Audi’s A3 entered the market in 1996 as a subcompact family car and still serves the same purpose today. For over almost three decades, Audi 3 has had four different generations: 8L A3 (1996–2005), 8P A3 (2005–2013), 8V (2014–2021), and the latest version, 8Y A3 (2022 – date).
The vehicle has been in the market for a long time, hence you can expect many engines in its different models. Audi A3s have 1.9TDI, 2.0TDI, 1.8t, 1.4TFSI,1.8TFSI, and the 2.0TFSI.
The article will look at the common faults and problems with the Audi A3 to help owners and potential buyers.
Table of Contents
Audi 3 popularity and trends
Audi 3 engine faults
Final thoughts
Audi 3 popularity and trends
Audi 3 is part of the more prominent Audi brand known for premium quality and sleek-looking automobiles. It is a prominent feature on roads across the United States due to its superior standing. Its premium vehicles have made it a competitor to other luxury vehicle giants such as Mercedes-Benz and BMW.
Recently, Audi 3 has become popular with luxury vehicle lovers as a status car. New versions are equipped with the latest technology capabilities, including the MMI navigation system, to give easy navigation to drivers. Other high-tech features include Audi Virtual Cockpit and WiFi hotspot.
Audi 3 engine faults
Ignition coil fault
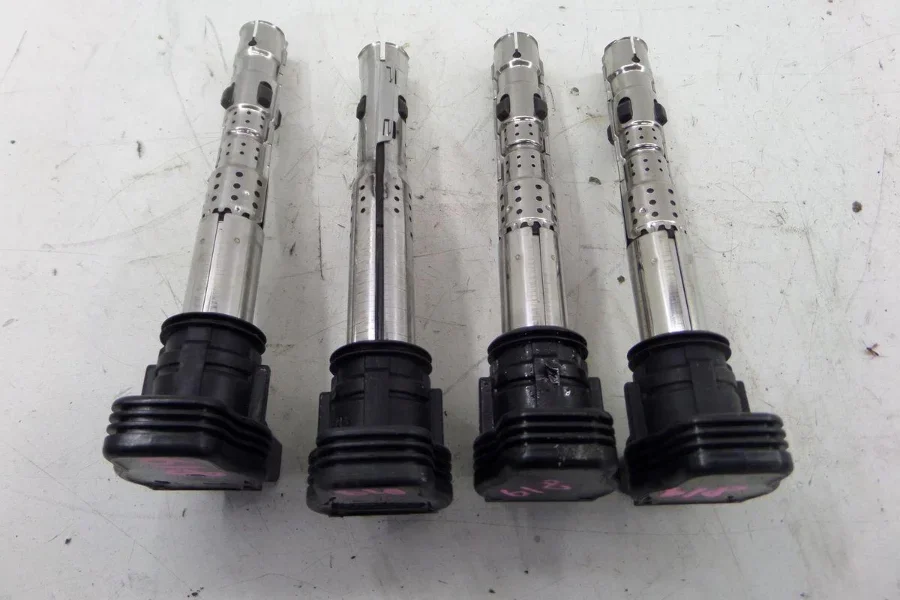

Premature ignition coil failure has become common in Audi 3. The ignition coil is a component that converts low-voltage power from the battery into the high-voltage power needed to ignite the fuel in the engine. When the ignition coil fails, it can cause several problems, including:
- Misfiring: A misfire is when the engine skips a beat or runs rough. It is often caused by a faulty ignition coil not delivering the proper voltage to the spark plug.
- Poor fuel economy: When an ignition coil fails, it can cause the engine to run poorly, leading to decreased fuel economy.
- Check engine light: A faulty ignition coil can trigger the check engine light to come on. This is because the engine control module (ECM) detects a problem with the ignition system.
Fuel tank suction pump fault
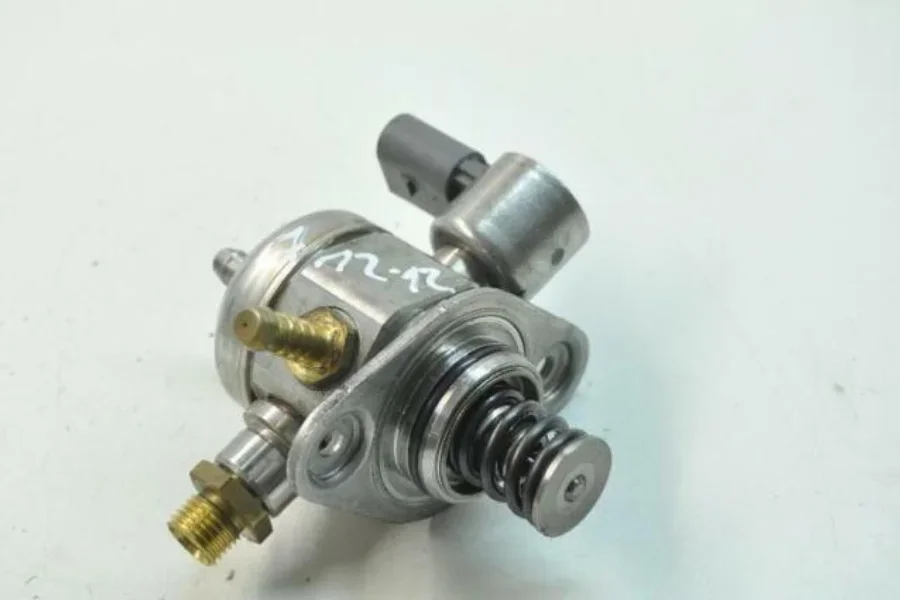

A defective fuel tank suction pump is a common problem in Audi A3, which led to a recall in 2016. The fuel tank suction pump draws fuel from the tank and delivers it to the engine. If it fails, you may experience problems starting your engine, poor fuel economy, or stalling while driving.
Here are some steps you can take to diagnose and fix the problem:
- Check the fuel pump fuse: The first thing you should do is check the fuse for the fuel pump. If the fuse is blown, it can prevent the pump from working. Replace the fuse with a new one of the same amperage.
- Check for a clogged fuel filter: A clogged fuel filter can restrict fuel flow to the engine, which can cause the fuel pump to work harder than it should.
- Check the fuel pump relay: The fuel pump relay is another component that can cause problems with the fuel pump. Use a multimeter to check for continuity between the relay terminals.
Faulty N80 valve
If you have a faulty N80 valve in your Audi A3, you may experience issues such as rough idle, engine misfires, or difficulty starting the car. The N80 valve is part of the evaporative emission control system, which helps to reduce harmful emissions from the engine.
Here are some steps you can take to diagnose and fix the problem:
- Check for error codes: The first step in diagnosing a faulty N80 valve is to check for error codes using an OBD-II scanner. The N80 valve is also known as the EVAP purge valve, and you may see error codes such as “P0441” or “P0455” if it is malfunctioning.
- Inspect the valve and hoses: If you suspect the N80 valve is the problem, you can inspect it and the associated hoses for any damage or wear. Make sure that the hoses are correctly connected and not cracked or leaking.
- Test the valve: To test the N80 valve, you can use a multimeter to check the resistance across the valve terminals. You should see a reading of around 30 ohms. If the resistance is outside this range, the valve may need replacing.
Diverter valve fault
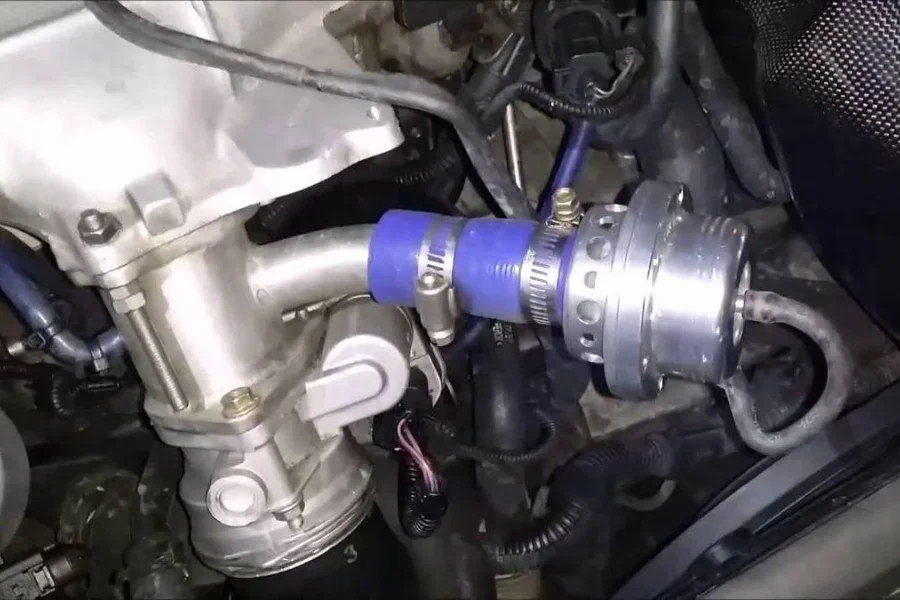

If you have a diverter valve failure in your Audi A3, you may experience issues such as reduced engine performance, poor fuel economy, or trouble with the turbocharger. The diverter valve controls the flow of air in the turbocharger system.
Here are some steps you can take to diagnose and fix the problem:
- Check for error codes: The first step in diagnosing a diverter valve failure is to check for error codes using an OBD-II scanner. If the diverter valve malfunctions, you may see error codes such as “P0234” or “P0299.”
- Inspect the valve: If you suspect the diverter valve is the problem, you can inspect it for any signs of damage or wear. Make sure that the valve is connected correctly and not cracked or leaking.
- Test the valve: To test the diverter valve, you can use a vacuum pump to apply a vacuum to the valve and observe whether it opens or closes. You can also use a multimeter to check the resistance across the valve terminals. If the valve does not respond appropriately, it may need to be replaced.
Faulty throttle body
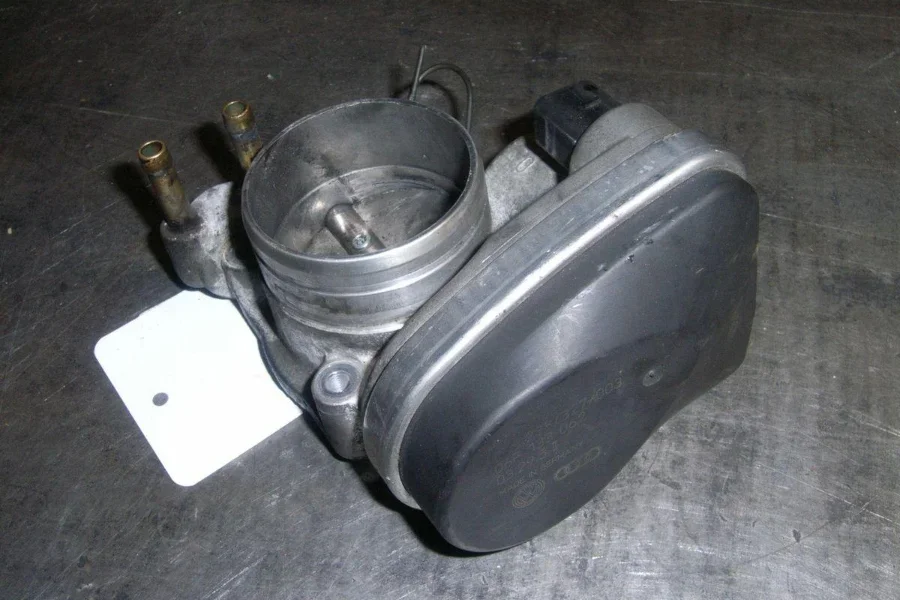

If you have a faulty throttle body in your Audi A3, you may experience issues such as reduced engine performance, poor fuel economy, or difficulty with acceleration. The throttle body regulates the amount of air that enters the engine.
Here are some steps you can take to diagnose and fix the problem:
- Check for error codes: The first step in diagnosing a faulty throttle body is to check for error codes using an OBD-II scanner. If the throttle body malfunctions, you may see error codes such as “P0121” or “P0221.”
- Inspect the throttle body: If you suspect it is a problem, you can inspect it for any signs of damage or wear. Ensure the throttle plate is not sticking, and the electrical connections are clean and secure.
- Test the throttle body: To test the throttle body, you can use a multimeter to check the resistance across the throttle position sensor terminals. You should see a smooth change in resistance as you move the throttle plate.
- Clean the throttle body: If it is dirty, clean it using a throttle body cleaner and a soft-bristled brush. Be sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use the correct tools to avoid causing any damage.
Final thoughts
Audi 3 remains one of the best cars of choice for millions of people due to mechanical reliability. The average annual cost of maintenance is US $741. The 8P (2005–2013) generation seems to have the most problems and should be avoided.
This article serves as a guide for Audi 3 owners and potential owners on the common problems and the processes of addressing them.



