Have you heard that email bounces are harmless and can be ignored? That every email marketer gets them so it’s no big deal?
If so, you’ve heard wrong.
Email bounces can sabotage your marketing efforts and stain your business reputation.
Maintaining a low bounce rate is key to achieving high email deliverability and keeping potential domain blacklisting at bay.
In this article, we help you understand the root cause of email bounce and offer best practices to avoid finding yourself in the spam folder or, worse, blacklisted.
What is email bounce?
An email bounce is an email message rejected by a mail server. It is not delivered to the recipient’s inbox and sent back to the sender, or marked as spam.
Post-bounce, the sender receives a bounce message indicating delivery failure.
A higher bounce rate can profoundly impact your email sender reputation if left unchecked.
But not all email bounces are the same.
There are two types of email bounce: soft and hard bounces.
Soft bounces indicate a temporary problem at the receiver’s end. For example, a full mailbox may need cleaning or memory extension and temporary server issues. After resolving the issue, contacts can continue receiving emails from you.
Hard bounces are a greater sign of concern as they indicate permanent issues. For example, the recipient’s domain may not exist, the server refuses to accept emails from your IP address, or there may be address typos.
Soft vs hard bounce—what’s the main difference? A higher hard bounce rate is more likely to put your sender reputation at risk and tag you as a fraudulent email sender.
Why should you reduce the email bounce rate?
Email bounces can damage your IP address and domain reputation, which can cause a number of problems including:
- Poor overall sender reputation due to multiple failed delivery attempts.
- Lower email deliverability rate and wasted marketing efforts and budget.
- Poor email campaign results and expected ROI.
- Delay in delivering essential transactional emails like product shipping updates, order confirmation emails, and other automated emails—leading to bad customer experience.
A zero bounce rate may not be realistic, but it’s essential that you monitor and address hard bounces to avoid potential consequences.
What are the reasons for email bounce?
The main reasons behind email bounces can be broadly classified under soft and hard bounces.
Let’s dive deeper into each bounce type and the reasons behind them.
Hard bounce causes
As previously mentioned, hard bounces are permanent issues causing email delivery failures. But what exactly causes them?
Serchii Chernenko, Omnisend’s Email Deliverability Manager, has identified the following main causes:
1. Invalid email addresses
Using an outdated email list that was refreshed years ago? You may be risking email deliverability.
Invalid or outdated email addresses can affect email deliverability, for example the person may have abandoned it, or it may have been a work email that got deleted when they moved to a new job.
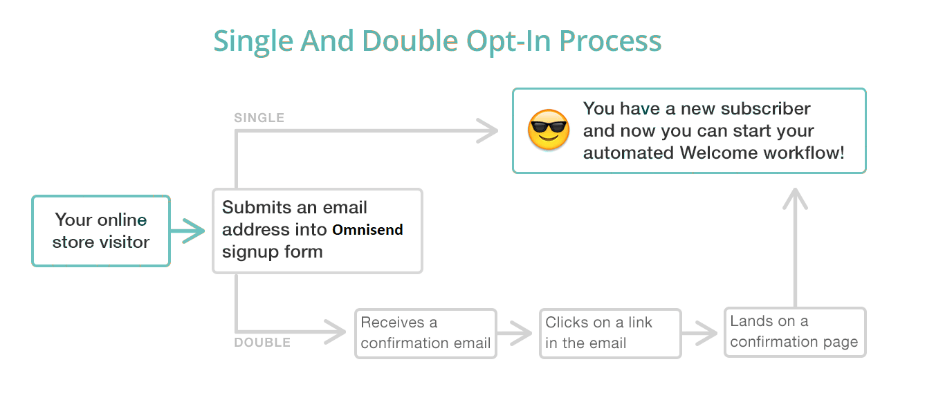
Also, some subscribers may have entered an invalid email address while submitting a subscription form—this could even be an innocent typo. The best way to avoid this is to use a double opt-in subscription form, where new subscribers are asked to click a link in their email or a landing page to confirm that they want to sign up. This removes the chances of accidental subscriptions, spam bots and fake signups.
2. DNS setup/authentication issues
Most ISPs and ESPs perform a reverse DNS search to verify the correct DNS configuration. If the DNS isn’t correctly configured, or there’s a server mismatch, mail servers may block your email from reaching its intended recipients.
Authentication issues are another major reason behind hard bounces. To avoid this, ensure you verify missing SPF records, misconfigured DKIM keys, and incorrect DMARC setup.
3. Server rejections due to policy violations
Email Service Providers (ESPs) have several policies to ensure that only secure and compliant information reaches their users.
If you’re noticing a higher bounce rate, check your compliance with the below policies:
- A fixed sending limit: Are you crossing a sending threshold set by your recipients’ ESPs? For example, you might be sending emails too frequently within a certain timeframe.
- Compliance with anti-spam regulations: Most ESPs followCAN-SPAM regulations (for the US) to target senders using misleading subject lines, deceptive information, and spam words.
- Blacklisting policies: A high rate of spam complaints may trigger mailbox providers to blacklist your domain and IP address—causing hard bounces.
4. Mailbox deactivated or unknown
A deactivated or unknown recipient email address can increase hard bounces as you continue emailing them.
This is why it’s important to segment your email subscribers to identify inactive ones and delete them from your future email marketing campaigns.
5. Mail server issues
Server downtime indicates you must delay sending emails until fixed, in order to avoid recurring hard bounces.
However, you may need a new server if there are continuous bounces on multiple emails.
6. Sender reputation
Frequent hard bounces and poor sender reputation go hand in hand. A high hard bounce rate, spam traps, and low engagement metrics weaken your email sender reputation with time.
Soft bounce causes
Below are some rectifiable, temporary email bounce reasons, a.k.a. soft bounces:
1. Temporary server or network issues
The recipient’s server may be temporarily down or experiencing network inconsistencies, such as high traffic or congestion, causing emails to soft bounce.
These issues often resolve themselves, after which you can try resending emails.
2. Rate limiting
Rate limiting refers to the threshold established by the email server and indicates the number of emails you can send to their users over a timeframe.
Monitor sending limits to ensure your emails don’t surpass recipient server limits and cause a higher soft bounce rate.
3. Content issues
Email content-related issues causing soft bounces include adding unoptimized images, attaching heavy files, triggering spam filters using clickbait words, and poor formatting.
These can be fixed by optimizing images and attachments, compressing large files, and avoiding words that could trigger spam filters (Omnisend’s subject line tester can help you identify these).
4. DNS issues
DNS issues are never long-lasting. Your recipients may face a temporary DNS outage, causing their servers to temporarily defer your email.
Best practices to reduce email bounces
Reduce email bounces using our expert-curated list of best practices:
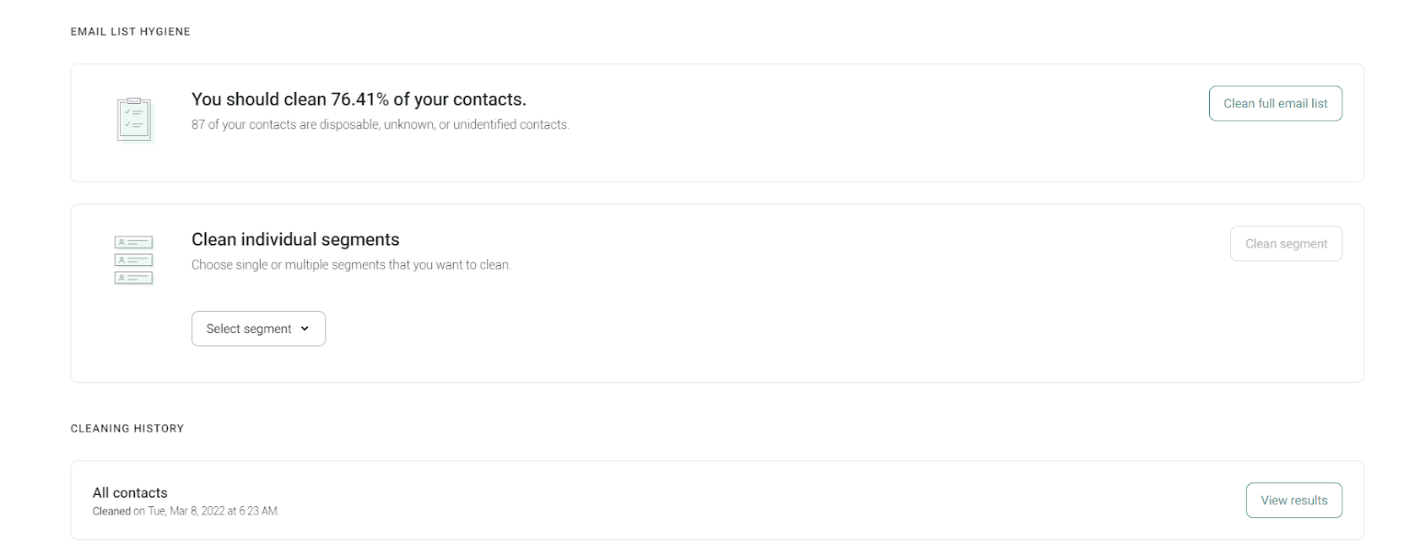
1. Regularly cleaning your email list
A well-maintained email list is the secret to not just boosting email deliverability but also increasing user engagement. Maintaining list hygiene ensures you only contact interested recipients who will most likely engage with your content and offers.
Here are four email scrubbing rituals you must follow to maintain a clean email list:
1. Use verification tools
Verification tools like NeverBounce, MailerCheck, and ZeroBounce help you verify email authenticity in seconds. You could check for valid email formats, domains, and potential typos.
2. List segmentation and maintenance
No two subscribers are exact replicas of each other.
Segmenting your email list into targeted groups of subscribers sharing similar characteristics, such as demographics, preferences, purchase behaviors, and loyalty, lets you personalize messaging and signal to ESPs that your communication is relevant and useful.
Email list hygiene and maintenance are equally essential practices to maintain healthy, verified subscriber contacts. Weed out inactive, outdated, and faulty email addresses periodically to optimize sales.
3. Sunsetting policy
The sunsetting policy is a gradual removal of constantly disengaged subscribers from your future email communications. Doing so lets you hyper-target subscribers keen to open your emails, thus improving important email marketing metrics like open, click-through, and conversion rates.
4. Using double opt-ins for collecting user’s emails
Double opt-ins set subscribers’ intent on receiving your emails in stone. For example, instead of just confirming their subscription through a home page form, you can additionally send them an email requesting reconfirmation.
2. Following email sending practices
Want to avoid the spam folder and cap bounce rates? Here are two simple tricks:
1. Following the warm-up phase for new email accounts
2. A warm-up phase is when you gradually send emails in smaller batches so your new email accounts’ service providers learn to trust you. Consistent email sending volumes
Most ESPs see inconsistency in email sending volumes as suspicious activity. As a result, your emails hard bounce, or worse, the mail servers permanently block your domain and IP address.
So maintain a consistent email sending volume to create a predictable pattern that your subscribers’ email clients recognize and trust.
3. Following good content and design practices
Engaged subscribers lead to reduced bounce rates and spam complaints. Carefully curated email content and design is your gateway to achieving extraordinary subscriber engagement.
Here are some content and email design tips:
1. Avoid spam filters through smart content choices
Getting content right the first few times may be challenging. But as you grow, you learn what triggers spam filters and ways to avoid them.
The most common content mistakes newbie marketers make are using deceptive subject lines, not personalizing messaging, creating lengthy emails, and using spammy words like “Limited time,” “Fantastic deals,” etc.
2. Mobile-friendly (responsive) and accessible design
61.9% of all emails are opened on mobile devices. A major chunk of your subscribers may be reading your emails on their mobile rather than desktop browsers.
A responsive and accessible mobile-friendly email design is key to enhancing reader engagement. For example, offer clear and concise content to improve mobile readability, use simpler navigation, as well as smaller fonts and alt texts for better accessibility.
3. Practice good text-to-image ratio
Over-reliance on images can trigger some spam filters. So, ensure you maintain a healthy text-to-image ratio balance in every email. And if you include images, make sure their size isn’t too large and that you’ve included alt-text.
4. Implementing technical strategies
Technical errors are some of the biggest reasons behind email bounces. Ensure you stay compliant with authentication protocols so mail servers see you as a credible source.
Here are two technical strategies for a low bounce rate:
1. Implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) is a widely accepted policy that authorizes senders. DKIM setup adds a digital signature to your outgoing emails as a testament to their authenticity. Meanwhile, DMARC ensures domain protection and authentication.
2. Understanding feedback loops with ISPs
Feedback loops (FBLs) are services offered by ISPs where senders can access user feedback, such as spam complaints and junk email reports.
FBLs offer valuable insights so senders can proactively act on future email marketing campaigns and reduce bounce rates.
5. Monitoring bounce rates
Monitor your email delivery. Keeping a close eye on your email marketing metrics, especially bounce rates, lets you catch problems early on and mitigate potential damage.
Conduct A/B testing of your email campaigns to assess email content, sending frequency, and send times.
Along with tracking email metrics, learn about the typical thresholds and benchmarks most ISPs follow so that you can fine-tune your email campaigns to limit bounces. For example, spam complaint rate thresholds, authentication protocols, sending volumes, and reputation scores.
6. Responding to bounces
Email bounces, especially soft bounces, are sometimes out of the sender’s control. Typical responses to such bounces may need the cooperation of both sender and recipients, be it rectifying server or DNS issues.
On the other hand, immediate actions for hard bounces include understanding ISPs’ feedback reports to improve future email campaigns.
Let’s recap some long-term strategies for efficient bounce management:
- Maintaining list hygiene through regular list cleaning to eliminate outdated and incorrect email addresses
- Using double opt-ins to reconfirm subscription and collect valid email addresses
- List segmentation for better personalization and engagement
- Adhering to authentication and security protocols
- Maintaining a good email sender reputation
- Monitoring your email delivery and bounce rates to identify outliers and mitigate risk early on
Wrap up
Email bounce can be frustrating, but you can mitigate it by understanding the reasons and following best practices.
It’s also important to remember that your priority should be hard bounces, rather than soft bounces, as they can negatively affect your sender reputation.
Source from Omnisend
Disclaimer: The information set forth above is provided by omnisend.com independently of Alibaba.com. Alibaba.com makes no representation and warranties as to the quality and reliability of the seller and products.