With the advent of technology, driving is becoming smarter and safer than ever before. But one area that can still trip up even the most experienced drivers is their blind spot. According to the National Highway Safety Administration statistics, over 800,000 accidents occur each year in the U.S. because of blind spots.
Blind spots are areas that cannot be seen when the driver looks using mirrors alone. They are caused by the A-pillar, which is the post between the windshield and side window, as well as any obstruction in the driver’s line of sight. But what if there was a way to eliminate blind spots?
Well, we have good news: there is! And it’s called Blind Spot Detection System (BSD). But what is a BSD system? How does it work? What are the different available types? And which features should buyers look for when choosing compatible models? Continue reading this article to find answers to all these questions.

Table of Contents
What is a BSD system?
Why is it important to have a BSD system in vehicles?
Two main types of BSD systems you should know about
5 things to look for in a blind spot detection system
BSD systems for a worry-free driving experience
What is a BSD system?
A blind spot detection system, or BSD for short, is an automotive technology that uses sensors and detectors to monitor adjacent lanes of traffic, and a processor to interpret the information received from the sensors. The system then alerts the driver of potential hazards by providing visual, audio, and even haptic alarms. This keeps drivers aware of their surroundings and prevents accidents from occurring.
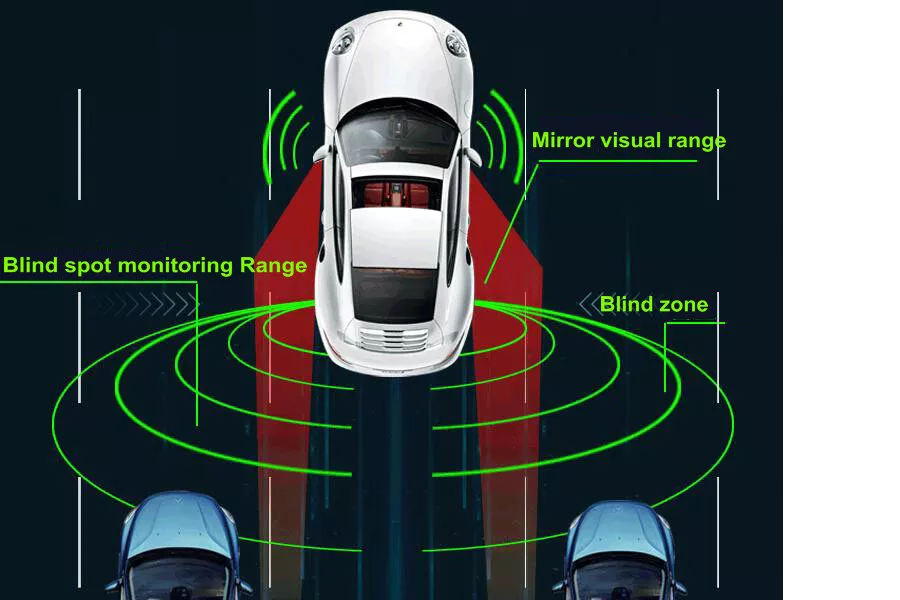
The primary purpose of a BSD system is to help drivers avoid hitting other cars while changing lanes. It detects vehicles approaching either side of the vehicle and alerts the driver before making a lane change maneuver.
Beyond blind spots, such electronic systems can be especially helpful when driving at night or on roads where visibility is limited due to weather conditions like rain or snow.
Why is it important to have a BSD system in vehicles?
The number of vehicles adopting advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) is increasing at a rapid pace as drivers realize the importance of such technologies in avoiding collisions. In addition to helping keep drivers safe, blind spot detection systems can also make driving easier. Here are some of their benefits on the road:
Reduced risk of accidents
Many drivers fail to check their blind spots before changing lanes, and this can lead to serious accidents. This is where a blind spot detection system comes in handy—it alerts drivers to cars that are approaching from their side or rear.
This helps drivers avoid accidents and keeps everyone safe on the road. The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) found that BSD systems can reduce line-change crashes with injuries by as much as 23%.
Improved response time
A study about drivers’ behavior in simulated emergency situations found that the response time is greater than half a second for most drivers. Moreover, most of the drivers’ attention is focused on the front visual view, which can lead to slower reaction times when changing lanes or merging onto a highway.
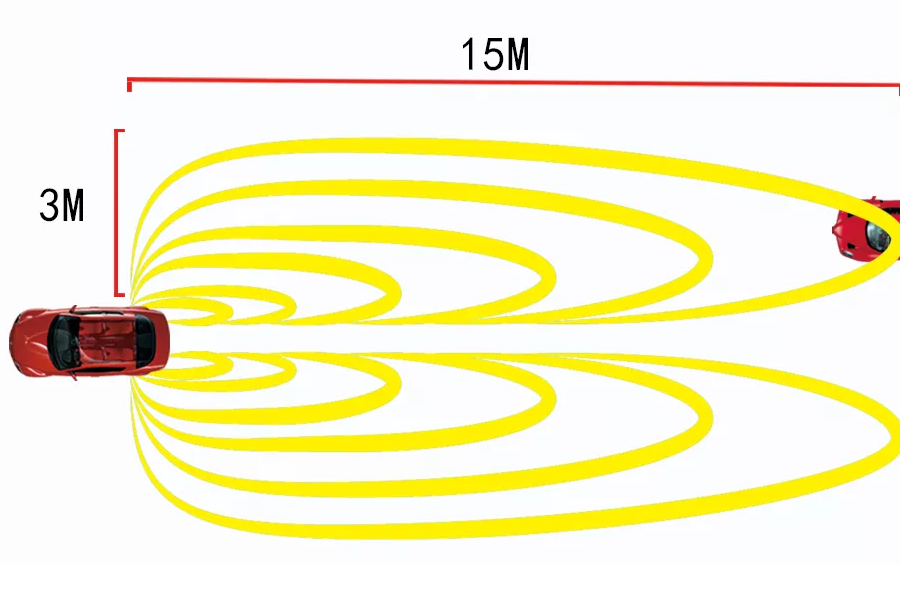
The human brain has a very difficult time processing what’s going on in the peripheral vision, which is why most of our attention is focused on the front visual view. A radar anti-collision BSD system is an effective solution for this problem, as it can alert drivers when a vehicle or other objects approach their blind spots by 3 meters, which gives them enough time to avoid a collision.
Increased driver awareness
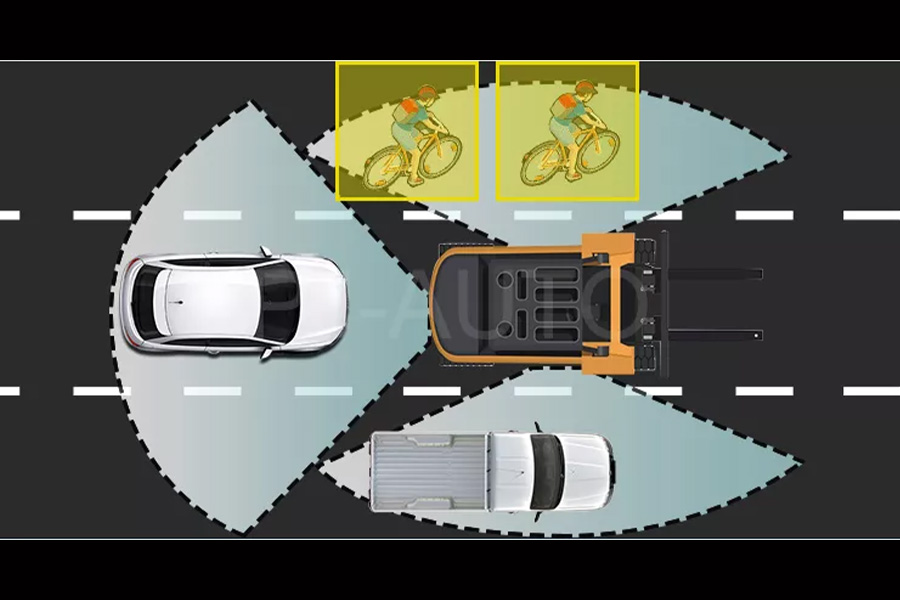
A BSD system increases the field of vision, which makes it easier for drivers to stay aware of what’s going on around them. This technology is especially useful for large vehicles, where the driver’s visibility can be limited and blind spots are larger.
For instance, the Truck BSD system is powered by the latest AI technology and uses clear circadian imaging to detect vehicles, pedestrians, and cyclists. This increased awareness helps prevent accidents from occurring, as well as reduce stress on drivers who might otherwise feel anxious about driving in tight spaces or around large objects.
Peace of mind
There’s nothing worse than being stuck in traffic with a truckload of stress. And it can happen to anyone who drives long distances. With these electronic car reversing aids installed in the vehicle, both the driver and passengers will feel safer on the road knowing they have an extra layer of protection against unexpected hazards or sudden line changes on the road.
Two main types of BSD systems you should know about
Blind spot detection systems can come factory-installed on new vehicles or be added as an aftermarket feature. Let’s look at the difference between these two types.
Factory-installed BSD systems

When it comes to blind spot detection systems, factory-installed models are the most common type. Automotive manufacturers like Honda, BMW, and Toyota install them as a built-in feature in most new vehicles, especially luxury cars, and they are custom-tailored for specific models to ensure a proper fit and function.
Unfortunately, these factory-installed systems are difficult to replace if they break or stop working properly. And since they are built into the vehicle, they are much more expensive to repair.
Aftermarket BSD systems
Not all vehicles come with built-in BSD systems, some cars require their owner to install such auto electronics to improve safety on the road. Aftermarket blind spot detection systems are not only less expensive, but they can also be installed on almost any vehicle—even older models that weren’t originally equipped with a driver assistance system.
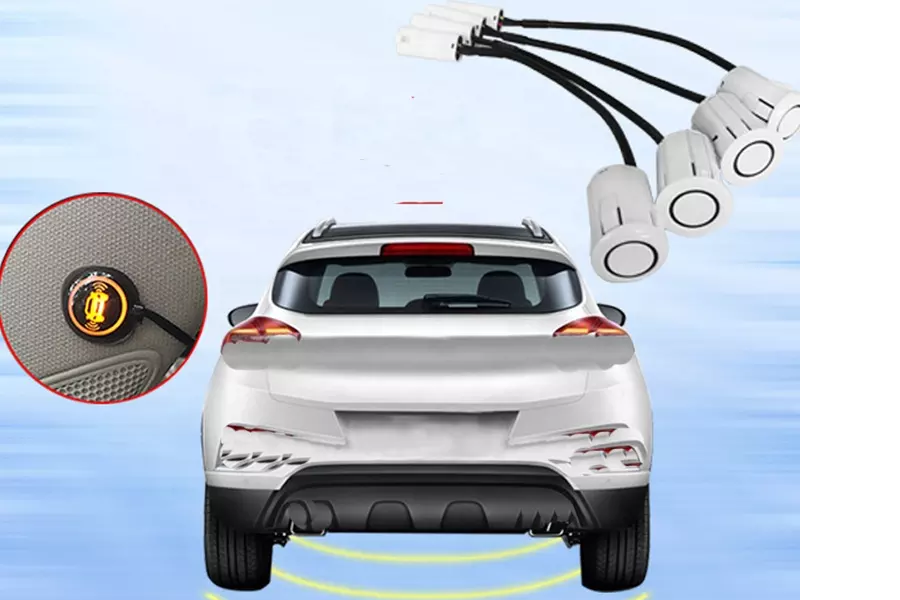

Aftermarket BSD systems are made to be near-universal, so they can easily be installed on most makes and models of vehicles. Moreover, they come in kit form, making them easy to install by even the most inexperienced mechanic.
5 things to look for in a blind spot detection system
Getting the right blind spot detection system can mean the difference between a safe trip and an accident. A sound driver assistance system should be accurate, reliable, and easy to install. But what features should buyers look for in a blind spot detection system? This section will take business buyers through everything they need to know about these automotive electronics.
Accuracy and detection range
When selecting a blind spot detection system, it’s important to check the accuracy and detection range of the sensors. Accuracy refers to how precise the sensors are at detecting vehicles and/or objects, while the detection range refers to how far away from the vehicle they can detect objects before triggering the warning indicators.
The sensors are the eyes of any BSD system, so they need to be able to see as much as possible around the vehicle. They can use radar, sonar, or LiDAR technologies. Radar uses electromagnetic waves, sonar transmits sound waves, and LiDAR technology uses light pulses or laser beams.
The detection range is highly dependent on the type of sensor used. Radar sensors operate at a longer range than sonar or lidar sensors, although they require a longer time to return data regarding the distance of the object.
A great example is the ultrasonic BSD system, which uses sonar and radar sensors to detect objects that are within a 5-meter range. Whenever an object is detected, the buzzer alarm will sound and the LED display will light up so the driver knows what’s going on.
Position and type of indicators
When choosing a BSD system, drivers want to be sure that the system has indicators that are easy to see, hear, and feel.
LED indicators
LED indicators are the most intuitive way to alert drivers about potential hazards and oncoming vehicles. The placement should allow the driver to easily see the indicator from their seated position. If the indicator is on the side of the vehicle, for example, it should be placed in a place where the driver can see it without having to turn their head too far.
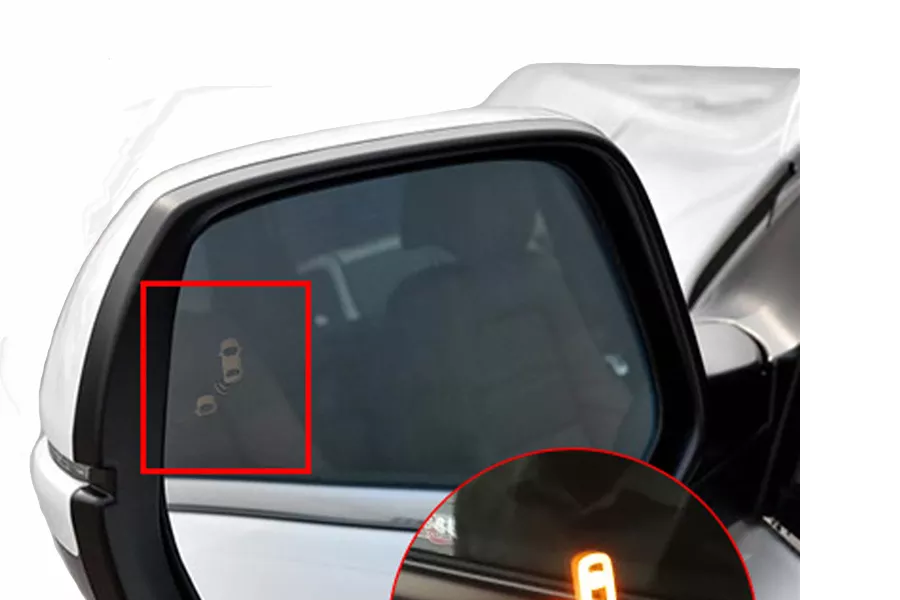

Some models come with a “time-to-collision” indicator as well—this will tell the driver how many seconds before an approaching car enters the road line or hits their vehicle if they don’t take action. For example, the 77GHz Millimeter-wave BSD system can display the distance between the vehicle and the object that it is approaching, which makes it much easier to judge how quickly the driver should slow down or change lanes.
Audible indicators
Audible alarms use sound waves to alert drivers that another vehicle is approaching them. This can be done through a loud beep or chime, or it can even be a voice telling the driver to change lanes. The length and volume of the noise will vary depending on how close the vehicle is.
Haptic indicators
Haptic alarms use a series of vibrations to alert drivers to the presence of vehicles nearby. The vibration is typically located at the side window or door pillar, and it occurs when there’s a vehicle in the blind spot. When drivers feel the vibration, it’s a reminder for them to check over their shoulders before changing lanes.

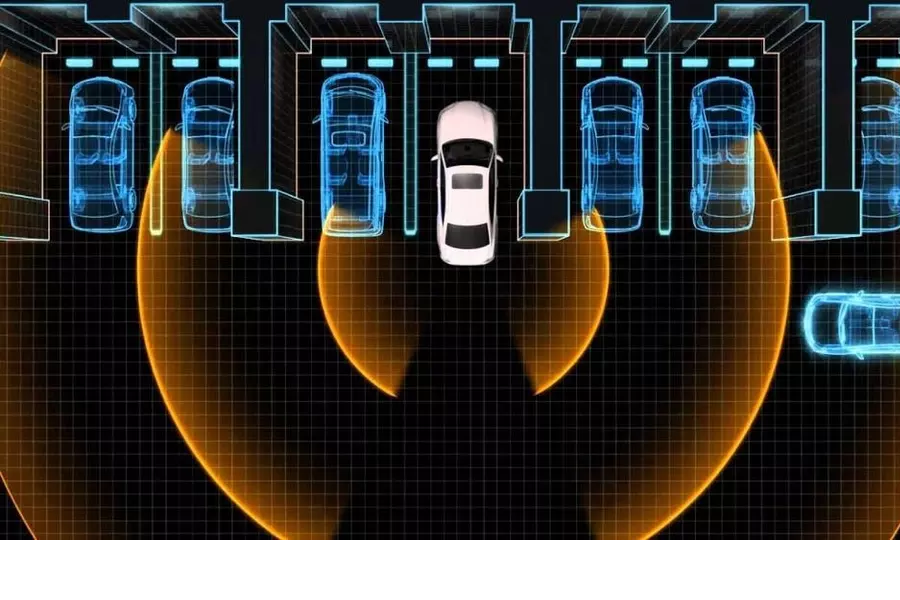
Rear-cross traffic alert
Some BSDs, like the 77GHz microwave radar monitoring system, include a feature called rear-cross traffic alert (RCTA). This safety feature can reduce parking lot backing crashes, which make up 20% of car accidents according to the National Safety Council.
RCTA uses corner radar sensors located on the sides of the vehicle’s rear bumper to detect vehicles, motorcycles, and pedestrians when reversing out of a parking space.
Braking and collision avoidance
The most effective BSD systems aren’t just about detecting other vehicles, they should help drivers avoid accidents by automatically taking control of steering and braking systems. If a possible collision is detected, then anti-collision detection systems will activate the braking system and lock the wheel to prevent the driver from taking wrong and fatal turns.
When the collision avoidance system is activated, it can be disconcerting for drivers who aren’t used to having their vehicles taken over by technology! That’s why such electronic technologies allow drivers to manually override this function by pressing the brake pedal.
Easy installation
The installation process can be simple or complicated, depending on the model. For example, the 24GHz BSD system has its components pre-installed and needs only minimal wiring to connect them to the vehicle’s electrical system. Others require more in-depth installation processes with the help of a professional mechanic.
Easy-to-install BSD systems should come with an installation kit, which includes all of the parts needed for installation. They should also have an instruction manual that provides detailed, step-by-step instructions on how to install the system. A great BSD system will require minimal installation and will get up and running in no time.
BSD systems for a worry-free driving experience
Blind spot detection systems are important to having a worry-free driving experience. They can help drivers avoid getting into accidents or lane-change collisions.
BSD systems are also beneficial for ensuring that drivers don’t miss pedestrians, cyclists, or other hazards in their blind spots. Check more BSD systems and other auto electronics from top-rated and verified suppliers and make the next drive safer!




