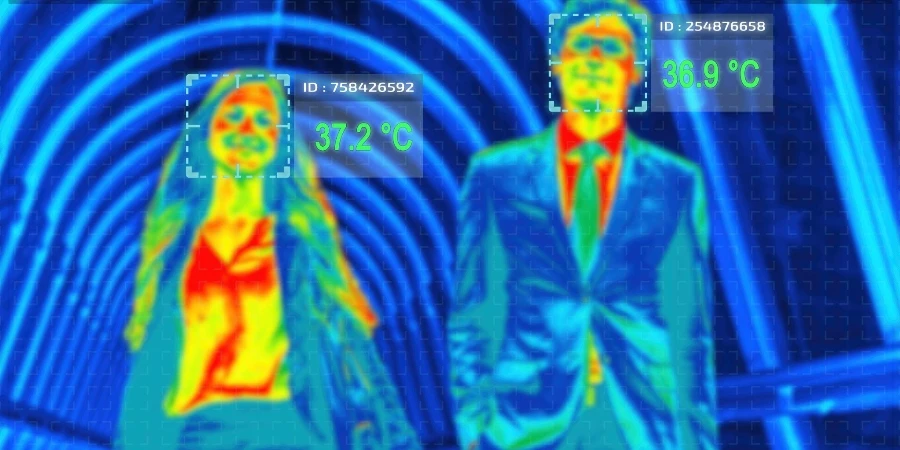
Thermal imaging technology has become an indispensable tool across a broad spectrum of industries, from security and surveillance to maintenance and health monitoring. These devices translate heat—emitted by objects into visible data, revealing what the naked eye cannot see. This capability allows for precise diagnostics, efficient monitoring, and enhanced safety, providing essential insights that are critical in optimizing operational processes. As technology evolves, the applications and effectiveness of thermal imaging continue to expand, making them a valuable addition to the technological arsenal of any business focused on innovation and quality control.
Table of Contents
1. Exploring the spectrum: Types and applications
2. Market pulse: Trends and forecasts for 2024
3. Precision in selection: What to look for in thermal cameras
4. Spotlight on innovation: Top models and their capabilities
Exploring the spectrum: Types and applications
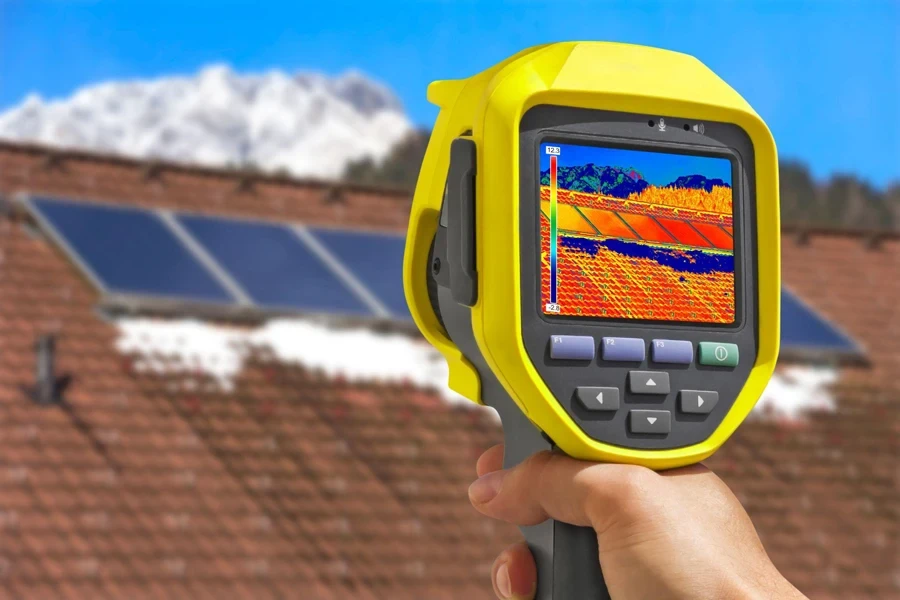

The landscape of thermal imaging technology is rich with diverse designs that cater to various professional needs, ranging from predictive maintenance to emergency response. This diversity in design is evident in the array of models available—each tailored to specific operational contexts and objectives.
Diversity in design: The array of thermal imaging cameras encompasses handheld models, drone-mounted systems, and smartphone enhancements. Handheld cameras remain popular for their portability and ease of use, making them ideal for on-site inspections and immediate diagnostics. In contrast, drone-mounted thermal cameras offer the advantage of accessing difficult-to-reach areas, such as overhead power lines or large infrastructure facilities, providing a comprehensive view from above. Furthermore, the advent of smartphone enhancements has democratized thermal imaging, allowing for broader access through an attachment that transforms a standard mobile device into a powerful thermal imaging tool. This integration into everyday technology underscores the accessibility and scalability of thermal imaging solutions in modern business practices.
Broadening horizons: The applications of thermal imaging cameras are as varied as their designs. In industrial settings, these cameras play a crucial role in maintenance and safety by identifying heat anomalies that precede equipment failures, thus preventing costly downtime and enhancing operational safety. The technology’s application extends to building inspections where it is indispensable for detecting heat losses and ensuring energy efficiency. In the realm of security, thermal cameras provide reliable surveillance regardless of lighting conditions, detecting intrusions or unauthorized activities through heat signatures. Moreover, emergency services utilize these cameras for search and rescue operations, navigating smoke-filled environments or night-time scenarios to locate individuals by their heat signatures. This capability is critical in enhancing the effectiveness and safety of rescue missions.
Each application not only illustrates the versatility of thermal imaging cameras but also highlights their integral role in augmenting human capabilities across various professional landscapes. The ongoing enhancements in camera technology continue to expand these horizons, promising even greater integration into industrial and commercial operations.
Market pulse: Trends and forecasts for 2024
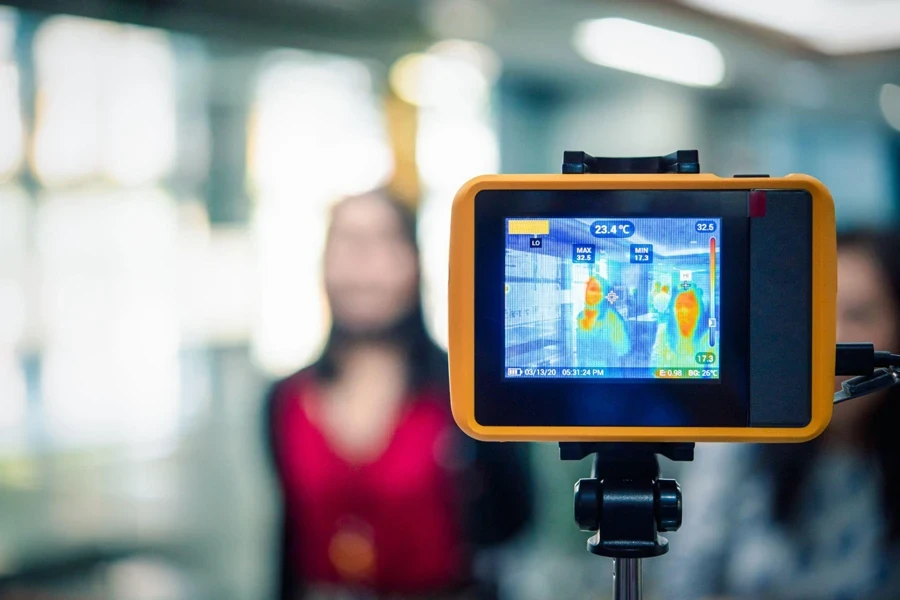

The thermal imaging camera market is poised for consistent growth through 2024 and beyond, driven by relentless technological innovations and a widening scope of applications across industries.
Growth trajectories and technological evolution: Recent market analysis indicates a robust trajectory for the thermal imaging camera industry, with projected market values expected to rise significantly. The market, valued at over $2628.6 million in 2023, is anticipated to climb to approximately $3276.2 million by 2030. This steady growth, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of about 3.3%, underscores the increasing reliance on thermal imaging technology in sectors ranging from healthcare to industrial maintenance and security. Technological advancements are at the heart of this growth, as newer models feature enhanced resolutions, reduced costs, and improved user interfaces, making these tools both more accessible and effective.
Global perspectives: The expansion of the thermal imaging market is not uniform across the globe but is influenced significantly by regional dynamics and economic developments. In regions with robust industrial sectors, such as North America and Western Europe, there is a substantial push towards adopting advanced monitoring and diagnostic tools, which include thermal imaging cameras. These tools are critical in preventive maintenance and energy management, areas receiving increased attention as industries seek to optimize operations and reduce overheads. Conversely, in emerging markets in the Asia-Pacific region, the growth is spurred by rapid industrialization and urban development, leading to heightened demand for thermal imaging solutions in building inspections, public security, and healthcare monitoring. This geographical variance is critical for stakeholders aiming to capture and maximize market opportunities, as it necessitates tailored strategies that cater to specific regional needs and compliance standards.
Each market segment, from security and surveillance to automotive and healthcare, shows a distinct pattern of demand influenced by regional industrial policies, technological literacy, and economic capabilities. Understanding these patterns is essential for businesses to align their offerings with market expectations and to leverage growth opportunities effectively.
Precision in selection: What to look for in thermal cameras
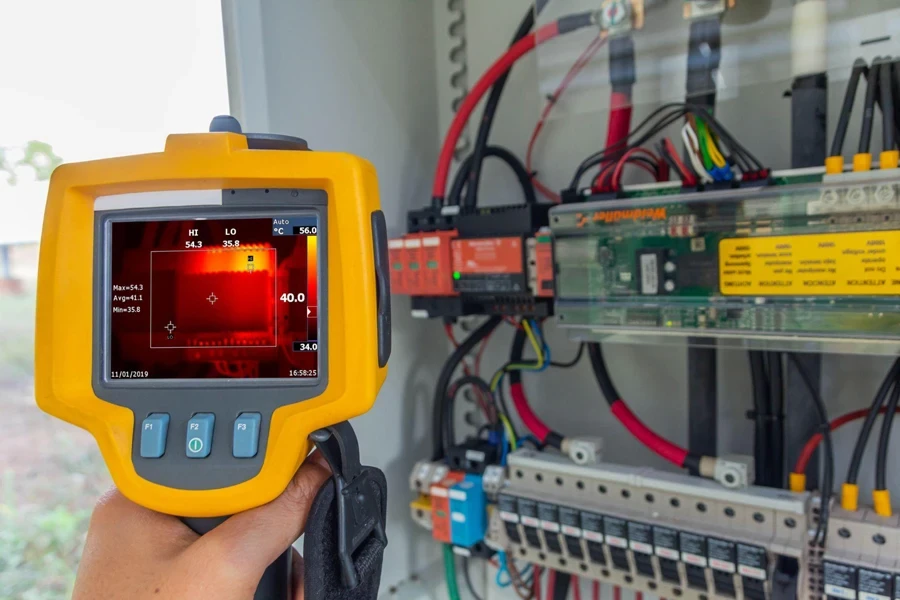

Choosing the right thermal imaging camera involves assessing several critical features to ensure clarity, accuracy, durability, and user-friendliness. These features are vital for maximizing the camera’s utility and efficiency in professional settings.
Clarity and accuracy: Resolution and Thermal Sensitivity (NETD) are fundamental when selecting thermal imaging cameras for professional applications. The resolution of a thermal camera, typically measured in pixels, directly influences the detail and quality of the images it can produce. Higher resolution cameras can detect finer details and smaller objects, which is crucial for applications requiring precise diagnostics. For instance, cameras with resolutions of 640×480 pixels allow for superior image quality and finer detail compared to standard 320×240 units. This higher resolution is particularly beneficial in settings such as electrical inspections or mechanical systems monitoring, where small temperature differences can signify potential issues.
Thermal sensitivity, or Noise Equivalent Temperature Difference (NETD), is another critical spec that indicates the smallest temperature difference the camera can detect. A lower NETD value means the camera can capture the slightest differences in heat, which is essential for applications where high detail is necessary, such as detecting moisture infiltration in buildings or subtle electrical failures. Cameras with an NETD of less than 50mK are highly sensitive and can provide more accurate measurements of temperature differences.
Built to last: The durability of a thermal imaging camera is crucial, particularly for those used in challenging environmental conditions. Cameras designed for industrial applications often come with rugged casings that protect against dust, water, and shock. For example, cameras with an IP rating of IP54 are deemed sufficient for most industrial environments as they offer protection against dust ingress and water spray from any direction.
User-friendliness also plays a significant role in a camera’s operational efficacy. This includes aspects such as the ease of handling the device, the intuitiveness of the software, and the support provided for the camera. Features like a responsive touchscreen interface, customizable menus, and Wi-Fi connectivity for quick data transfer enhance the user experience and operational efficiency. Additionally, features like direct streaming to a central monitoring system can be crucial for real-time applications such as surveillance or process control.
Each feature—from the technical specifications of image resolution and thermal sensitivity to the ergonomic design and robustness—should be carefully evaluated against the requirements of the intended application. This approach ensures that the selected thermal imaging camera not only meets the immediate needs of the task at hand but also aligns with long-term operational objectives, thereby optimizing both performance and investment.
Spotlight on innovation: Top models and their capabilities

As thermal imaging technology continues to evolve, certain models distinguish themselves through superior performance, marrying innovative features with robust functionality to address diverse professional demands.
Leaders of the pack: FLIR TG267 Thermal Camera stands out for its precision and utility in rigorous environments. It features a 160 x 120 resolution that, while not the highest available, offers clear and detailed thermal images sufficient for most industrial and commercial applications. What sets the FLIR TG267 apart is its MSX image enhancement technology, which overlays digital image details onto thermal readings to produce more contextually rich pictures. This function proves invaluable in identifying problematic areas in mechanical and electrical systems, where clarity can significantly impact diagnostic accuracy.
GUIDE PC210 Thermal Imaging Camera excels with its IR resolution of 256×192, providing high-definition thermal images that are crucial for detecting subtle temperature differences in complex industrial settings. The PC210 is known for its robust build, featuring an IP54 rating that ensures it can withstand dust and water exposure, making it ideal for tough environments. Additionally, the camera’s fast boot time and user-friendly interface enhance its operational efficiency, making it a preferred choice for professionals who require a reliable tool for rapid diagnostics.
MILESEEY TR256B Thermal Imager combines affordability with effective performance, featuring a straightforward interface and essential functions that meet the needs of most standard thermal imaging tasks. Its balance between cost and capability makes it a popular choice among professionals seeking a no-frills, dependable thermal imaging solution.
INFIRAY P2PRO Thermographic Camera offers high thermal sensitivity and resolution, which are critical for applications that involve detailed thermal mapping, such as electronic circuit board inspections or composite material analysis where high precision is mandatory.
UNI-T UTI260B Industrial Thermal Imager rounds out the list with its comprehensive feature set tailored for heavy-duty use. This model is particularly noted for its wide temperature measurement range, which allows for applications that operate at extremely high temperatures, such as metal processing or furnace inspections.
Each of these models demonstrates a commitment to innovation in thermal imaging, providing tools that not only meet but anticipate the evolving needs of professionals across various industries. These cameras stand out not just for their technical specifications but also for the practical enhancements they bring to everyday diagnostic, maintenance, and inspection tasks.
Cost vs. Capability: Evaluating the price-performance ratio of thermal imaging cameras reveals how these tools balance cost with their advanced capabilities. Here, we delve into the specific features and scenarios that differentiate the five models discussed previously, providing a clear picture of what each offers relative to its price.
FLIR TG267 Thermal Camera is mid-range in terms of cost but offers robust features for professional use. Its standout feature is the MSX technology, which enhances thermal images with visual details, providing clearer context. This is crucial in environments where detail can influence critical decisions, such as in electrical inspections where precise fault detection is necessary. Priced around $500, the FLIR TG267 offers a solid balance between advanced features and cost, making it a suitable investment for professionals seeking reliability without the premium cost of higher-end models.
GUIDE PC210 Thermal Imaging Camera stands out for its superb price-quality ratio. At approximately $300, it provides excellent resolution (256×192) for detailed imaging, which is pivotal for applications requiring fine gradation in temperature differences, such as electronic circuit diagnosis. The PC210 is also noted for its durability (IP54 rating) and ease of use, with features like auto hot & cold spot tracking that enhance its practicality in fast-paced environments.
MILESEEY TR256B Thermal Imager offers an affordable option for those who require basic thermal imaging capabilities without the extensive features of more expensive units. Priced around $200, it is ideal for users who need thermal imaging for general maintenance or HVAC applications where high resolution is less critical.
INFIRAY P2PRO Thermographic Camera is designed for high-sensitivity applications, making it suitable for sophisticated industrial use where high thermal sensitivity is required to detect slight temperature variations. The cost, while higher at around $400, reflects its enhanced capabilities, particularly in complex diagnostics and research applications where detecting subtle thermal differences can prevent costly equipment failures.
UNI-T UTI260B Industrial Thermal Imager rounds out the selection as a high-performance model tailored for demanding industrial applications. It is priced around $350, which is justified by its wide temperature range and high resolution, essential for detailed thermal analysis in high-temperature environments like metal processing facilities.
Each of these models demonstrates a strategic balance between cost and capability. The decision on which model to choose should be guided by specific needs:
- FLIR TG267 and INFIRAY P2PRO are excellent for settings where detail and image clarity are paramount.
- GUIDE PC210 offers the best value for users needing a durable and versatile camera with good imaging capabilities.
- MILESEEY TR256B serves well for basic, budget-conscious applications.
- UNI-T UTI260B is ideal for intensive industrial applications where higher temperature ranges and detailed thermal analysis are routine.
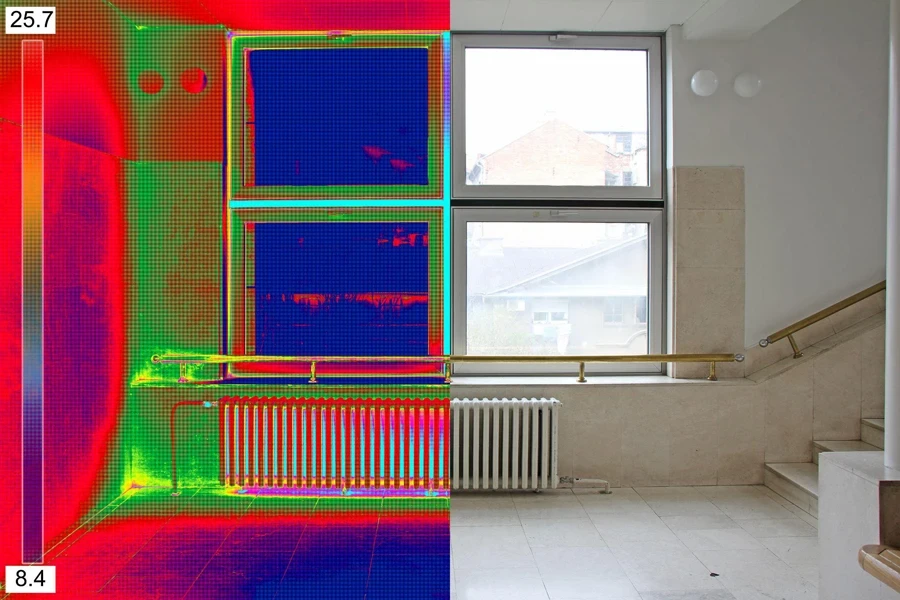

Conclusion
The exploration of thermal imaging cameras for 2024 reveals a diverse array of models tailored to meet specific professional needs, from detailed diagnostics to robust industrial applications. This guide underscores the importance of considering both technical specifications and practical applications when selecting a thermal camera. For businesses looking to enhance operational efficiency and safety, integrating these insights into their purchasing strategy ensures a sound investment in technology that aligns with their operational goals and budget constraints. Embracing these advanced tools can significantly influence productivity and preventative maintenance approaches in the coming years.